导图社区 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第二章
- 47
- 0
- 0
- 举报
国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第二章
Chapter 2 Harmonization Financial Reporting Standards Globally第二章全球统一财务报告准则、包含定义、压力、 障碍、参与的组织、场景、现有证据等。
编辑于2024-01-07 19:10:16- accounting
- 国际会计
- International
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第四章
Chapter 4 Slected Financial Reporting and Disclosure Issues in the Global Contex,价格变动会计、商誉会计、无形资产的核算、地理和业务分部报告等。
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第三章
Chapter 3 Accounting for Currency Exchange Rate Changes,包含概述-术语、 外汇风险、汇率波动会计、在美国的外币折算等。
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第二章
Chapter 2 Harmonization Financial Reporting Standards Globally第二章全球统一财务报告准则、包含定义、压力、 障碍、参与的组织、场景、现有证据等。
国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第二章
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第四章
Chapter 4 Slected Financial Reporting and Disclosure Issues in the Global Contex,价格变动会计、商誉会计、无形资产的核算、地理和业务分部报告等。
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第三章
Chapter 3 Accounting for Currency Exchange Rate Changes,包含概述-术语、 外汇风险、汇率波动会计、在美国的外币折算等。
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第二章
Chapter 2 Harmonization Financial Reporting Standards Globally第二章全球统一财务报告准则、包含定义、压力、 障碍、参与的组织、场景、现有证据等。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
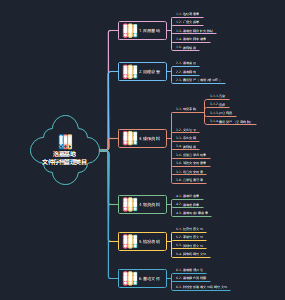
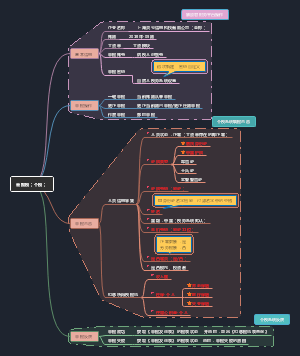
Chapter 2 Harmonization Financial Reporting Standards Globally
1. Definition
Concept
Accounting Harmonization
A movement away from total diversity
Accounting Standardization
A movement towards uniformity
Rationale Arguments
FOR
Major differences in accounting practices act as a barrier to capital flowing, hamornization will enhance comparability of financial statements, thus making them easier to use across countries.
AGAINST
Full harmonization is Not practical nor truly valuable
Investors can make investment decisions without the presence of international accounting standards.
Differences in the environment in countries.
Economic
Political
Legal
Cutural
Western Domination
Accounting Colonialism
2. Pressure
Investors Groups
They perceive that it can lower the cost of investing abroad and enhance their ability to make effective decisions across borders.
Multinational Companies
The can get additional benefits from harmonization
the reduced cost of preparing consolidated financial statements
ease in monitoring subsidiaries abroad
more meaningful managerial accounting reports
more relevant performance evaluation methods
Regulators
Reduce the higher costs that monitor compliance by foreign firms
Require foreign firms to provide financial statements conform to the host country's requirements.
Aimed at streamlining and harmonizing financial reporting requirements for cross-border listings.
Securities Industries and Stock Exchanges
In order to make their stock exchages more attractive to foreign companies
They support facilitating the listing process and reducing differences in financial reporting requirements globally.
Developing Countries
Provide a low-cost option for developing countries.
Saves developing countries from having to provide expensive reconciliations to the GAAP of foreign providers of capital.
3. Obstacles
①Nationalism
②The perceived negative impact countries.
③The absence of strong professional accounting bodies in a number of countries.
④The divergence between the needs of large multinationals and smaller business entities in development countries.
⑤Difficulties in coordinating change among the large number of IASC members.
⑥Emotional resisitance to change proposed.
4. Organizations Involved
IASC
International Accounting Standards Committee
1973
IFAC
International Federation of Accountants
150 member organizations, 103 countries, 2 million accountants
Aimed at harmonizing auditing practices globally
IOSCO
International Organization of Securities Commission
1983
UN
United Nations
OECD
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
5. Scenarios
Bilateral or mutual agreements 双边/多边协定
MDS (The Multijurisdictional Disclosure System)
US
Canada
World-class issuer (NYSE) 世界级发行人 (蓝筹股)
The IASC/IOSCO Initiative
GAAP is issued by the IASC and supported by IOSCO.
The G4+1 Alternative
G4
Australia, Canada, UK, US
+1
IASC
1993
Alternative
New Zealand
6. Current Evidence
Global Level
the number of stock exchanges accept IAS
the number of companies reporting under IFRS
Regional Level
EU (European Union) 欧盟
ASEAN (Association of South East Asian Nations) 东盟