导图社区 三大从句
- 1.4k
- 55
- 10
- 举报
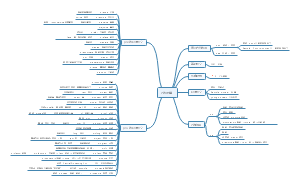
三大从句
英语语法之三大从句思维导图,包括名词性从句、状语从句和定语从句的相关知识点,非常实用,值得收藏。
编辑于2022-01-17 13:25:24- 从句
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
从句
名词性从句
宾语从句
由that引导的宾语从句
许多动词后可以跟由that引导的宾语从句,that有时可以省略
例子:I don't think (that) it is right for him to treat you like that.
that 不能省略的情况
当句中的动词后接多于两个由that引导的宾语从句时,第一个that可省略,后面的不能
例子:He said (that) you were too young to understand the matter and that he was asked not to tell you.
当主句的谓语动词与that宾语从句之间有插入语时,that一般不可省略
例子:Just when I noticed, for the first time, that our master was wearing his fine green coat and his black silk soap.
当that从句是双宾语中的直接宾语时,that不可省略
由连接代词引导的宾语从句
连接代词与疑问代词同形,包括:who,whom,whose,which,what
连接代词在宾语中可作
主语
例子:Do you know who will come this afternoon?
宾语
例子:Do you hear what he said?
表语
例子:Please tell who that girl is
定语
例子:Could you tell me which gate we have to go to?
由连接副词引导的宾语从句
连接副词包括:when, where, why, how
例子:We didn't know when she would come back.
由whether和if引导的宾语从句
例子:Nobody knows whether it will rain.
由what引导的·宾语从句
例子:I wonder what is your purpose?
由whatever,whichever,whoever,whomever引导的宾语从句
例子:I don't believe whatever she said.
由连接副词或连接代词加不定式组成的宾语从句
例子:I can't decide whom to vote.
例子:We must decide what to do with her.
宾语从句在句中的位置
直接位于动词后
有时宾语从句不直接位于动词后,而是位于间接宾语后做直接宾语
宾语从句作介词的宾语
例子:The movie is about a dog and a cat.
be + adj. +宾语从句
宾语从句的特殊形式
例子:I'm glad (that) you like it.
v. + to + n.+宾语从句
例子:You should indicate to the team where they are to assemble
宾语从句的否定转移
当主句谓语动词为think,believe,suppose,expect,imagine等表示“认为”的动词的意思,主句主语为第一人称,且主句时态为一般现在时的时候,宾语从句的否定一般要转移到主句上来,其反意疑问句一般与宾语从句一致。
例子:I don't think he will let you down
宾语从句的时态呼应
如果主句为过去时态那么从句通常要采用相应的过去时态
在一些特殊情况下,从句时态不随着主句时态变化
表示永恒真理
使用虚拟语气时
例子:If you had come earlier, you would have seen him.
用it作形式宾语的宾语从句
例子: I take it for granted that you will win the prize.
主语从句
由that引导的主语从句
例子:That he failed the exam was not true.
由连接代词引导的主语从句
例子:Who broke the window remains unknow.
由连接副词引导的主语从句
例子:Why he late for class is not clear.
由whether引导的主语从句
例子:Whether it is right remains a mystery.
由what引导的主语从句
例子:What he said is true.
以it作形式主语的主语从句
it+be+adj.+从句
例子:It is important that students develop a good habit.
it+be+n.+从句
例子:It is a pity that you missed the exciting football match.
it+v.(+宾语或状语) +从句
例子:It remains to be seen whether it will do us harm or good.
it+动词被动形态+从句
例子:It is estimated that the project will last four years.
由just because引导的主语从句
只用于“just because…doesn't mean…”句型
同位语从句
同位语从句引导词
由that引导的同位语从句
例子:We heard the news that our team had won
有链接代、副词引导的同位语从句
例子:I have no idea how I can make myself understood.
由whether引导的同位语从句
例子:There is some doubt whether he will come.
由what引导的同位语从句
例子:I have no idea what he was doing.
同位语从句有时与前面的名词分开
分离式同位语从句
例子:The news must be true that these products will no longer be available in the market.
表语从句
位于系动词后
由that引导的表语从句(that有时可省略)
例子:The trouble is that he misunderstood me.
由连接代词引导的表语从句
例子:The question is who we should trust.
由连接副词引导的表语从句
例子:The problem is how we can find him.
