导图社区 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第四章
- 55
- 0
- 0
- 举报
国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第四章
Chapter 4 Slected Financial Reporting and Disclosure Issues in the Global Contex,价格变动会计、商誉会计、无形资产的核算、地理和业务分部报告等。
编辑于2024-01-07 19:22:15- accounting
- 国际会计
- International
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第四章
Chapter 4 Slected Financial Reporting and Disclosure Issues in the Global Contex,价格变动会计、商誉会计、无形资产的核算、地理和业务分部报告等。
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第三章
Chapter 3 Accounting for Currency Exchange Rate Changes,包含概述-术语、 外汇风险、汇率波动会计、在美国的外币折算等。
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第二章
Chapter 2 Harmonization Financial Reporting Standards Globally第二章全球统一财务报告准则、包含定义、压力、 障碍、参与的组织、场景、现有证据等。
国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第四章
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第四章
Chapter 4 Slected Financial Reporting and Disclosure Issues in the Global Contex,价格变动会计、商誉会计、无形资产的核算、地理和业务分部报告等。
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第三章
Chapter 3 Accounting for Currency Exchange Rate Changes,包含概述-术语、 外汇风险、汇率波动会计、在美国的外币折算等。
- 国际会计 International Accounting 知识点总结 第二章
Chapter 2 Harmonization Financial Reporting Standards Globally第二章全球统一财务报告准则、包含定义、压力、 障碍、参与的组织、场景、现有证据等。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
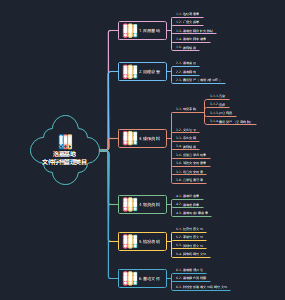
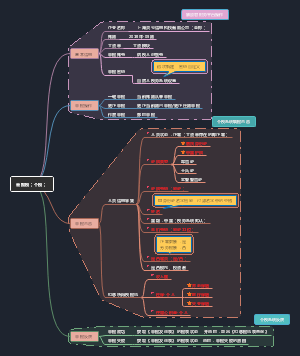
Chapter 4 Slected Financial Reporting and Disclosure Issues in the Global Context
1. Accounting for Changing Prices
Reasons
Ignores changes in the purchasing power of the reporting currency over time
Adding monetary amounts from very different time periods has little information content
Inflating profit and damaging capital maintenance
Two inflation-adjusted accounting models
GPLA
General Price Level Adjusted model, use price indexes to adjust for general changes in the purchasing power of the country's monetary unit.
Net Monetary gain/loss
Net Operating Income
CCA
Current Cost-Adjusted model, take a physical asset perspective to measuring performance and financial position, focus on the specific price changes of physical assets and expenses are recorded based on the current replacement cost of the assets.
Realized Hoding gains/losses
COGS(replacement - historical) + Depreciation(replacement - historical)
Unrealized Hoding gains/losses
Inventory(replacement - historical) + Fixed asset book value(replacement - historical)
Net Operating Income in Historical Cost Model
Revenue - expenses(historical)
Net Income in Replacement Cost Model
Revenue - expenses(replacement)
CPI
Laspeyres Index 拉式
全部使用基期的数量
Passche Index 派式
全部使用当期的数量
2. Accounting for Goodwill
Definition of Goodwill
The excess of the value of an ongoing business over the value of the individual indentifiable net assets of the business.
Two issues
Should it be recognized as an asset on a balance sheet?
Should recognized goodwill be systematically amortized or impairment?
Recognition Criteria
The future economic benefits from the asset are likely to come to the company.
The cost of the asset can be measured reliably.
Purchased goodwill meets the criteria for asset recognition
Internally generated goodwill doesn't meet the criteria.
Purchased goodwill
Positive goodwill
The total price paid for acquisition is higher than the fair value of business's net identifiable assets.
Negative goodwill
The total purchase price is lower than the fair value of the company's net identifiable assets.
Amortization or Impairment?
Proponents for amortization
Goodwill has a finite life and erode over time.
The purchased goodwill is of necessity replaced by internally generated goodwill.
Opponents for amortization
Goodwill has an infinite life and even enhanced over time.
Adding amortization as an expense would result in a double hit against future earnings.
It is inherently arbitrary, with no clear measure of its decline nor of the appropriate period of amorization.
Views
When there is evidence of a permanent impairment in the value of goodwill, charge a write-down of goodwill against earnings.
History
1970 APB No.17
The amortization of goodwill had been required with a maximum amortization period of 40 years.
1983 IAS 22
Permit both amotization and an immediate write-off against equity.
1993 Revised
With an amortization period of 5-20 years.
1998 IAS 36
Goodwill acquired in a business combination should be measured annually whether or not there is any indication that it may be impaired.
2001 June SFAS No.142
Goodwill with indefinite useful life should't be amortized, but rather tested at least annually for impairment using a fair-value-based test.
3. Accounting for Intangible Assets
Definition
An identifiable non-monetary asset without physical substance.
Computer software, patents, licenses, trademarks, copyrights, costomer and supplier relationships
Classification
Acquired identifiable
Generally meet the asset recognition criteria.
Internally generated identifiable
patents, liceses, trademarks are possible to indentify and capitalize directly related outlays.
Other internally generated identifiable intangible assets such as brands are controversial.
Research and Development
IAS 38
The enterprise should classify the internal project into two phases: a research phase and a development phase.
If this distinction can't be made for the internal project, then the entire project should be considered as a research phase.
Research costs
The activity that is aimed at inventing or creating a new product, method or system.
should be expensed immediately
Development costs
The activity converts the result of research to a marketable product.
also be expensed unless they meet the asset recognition criteria.
Asset Recognition Criteria
The technical feasibility of completing the intangible asset so that it will be available for use or sale.
Its intension to complete the intangible asset and use or sell it.
Its ability to use or sell the itangible.
How the intangible asset will generate probable future economic benefits.
4. Geographic and Business Segment Reporting
Objective
Reason
The emergence of large, diversified, transnational companies.
Objectives
Assist the user of financial statements in making judgments about the opportunities and risks facing an enterprise by the disclosure of fineer information than that provided in the primary financial statements.
Business Segment
Definition
A component of an enterprise that provides a single product or service or a group of related products and services and that is subjuect to risks and returns that are different from those of other business segments.
Factors
The nature of the products or services
The nature of the production processes
The type or class of customer for the products or services
The method used to distribute the products or provide the services
The nature of the regulatory environment
Geographic Segment
Definition
A component of an enterprise that provides products and services within a particular economic environment and that is subject to risks and returns that are different from those of components operating in other economic environments.
Factors
Similarity of economic and political conditions
Relationship between operations in different geographic areas
Proximity of operations
Special risks associated with operations in a particular area
Exchange control regulations
The underlying currenry risks
History
1976 FASB No.14
1981 IAS No.14
2006.10 IFRS No.8