导图社区 英语语言学-心理语言学 -胡壮麟 Language and Congnition
英语语言学-心理语言学 -胡壮麟 Language and Congnition
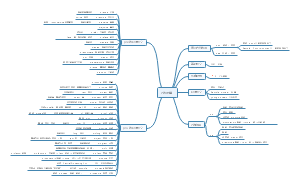
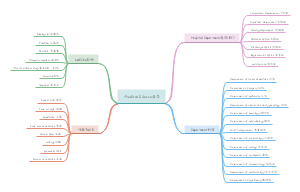
英语语言学-心理语言学 -胡壮麟 Language and Congnition psycholinguistics,Congnition、Psycholinguistics、Congnitive Linguistics,认知(Cognition)指的是心理过程或认识能力,包括意识、感知、推理和判断等。在语言与认知的关系中,语言被视为人类认知能力的一种体现。
编辑于2024-08-03 00:48:48- 心理语言学
- 胡壮麟
- psycholinguistics