导图社区 麦肯锡7S模型详解与思维导图框架(中英对照)
- 162
- 0
- 0
- 举报
麦肯锡7S模型详解与思维导图框架(中英对照)
这是一篇关于麦肯锡7S模型详解与思维导图框架的思维导图,主要内容包括:说明,1. 模型概述,通过系统化应用7S模型,组织可提升战略执行力、优化资源配置,并在变革中保持韧性。,7. 扩展建议,6. 思维导图总结,5. 优缺点分析,4. 实施步骤,3. 应用场景与案例,2. 七个要素详解。
编辑于2025-02-19 12:06:40- 麦肯锡
- 7S
- McKinsey
- 企业转型管理
- 《皇帝内经》的读书笔记
这是一篇关于《皇帝内经》的读书笔记的思维导图,主要内容包括:说明,现代应用与研究,养生与预防,诊断与治疗原则,医学思想与理论,《皇帝内经》结构,《皇帝内经》概述。
- DeePseek与Grop3详细对比分析
这是一篇关于DeePseek与Grop3详细对比分析的思维导图,竞争格局:两者虽技术路线迥异,但共同推动了大模型技术的多元化发展,未来可能在多模态、生态整合等方向形成交叉竞争。
- 麦肯锡7S模型详解与思维导图框架(中英对照)
这是一篇关于麦肯锡7S模型详解与思维导图框架的思维导图,主要内容包括:说明,1. 模型概述,通过系统化应用7S模型,组织可提升战略执行力、优化资源配置,并在变革中保持韧性。,7. 扩展建议,6. 思维导图总结,5. 优缺点分析,4. 实施步骤,3. 应用场景与案例,2. 七个要素详解。
麦肯锡7S模型详解与思维导图框架(中英对照)
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- 《皇帝内经》的读书笔记
这是一篇关于《皇帝内经》的读书笔记的思维导图,主要内容包括:说明,现代应用与研究,养生与预防,诊断与治疗原则,医学思想与理论,《皇帝内经》结构,《皇帝内经》概述。
- DeePseek与Grop3详细对比分析
这是一篇关于DeePseek与Grop3详细对比分析的思维导图,竞争格局:两者虽技术路线迥异,但共同推动了大模型技术的多元化发展,未来可能在多模态、生态整合等方向形成交叉竞争。
- 麦肯锡7S模型详解与思维导图框架(中英对照)
这是一篇关于麦肯锡7S模型详解与思维导图框架的思维导图,主要内容包括:说明,1. 模型概述,通过系统化应用7S模型,组织可提升战略执行力、优化资源配置,并在变革中保持韧性。,7. 扩展建议,6. 思维导图总结,5. 优缺点分析,4. 实施步骤,3. 应用场景与案例,2. 七个要素详解。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
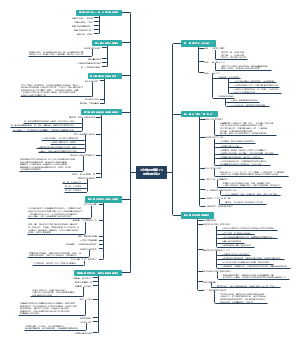
麦肯锡7S模型详解与思维导图框架
1. 模型概述
麦肯锡7S模型由汤姆·彼得斯(Tom Peters)和罗伯特·沃特曼(Robert Waterman)于20世纪70年代末提出,强调组织成功的内部要素需相互协调。其核心假设是“组织不仅仅是结构”,而是由七个相互关联的要素构成,分为硬性要素 (战略、结构、系统)和 软性要素 (共享价值观、技能、风格、人员)。这些要素的动态平衡是组织高效运作的关键。
2. 七个要素详解
核心框架(思维导图式结构)
各要素定义与作用
战略(Strategy)
定义:组织为达成长期目标制定的行动路径,包括对市场变化的响应计划。
关键点:需与使命、愿景一致,并体现组织身份。
示例:苹果公司通过差异化产品战略(如iPhone生态系统)实现竞争优势。
结构(Structure)
定义:组织架构设计,包括部门划分、层级关系和沟通渠道。
关键点:需与战略适配,例如矩阵式结构适用于多元化企业。
案例:中国邮政储蓄银行通过调整层级结构解决业务复杂性问题。
系统(System)
定义:支持日常运作的流程、政策和IT系统,如绩效考核、决策流程。
关键点:高效系统可提升执行力,例如麦当劳的标准化运营系统。
共享价值观(Shared Values)
定义:组织的核心价值观与文化,是其他要素的根基。
关键点:塑造员工行为准则,例如可口可乐以“全球联结”为核心理念。
技能(Skills)
定义:组织核心能力与员工专业技能,如技术创新或客户服务能力。
关键点:需与战略需求匹配,例如特斯拉在电池技术上的领先优势。
风格(Style)
定义:管理层的领导风格与组织沟通方式。
关键点:影响组织氛围,如谷歌的开放协作风格促进创新。
人员(Staff)
