导图社区 工程经济
- 241
- 12
- 0
- 举报
工程经济
工程经济知识总结,包括资金时间价值的计算与应用、技术方案经济效果评价、技术方案不确定性分析、技术方案现金流量表的编制等等。
编辑于2022-06-01 21:33:48- 工程经济
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
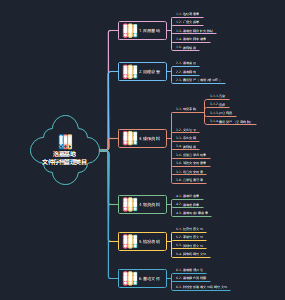
工程经济
资金时间价值的计算与应用
利息的计算
资金时间价值的概念
影响资金时间价值的因素
资金的使用时间(正比)
资金数量的多少(正比)
资金投入和回收的特点(晚投早收)
资金周转的速度(正比)
决定利率高低的因素
首先取决于社会平均利润率的高低,是利率的最高界限
借贷资本的供求情况
风险越高,利率也越高
通货膨胀
借出资本的期限长短(期限长,利率高)
利息的计算
单利(利不生利)
复利(利生利,利滚利)
间断复利,连续复利
资金等值计算及应用
现金流量图的绘制
1、横轴时间轴,0表示时间序列的起点
2、投资人而言,横轴上方现金流入,横轴下方现金流出
3、箭线长短和现金流量数值大小应成比例
4、箭线与时间轴的交点即为现金流量发生的时点
现金流量三要素:大小、方向、作用点
终值和现值的计算⭐⭐⭐
一次支付(现值/终值)
等额支付系列(终值/现值)
等值计算的应用
计息期数为时点或时标,本期末等于下期初
P是在第一计息期开始时(0期)发生
F是在考察期期末,即n期末
各期的等额支付A,发生在各期末
当问题包括A与F时,系列的最后一个A是与F同时发生,不能把A定在每期期初⭐
当问题包括P与A时,系列的第一个A与P隔一期,即P发生在系列A的前一期期末⭐
名义利率和有效利率的计算
名义利率的计算
r=i×m(r名义利率,i计息周期利率,m计息周期数)
通常年利率都是名义利率
有效利率的计算
计息周期有效利率
i=r/m
年有效利率(1+r/m)^m-1
计息周期小于(或等于)资金收付周期时的等值计算
技术方案经济效果评价
经济效果评价的内容
盈利能力、偿债能力、财务生存能力
经济效果评价方案
独立型方案(互不干扰)
互斥型方案(二选一)
技术方案的计算期
建设期、运营期(投产期、达产期)
经济效果评价指标体系
确定性分析
盈利能力
静态分析
投资收益率
静态投资回收期
动态分析
财务净现值
财务内部收益率
偿债能力
利息备付率
偿债备付率
借款偿还期
资产负债率
流动比率
速动比率
不确定性分析
盈亏平衡分析
敏感性分析
投资收益率R=A/I×100%
总投资收益率
ROI=EBIT/TI,Return on Investment
EBIT 运营期正常年息税前利润, 年息税前利润=年利润总额+计入年总成本费用的利息费用
TI 技术方案总投资(包括建设投资、建设期贷款利息和全部流动资金)
资本金净利润率
ROE=NP/EC
EC 技术方案资本金
NP 正常年份年净利润,净利润=利润总额-所得税
投资回收期分析
累计净现金流为0,Pt=T-1+线性插值
宜从建设期起算,从投产期起算应注明
优:适用技术更新迅速,资金短缺,特别关心资金补偿 劣:不能反映资金回收之后的情况,没有考虑资金时间价值,辅助评价指标
财务净现值分析FNPV
计算期内各年所发生的净现金流都折现到开始实施时的现值之和(折现、求和)
设定基准收益率,FNPV>0 可行
优:考虑资金时间价值,货币额表示盈利能力 劣:基准收益率确定困难,互斥方案构造相同分析期限,不能反映投资回收速度
