导图社区 宏观经济学失业知识梳理
- 861
- 32
- 104
- 举报
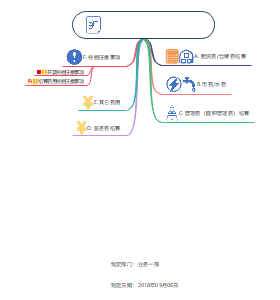
宏观经济学失业知识梳理
干货分享!宏观经济学中“失业”部分知识梳理总结!本思维导图包括关于失业率的计算、原因分析、就业变化趋势等内容,希望本图能够对你有所帮助!
编辑于2019-09-18 03:02:45- 失业率
- 就业变化趋势
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
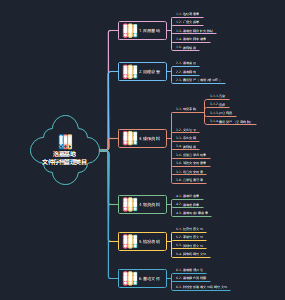
4.1 Full Employment of Labour 👷
🖋️ Definition of Full Employment (充分就业)
the lowest non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment/natural rate of unemployment (NAIRU 非加速性失业增长率)
NAIRU is the specific level of employment that does not cause unsustainable inflation
target rate: 5% of unemployment
Phillips Curve - the relationship between inflation (price stability) and full employment (UE rate) ➡️ inverse relationship in the short run, similar to law of demand
💡 Indicators of unemployment
分类 civilians over 15
in the Labour Force
employed
full time
part time
unemployed
actively seeking work
available to start work in reference week
not in the Labour Force
unemployed
actively seeking work
not available to start work in reference week
not actively seeking work
Labour Force Participation Rate
measures an economy active labour force and is the sum of all employed divided by the working age population (15岁以上可以参与劳动的公民)
LFPR%=labour force / Civilian population over 15 yrs old
Unemployment Rate
measures the percentage within the labour force that is currently without a job (actively seeking)
UE%=total number of unemployed/labour force
LFPR VS UE%
UE (find jobs) usually falls when the LFPR (civilian population enters the labour force)rises (常态)
AFTER recession, LFPR and UE will both increase (会发生,不是常态)
UE% is the official indicator for full employment, HOWEVER, LFPR is essential to full employment as well
🌟outcome
higher UE%
lower economic production/output ➡️economic distress 经济不景气 ➡️ unemployed workers still need to maintain at least basic consumption (subsistence 生存)
signal serious distress in an economy ➡️ social and political upheaval 变动
lower UE%
overheated economy 经济过热 (increase inflation)
🔗causes of unemployment
Cyclical (general) Unemployment 周期性失业
demand < supply / general lack of demand ➡️the troughs and peaks of business cycle ➡️ ups and down in unemployment
Frictional Unemployment 摩擦性失业
people who are between jobs
eg. graduates, re-entering the workforce
Seasonal Unemployment 季节性失业
workers are temporarily unemployed between seasons
eg. fruit pickers
Structural Unemployment结构性失业
labour no longer required, reduce size of workforce
eg. typists 打字员
Hard-core Unemployment顽固性失业
personal attributes 个人特点
eg. disabled, attitude problems (在澳大利亚,算劳动力)
Not included in UE
The Hidden Unemployed 隐性失业
people who would like to work but are not actively seeking employment (不算劳动力)
The Underemployed 未充分就业的
people want more hours (是劳动力但不是失业的)
eg. casual and part-time works
📈 Changing employment trends
Casualisation 临时工
work casual (非正式的、临时的) or under contract (按任务录用) ≠ part-time job (有固定的工作时间)
shift in recent years: full time worker ➡️ casual workers
Reasons
competition: less labour costs
women: work and take care of the family
work-life balance: more free time to do what he or she wants
negative aspects
underemployed: want more work/ resource labour idle 劳动力资源闲置
lower incomes: leads to decline in standard of living
job security: poor 没有稳定工作,甚至不能为贷款提供未来收入证明
advantages (business)
do not have to pay benefits, such as health insurance, sick leave and annual leave
reduce cost of production (COP), just hiring employees when needed
improve productivity and efficiency
can fire any employees that are under performing without any major costs
子主题
disadvantages (business)
hard to plan for the future: as there is no stable workforce
require to pay more per hour (单位时间工资高)
unproductive work: workers are not settled-in 安顿下来
workers (talented and skilled) seek for full-time employment
labour market reform 劳动力市场改革
now employers and employees can negotiate about wages and working conditions directly
before: negotiated by unions
flexible working arrangements
more freedom during work hours
a modern trend in western countries, supported by technologies (internet, phone, email...)
💰 Cost of Unemployment
Economic Costs
Idle resources (labour)
need money to subsistence 生存, the able to maintain basic living
Budget Impacts
less government revenue (tax) and more government spending (social secuirty) ➡️ change budget plans
Individual Costs
self esteem自尊 / reduced income / savings are lost / jobs skill deteriorate退化 / increased violence and crime / family relationship / next generation