定义:人力资源配置与发展,包括招聘、培训和人才保留。
关键点:员工能力与组织目标需对齐,如IBM通过技能重塑应对数字化转型。
3. 应用场景与案例
主要应用领域
组织诊断与改进:识别结构冗余、文化冲突等问题。
战略实施:确保新战略与现有要素协调,例如微软在云转型中调整结构与技能。
并购整合:协调双方文化(共享价值观)和流程(系统)。
数字化转型:评估技术对组织各要素的影响,如某企业通过7S模型确定数字化成熟度。
典型案例
中国邮政储蓄银行:应用7S模型解决基础设施落后、员工素质不足问题,推动组织升级。
通用电气(GE):在业务重组中调整战略与结构,剥离非核心业务以聚焦数字化转型。
4. 实施步骤
评估现状:分析当前7S要素的匹配度,识别矛盾点(如战略激进但技能滞后)。
定义目标状态:明确各要素的理想状态,例如“建立扁平化结构以加速决策”。
制定行动计划:针对差距设计行动(如培训计划提升技能),分配资源与责任。
执行与监控:定期评估进展,动态调整(如因市场变化修订战略)。
5. 优缺点分析
优势
全面性:兼顾硬性流程与软性文化,避免单一视角盲区。
行业普适性:适用于企业、非营利机构等多类型组织。
变革管理支持:帮助企业在合并、转型中保持要素平衡。
局限
复杂性:要素相互关联导致调整耗时,难以快速响应变化。
缺乏优先级:未明确要素改进顺序,需依赖外部顾问。
静态倾向:更适合稳定环境,对动态市场的适应性较弱。
6. 思维导图总结
麦肯锡7S模型 ├─ **核心目标**:通过七大要素协调实现组织效能 ├─ **硬性要素** │ ├─ 战略 → 长期计划 │ ├─ 结构 → 组织架构 │ └─ 系统 → 流程制度 ├─ **软性要素** │ ├─ 共享价值观 → 文化根基 │ ├─ 技能 → 核心能力 │ ├─ 风格 → 领导方式 │ └─ 人员 → 人力资源 └─ **应用关键**:动态平衡与持续迭代
7. 扩展建议
结合其他工具:如SWOT分析(外部环境)弥补7S模型的内部聚焦局限。
数字化整合:利用数据分析评估系统与技能的匹配度。
文化驱动:优先强化共享价值观,以软性要素推动硬性变革。
通过系统化应用7S模型,组织可提升战略执行力、优化资源配置,并在变革中保持韧性。
说明
导图制作工具:Mindmaster,制作:空茶杯
McKinsey 7S Model Explanation and Mind Mapping Framework
1. Model Overview
The McKinsey 7S model was proposed by Tom Peters and Robert Waterman in the late 1970s, emphasizing the need for internal elements of organizational success to coordinate with each other. The core assumption is that "organization is not just structure", but is composed of seven interrelated elements, divided into hard elements (strategy, structure, system) and soft elements (shared values, skills, style, personnel). The dynamic balance of these elements is crucial for the efficient operation of an organization.
2. Detailed explanation of the seven elements
Core Framework (Mind Mapping Structure)
Definition and function of each element
Strategy
Definition: The action path established by an organization to achieve long-term goals, including response plans to market changes.
Key point: It needs to be consistent with the mission and vision, and reflect the organizational identity.