由because引导的表语从句
例子:It's because I passed a slip of paper for John to Helen.
由whether引导的表语从句
例子:The qustion is whether the flim is worth seeing.
由like引导的表语从句
例子:It is like they can retrieve everything.
由as if/ as though 引导的表语从句
例子:It looked as though it was going to rain.
由as/ just as 引导的表语从句
例子:It may be just as we think.
状语从句
状语从句的定义
状语是一种句子成分,用于修饰动词、形容词、其他状语或整个句子。表示时间、地点、程度、方式、原因、结果、条件、目的、让步、比较、伴随、看法、态度、评价等,状语可以用一个词(如slowly慢慢地)来表达,也可以用一个短语(如in the room)来表达。但有时候我们要表达的状语成分的意思 不能用简单的一个词或者短语来表达,而是需要用到一个句子(即从句)来表达,这时就需要用到状语从句。
状语从句几个特点
状语从句的句首一般由连词引导,如when, where, although, as, because, as long as, since, so, if, wherever, where等
从功能上来看,状语从句一般用于修饰主句的谓语动词
状语从句位于主语之前时,常用逗号隔开(但在不易让读者误解的情况下,有时也可以省略逗号,如:When he got up he felt dizzy)
状语从句的位置除了句首和句末外,还可以作为插入成分
例子:This animal, although they spend a great deal of time in water, does not feed in the water.
时间状语从句
时间状语从句指用来表示时间,修饰主句的从句。引导时间状语从句的引导词有when, while, before, since, until, as等等
表示某个时刻发生的动作:when, while, as, once
表示某个时刻前发生的动作:before, until
表示某个时刻之后发生的动作:after, since
when引导从句时,主从句的动作有先有后,也可以同时进行, 从句的动作可以时持续性的,也可是短暂的
while侧重主从句动作的对比,且从句的动词必须是持续性的
例子:While my heart is willing, my flesh is weak. (心有余而力不足)
as引导从句时侧重主从句动作几乎同时进行,从句动作可以时持续性的,也可以是短暂的
例子:He sang as he walk in the road.
地点状语从句
地点状语从句表示地点、方位,这类从句通常用where,wherever等引导,地点状语从句可置于句首、句中或句尾
地点状语从句的用法
where在地点从句中,除了指地点以外,还可以指处境等
有时地点状语从句中的某些词可以省略
地点状语一般置于主语后
定语从句
限制性定语从句
用于限定或说明其所修饰的词的范围或性质等。从句与先行词关系紧密,省略则会造成主句不完整,先行词在定语从句中充当某种语法成分(如主语、宾语或状语)
例子:Do you remember the girl who taught us English?
非限制性定语从句
该从句与先行词的关系松散,只起补充说明的作用,去除非限制性定语从句对主句的影响不大。非限制性定语从句由逗号隔开,在翻译成中文时,常可译成并列句。引导非限制性定语从句的关系代词有which, who, whom, whose, as;关系副词有when和where,注意非限制性定语从句不能由关系代词that引导。
例子:Mr. Zhang, who came to see me yesterday, is an old friend of mine.
关系代词引导的定语从句
由that引导的定语从句(that可以指人或物,在定语从句中作主语,宾语或表语,作宾语或表语时可省略。
例子:He is the man that I saw yesterday.
由which引导的定语从句(which指物,在定语从句中作主语或宾语
例子:China is a country which has a large population.
由who引导的宾语从句(who指人,在宾语从句中充当主语)
例子:The boy who is in red over there is my brother.
由whom引导的宾语从句(whom指人,在宾语从句作宾语或表语)
关系副词引导的定语从句
由when引导的定语从句
例子:Do you know the date when Lincoln was born.
由where引导的定语从句
例子:That is the house where he lived ten years ago.
由why引导的定语从句
例子:Tht is the reason why he is leaving so soon.
有一些定语从句常可省略引导词
when一般不可省略, 但当其用于day,time,year等少数几个词后时可以省略
例子:That was the year I first went abroad
where一般不可省略,但用于place, somewhere,anywhere, everywhere,nowhere等少数几个词后面可以省略
例子:This is the place they met yesterday.
先行词why一般位于the reason后,且通常可换成that或for which,均可以省略
例子:Give me one reason we should help you.
宜用that而不宜用which引导定语从句的情况
当先行词为anything, everything, nothing, few, all, none, little, some等不定代词时
但是something用which或that都行
例子:Is there anything that you have forgotten.
