导图社区 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第三章
- 55
- 0
- 0
- 举报
国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第三章
Chapter 3 Accounting for Currency Exchange Rate Changes,包含概述-术语、 外汇风险、汇率波动会计、在美国的外币折算等。
编辑于2024-01-07 19:15:20- accounting
- 国际会计
- International
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第四章
Chapter 4 Slected Financial Reporting and Disclosure Issues in the Global Contex,价格变动会计、商誉会计、无形资产的核算、地理和业务分部报告等。
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第三章
Chapter 3 Accounting for Currency Exchange Rate Changes,包含概述-术语、 外汇风险、汇率波动会计、在美国的外币折算等。
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第二章
Chapter 2 Harmonization Financial Reporting Standards Globally第二章全球统一财务报告准则、包含定义、压力、 障碍、参与的组织、场景、现有证据等。
国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第三章
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第四章
Chapter 4 Slected Financial Reporting and Disclosure Issues in the Global Contex,价格变动会计、商誉会计、无形资产的核算、地理和业务分部报告等。
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第三章
Chapter 3 Accounting for Currency Exchange Rate Changes,包含概述-术语、 外汇风险、汇率波动会计、在美国的外币折算等。
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第二章
Chapter 2 Harmonization Financial Reporting Standards Globally第二章全球统一财务报告准则、包含定义、压力、 障碍、参与的组织、场景、现有证据等。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
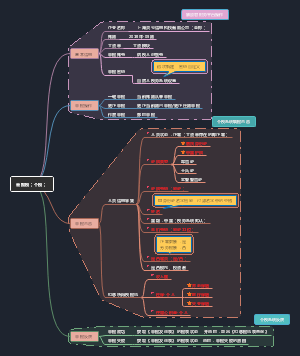
Chapter 3 Accounting for Currency Exchange Rate Changes
1. Overview - Terminology
Foreign Exchange
Direct Quote 直接汇率
the price of one unit foreign currency in exchange for domestic currency.
China/Canada/Japan
Indirect Quote 间接汇率
the price of one unit domestic currency in exchange for foreign currency.
UK/US/Australia
ask rate(sell rate, offer rate) 现汇银行卖出价
the price at which a financial institution is willing to sell a currency
bid rate(buy rate) 现汇银行购入价
the price at which a financial institution is willing to buy a currency
the spread
the spread 价差
difference between the bid and ask rates
Foreign Exchange Market
Definition
a mechanism through which the money of one country is exchanged for that of another, the exchange rate between currencies is set and exchange transactions are completed.
spot market
spot transaction 即期交易
immediate purchase or sale of foreign currency
forward market
Premium 溢价
Discount 折扣
currency option 货币期权
a contract that provides the right but not the obligation to trade a foreign currency at a set exchange rate or before a given date in the future.
currency swap 货币互换
a transaction that involves a simultaneous purchase and sale of two different currencies, with the purchase being effective and the sale back to the same party at a price agreed upon today but to be completed at a specified future date.
forward contract 远期交易
a commitment to exchange currencies in the future at a rate set today
Foreign exchange transaction 外汇交易
Two parties agree to exchange one currency for another at a specified rate of exchange.
Comparison
Foreign transaction 跨国交易
financial transation between other countries
Foreign currency transaction 外币交易
settlement in a foreign currency other than the company's functional currency
Transaction Gain/Loss → Affect the cash flows
Foregn currency translation 外币转换
process of expressing financial statement into another currency
No gain/loss
Foreign operation 跨国经营
activites in a country other than the reporting enterprise
Exchange Rates
Current Exchage Rate
Historical Exchage Rate
Average Exchage Rate
2. Exchange Exposure
Definition
A measure of the potential for a firm's profitability, cash flow, and market value to change because of a change in exchange rates
Translation exposure 转换风险
accounting exposure
The potential for an increase or decrease in the parent's net worth and reported net income, caused by a fluctuation in the exchange rates since the date of the previous period's consolidated financial statements.
Transaction exposure 交易风险
The potential fluctuation of exchange rates between the initiation of the transaction and the settlement of the invoice amount.
Classification
quotation exposure 报价风险
backlog exposure 积压风险
billing exposure 账单风险
Situation
buy/selling goods or services on credit, whose prices are contractually denominated in foreign currencies.
borrowing or lending funds in a foreign currency
engaging in contranct to buy or sell foreign currency at a future date
acquire assets or incur liabilities denominated in foreign currencies
gain/loss
Economic exposure 经济风险
the extent to which the value of the firm would be affected by unexpected changes in currency exchange rates
3. Accounting for Exchange Rate Fluctuations
transaction without credit
spot exchange rate
Credit transaction 赊销赊购
Single-transaction approach
Definition
be considered as an essential part of the transaction
The amount initially recorded is considered an estimate until the final settlement.