Example: Apple achieves competitive advantage through a differentiated product strategy, such as the iPhone ecosystem.
Structure
Definition: Organizational structure design, including department division, hierarchical relationships, and communication channels.
Key point: It needs to be adapted to the strategy, for example, matrix structure is suitable for diversified enterprises.
Case: Postal Savings Bank of China solves the problem of business complexity by adjusting its hierarchical structure.
System
Definition: Processes, policies, and IT systems that support daily operations, such as performance evaluations and decision-making processes.
Key point: Efficient systems can enhance execution, such as McDonald's standardized operating system.
Shared Values
Definition: The core values and culture of an organization are the foundation of other elements.
Key point: Shaping employee behavior standards, such as Coca Cola's core concept of "global connectivity".
Skills
Definition: Organizational core competencies and employee professional skills, such as technological innovation or customer service capabilities.
Key point: It needs to match strategic needs, such as Tesla's leading advantage in battery technology.
Style (Style)
Definition: The leadership style and organizational communication style of the management team.
Key point: Affects organizational atmosphere, such as Google's open collaboration style promoting innovation.
Personnel (Staff)
Definition: Human resource allocation and development, including recruitment, training, and talent retention.
Key point: Employee capabilities need to align with organizational goals, such as IBM responding to digital transformation through skills reshaping.
3. Application scenarios and cases
Main application areas
Organizational diagnosis and improvement: Identify issues such as structural redundancy and cultural conflicts.
Strategy implementation: ensure that the new strategy is coordinated with the existing elements, such as Microsoft adjusting its structure and skills in the cloud transformation.
Merger and acquisition integration: Coordinate the cultures (shared values) and processes (systems) of both parties.
Digital transformation: Evaluating the impact of technology on various elements of an organization, such as a company determining digital maturity through the 7S model.
classic case
Postal Savings Bank of China: Applying the 7S model to solve the problems of outdated infrastructure and insufficient employee quality, promoting organizational upgrading.
General Electric (GE): adjust the strategy and structure in business restructuring, divest non core businesses to focus on digital transformation.
4. Implementation steps
Evaluate the current situation: Analyze the matching degree of the 7S elements and identify contradictions (such as strategic aggressiveness but skill lag).
Define target state: Clarify the ideal state of each element, such as "establishing a flat structure to accelerate decision-making".
Develop an action plan: Design actions to address gaps (such as training programs to enhance skills), allocate resources and responsibilities.
Execution and monitoring: Regularly evaluate progress and dynamically adjust (such as revising strategies due to market changes).
5. Analysis of advantages and disadvantages
advantage
Comprehensiveness: Balancing hard processes and soft culture, avoiding blind spots from a single perspective.
Industry universality: applicable to various types of organizations such as enterprises and non-profit organizations.
Change management support: helps enterprises maintain element balance during mergers and transformations.
limit
Complexity: The interdependence of elements leads to time-consuming adjustments and makes it difficult to respond quickly to changes.
Lack of priority: The improvement order of elements is not clear, and external consultants need to be relied upon.
Static tendency: More suitable for stable environments, with weaker adaptability to dynamic markets.
6. Summary of Mind Maps
Mckinsey 7S Model ∝ - * * Core Goal * *: Achieving organizational effectiveness through coordination of seven key elements ∝ - * * Hard Elements** │∝ - Strategy → Long term Plan │∝ - Structure → Organizational Structure │└ - System → Process System ∝ - * * Soft elements** │∝ - Shared Values → Cultural Foundation │∝ - Skills → Core Competencies │∝ - Style → Leadership Style │└ - Personnel → Human Resources └ - * * Application Key * *: Dynamic Balance and Continuous Iteration
7. Extension suggestions
Combining other tools such as SWOT analysis (external environment) to address the internal focus limitations of the 7S model.
Digital integration: using data analysis to evaluate the matching degree between systems and skills.
Culture driven: Prioritize strengthening shared values and driving hard change with soft elements.
By systematically applying the 7S model, organizations can enhance strategic execution, optimize resource allocation, and maintain resilience in the face of change.
explain
Map making tool: Mindmaster, Production: Empty Tea Cup