先行词被序数词或最高级修饰时
例子:This is the most interesting film that I 've ever seen.
先行词是并列结构,既有人又有物
例子:Do you know thue things and persons that they are talking about.
主句主语是疑问词who或which时
例子:Which is the machine that we uesd last Sunday?
先行词前有the same, the very, the only, the last修饰时
例子:This is the same that I lost yesterday.
较少见的定语从句
as和such相互搭配引导的定语从句
例子:There are few poets such as Keats and Shelly.
定语从句用who不用that的情况
当先行词为人称代词he\she\they或one(s),anyone, nobody等时
例子:He who doesn't reach the Great Wall is not a true man (不到长城非好汉)
例子:Anybody who breaks the rules would be punished
当先行指代词those,或先行词是those所修饰的人时
例子:God helps those who help themselves (天助自助者)
当先行词是people或是代表人的集体名词时
例子:People who are more confident are more likely to be successful.
当先行词与定语从句被其他句子成分分开时
例子:Do you know the student in white with books in his hand who is standing under the tree?
当关系代词在从句中作主语且与谓语动词被隔开时
例子:She is a girl who, if is properly encouraged, will try her best.
先行词是人时,后面有两个定语从句时,第二个必须是who引导且不能省略
例子:The scientist that won the Nobel Prize is the hero who dedicated his life for the cause of the people.
定语从句用that不用who的情况
在疑问句中如果开头的疑问代词是who,为了避免重复,定语从句宜使用that引导而不用who
例子:Who was it that was lost?
当先行词为疑问代词who,which时
例子:He is the student that I have ever see who can jump highest.
当关系代词在定语从句中作表语或宾补时,定语从句也不用who引导,而用that,或者省略关系代词
例子:He is no longer the man that he was.
当先行词同时包含人或物时
例子:The professor and his achievement that I heard about are admired by them.
双重定语从句
一个句子中含有两个定语从句,其层次不同,修饰的先行词也不同
例子:The boss at last got a chance to visit the village where he uesd to work which he had been dreaming of for 20 years.
限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句的区别
that, why, how 只能用于引导限制性定语从句,而不能引导非限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句只修饰其先行词(名词或代词);而非限制性定语从句除了修饰名词和代词,其修饰对象还可以是整个主句、主句中的动词短语或表语等
限制性定语从句中关系代词有时可以省略,但是非限制性定语从句不能
当先行词是指上问题提到的人或物时,一般要用非限制性定语从句
修饰专有名词不能用限制性定语从句,需要用非限制性定语从句
定语从句用which不用that的情况
非限制性定语从句肯定不能用that做引导词。非限制性定语从句有逗号隔开,所以在阅读时如果看见逗号后有that的情况,这个that一定不是用于引导定语从句
限制性定语从句只用which不用that的情况比较少见,但需要注意以下情形
当定语从句的先行词是有介词+关系代词引导时,其中的关系代词就只能用which而不能用that
当先行词为that时,关系代词只能用which而不用that,避免重复
定语从句和状语从句的区别
多数定语从句都是由关系代词that, which, who, whom, whose等引导,而状语从句不能使用这些引导词。状语从句需要连词如when, where, because, while, since等引导
有两种情况可能造成定语从句被误认为是状语从句
where引导的定语从句
where引导的定语从句,其先行词时表示地点的;另一方面,与大多数定语从句一样,where在定语从句中代表缺失的句子成分——地点状语
where引导的状语从句用于表示主语谓语动词的地点,与定语从句不同,它前面没有表示地点的先行词
when引导的定语从句
一般需要从意思上区分,when引导的定语从句前面的先行词多为表时间的名词如hour, day, evening, morning, time等,这一点也有助于辨别
如何区分同位语从句和定语从句
同位语从句和前面的名词是同位关系,定语从句和其先行词是修饰关系
同位语从句的句子是完整的,that引导词只起到连接作用;而定语从句的句子成分不完整,会缺某个成分,that引导词在从句中充当成分
定语从句对先行词没什么要求,可以修饰几乎所有名词;而同位语从句的先行词仅限于某些抽象名词,常见的有:news, idea, opinion, thought, fact, rumour, report, decision, evidence, hope等
例子: The idea that computers can recognize human voices surprises many people.
同位语从句
例子:The idea that he gave surprises many people
定语从句