The original cost or revenue is adjusted for any difference
Entry
at transaction date
Dr. Account Receivable Cr. Revenues
at settlement date
Dr. Cash ····Revenues Cr. Accounts Receivable
for balance sheet dates
初始交易日和资产负债表日之间,汇率发生的任何变动都要调整revenue (资产负债表日可以直接用retained earnings)
在资产负债表日和交易完成日之间,汇率发生的变动需要额外调整。
Two-transaction approach
Definition
be considered as a second transaction
The amount is distinct from the original transation to buy or sell goods or services
The original cost or revenue isn't adjusted, any difference would be treated as a foreign currency transaction gain or loss.
Entry
at transation date
Dr. Account Receivable Cr. Revenues
at settlement date
Dr. Cash ····Loss on Foreign Exchange Cr. Accounts Receivable
Dr. Cash Cr. Gain on Foreign Exchange ····Accounts Receivable
for balance sheet dates
现金资产要按资产负债表日的汇率调整
按公允价值入账的非现金资产应该按照确定公允价值时的汇率入账
Foreign currency debt
Debt record
借款最初按即期汇率以美元入账。
在随后的资产负债表日,借款必须按当日汇率以美元重新计量,由此产生的汇兑损益必须立即记入损益表
Paying expenses
由于利息会提前进行计提,并在后续特定日期支付,导致最后支付日的汇率与利息累计期的平均汇率之间的差额可能会产生外汇损益。
average exchange rate → interest expense
payment date exchange rate → cash
difference → foreign exchange gain/loss
Foreign currency translation 外币转换
Terminology
Current rate
the exchange rate prevailing at the balance sheet date
Historical rate
the exchange rate prevailed at the date on which a specific transaction occured
Average rate
a weighted average of the exchange rates prevailed during the period for which financial statements are being prepared.
Accounting issue
Single rate method
Current Rate Method
assume all assets and liabilities face currency risk
Overview
the easiest to apply
results in translated statements that retain the same ratios and relationships with local currency
gain or loss don't affect the income statement, a cumulative translation adjustment (CTA) in the year end Equity in the balance sheet,
Multiple rate methods
Monetary/Non-monetary Method
assume only the monetary items face currency risk
Overview
the supporters think it is more meaningfull to translate assets and liabilities on the basisi of attributes instead of time
gains or losses are included in the income statement and affect the company's earnings
Current/Non-current Method
assume only the current items face currency risk
Overview
was used in US at 1930s - 1970s when SFAS No.8 become effective
entirely unrelated to the economic effects of exchange rate fluctuations
gains or losses are included in the income statement and affect the company's earnings
Temporal Method
adjust balance sheet items according to the valuation basis used in financial statements
Overview
was originally proposed in Accounting Research Study 12 by the AICPA
was formally required in Statement No.8
gains or losses are included in the income statement and affect the company's earnings
Format
4. Foreign Currency Translation in the US
Historical Development
In the early 1930s, the US used current/non-current method
In the late 1960s to early 1970s, the accounting principles board (APB) was studying the translation issue
In 1972, Accounting Research Study 12 was issued.
In December 1973, FASB issued Statement No.1, "disclosure of foreign currency translation information,"
In October 1975, FASB issued Statement No.8, "accounting for the translation of foreign currency transactions and foreign currency financial statements", to be effective in January 1, 1976
In December 1981, Statement No.52, foreign currency translation, was issued.
FASB No.52: Functional Currency
The currency of the primary economic enviroment in which the foreign subsidiary operates and generates cash flows.
Foreign subsidiary financial statement to be translated to dollars
in dollars
No tanslation required
in foreign currency
Local currency is the functional currency
If the local currency is determined to be the foreign subsidiary's functional currency, using the current rate method.
using Current Rate Mehod translate to dollars
Local currency is not the functional currency
dollar is the functional currency
If the US dollar is deemed to be the functional currency of the foreign subsidiary, using the temporal method.
using Temoral Method translate to dollars
dollar is not the functional currency
If the functional currency is neither local currency nor the dollar, a two step tranlation process. The local currency to the functional currency using the temporal method; the functional currency to the US dollar using the current rate method.
using Temporal Method translate the local currency to the functional currency
using Current Rate Method translate the functional currency to the dollar
Format
Three Major Changes
allow multiple units of measure so that differing economics situations can be accounted for differently
required translation gains/losses under the current rate method to be taken directly to Equity in the SOFP by passing the SOPL.
created the concept of functional currency as the determining factor of the translation method to be used
Translation in highly inflationary economics
In hyperinflationary situations, the reporting currency of the parent must be designated as the functional currency.
Temporal Method
IAS No.21
The FS of subsidiaries in highly inflationary economies must be adjusted to reflect changes in general price levels before translation.
SFAS No.133: Derivative Instrument
A financial instrument or other contract
Characteristics
It has one or more underlyings and or more notional amounts or payment provisions or both
underlying 底层证券
notional amount 名义价值
payment provision 付款条款
It requires no initial net investment or an initial net investment is very small.
It's terms requires or permit settlement in the future.
Forward contract
not designated as a hedge
designated as a hedge
measured at fair value