财务内部收益率分析FIRR⭐⭐⭐
计算期内各年净现金流量的现值累计等于零时的折现率
线性插值计算
FIRR>基准收益率ic,则可行
优:适用于独立,常规现金流的技术方案。 劣:计算麻烦,多个解
基准收益率的确定
动态观点,可接受技术方案最低标准的收益水平
政府投资项目:根据政策导向
企业项目:参考行业财务基准收益率
境外投资项目:考虑国家风险因素
投资者自行测定技术方案:多因素综合测定,资金成本、机会成本、投资风险、通货膨胀
偿债能力分析
偿债资金来源
归还借款的利润、固定资产折旧(折旧基金)、无形资产及其他资产摊销费和其他还款资金来源
偿债能力指标
借款偿还期、利息备付率、偿债备付率、资产负债率、流动比率、速动比率
借款偿还期:Pd=(借款偿还开始出现盈余年份-1)+盈余当年应偿还借款额/盈余当年可用于还款的金额
利息备付率(ICR) 也称已获利息倍数:ICR=EBIT/PI(计入总成本费用的应付利息) ,(应大于1,不宜低于2)
偿债备付率(DSCR)=(EBITDA(企业息税前利润加折旧加摊销)-Tax(企业所得税))/PD(应还本付息的金额),应大于1,不宜低于1.3
技术方案不确定性分析
不确定性分析
盈亏平衡分析
量本利分析:产销量作为不确定因素
敏感性分析
不确定因素变化 ,对经济效果评价指标变化,敏感度系数和临界点
盈亏平衡分析
总成本、固定成本、可变成本
总成本:工资 福利费、折旧费、修理费、摊销费、其他
可变成本:原材料、燃油、动力费、包装费、计件工资
半可变:阶梯型曲线,分解为固定和可变,长期借款利息为固定成本
C=Cf+CuQ
销售收入及营业税附加
销售收入:线性和非线性
营业中税金和附加:S=p×Q-Tu×Q
量本利模型B=S-C
B=p×Q-Cu×Q-Cf-Tu×Q
量本利图
产销量盈亏平衡分析
BEP(Q)=Cf/(p-Cu-Tu)
生产能力利用率盈亏平衡分析
BEP(%)=BEP(Q)/Qd×100%
BEP(%)=Cf/(Sn-Cv-T)×100%
结果分析
1、投产达到设计生产能力后正常年份的数据计算
2、收入和成本不含增值税
3、BEP(%)≤70%,安全
敏感性分析
单因素分析
分析指标:财务净现值、财务内部收益率、静态投资回收期
不确定性因素:影响大、风险大
分析每个不确定因素波动对分析指标的增减变化
确定敏感性因素
敏感度系数Saf=(▲A/A)/(▲F/F)
敏感性分析表
敏感性分析图,斜率越大,敏感度越高;临界点越低
临界点,与判断基准线的相交点所对应的横坐标
技术方案现金流量表的编制
技术方案现金流量表
投资现金流量表
资本金现金流量表
投资各方现金流量表
财务计划现金流量表
技术方案现金流量表的构成要素
营业收入
=产品销售量×产品单价,销售量=生产量,产品为标准产品(多种转化)
补贴收入,计入或不计入
投资
总投资是=建设投资+建设期利息+流动资金
流动资金=流动资产-流动负债(不包括运营中需要的临时性营运资金)
技术方案资本金:由投资者认缴的出资额,是非债务性资金。
资本金现金流量表投资借款处理,借款本金的偿还和利息支付计入现金流入,
维持运营投资、在现金流量表中及现金流出,可以资本化(视情况),
经营成本
总成本费用=外购原材料、燃料及动力费+工资及福利费+修理费+折旧费+摊销费+财务费用(利息支出)+其他费用
经营成本=总成本费用-折旧费-摊销费-利息支出 或 经营成本=外购原材料、燃料及动力费+工资及福利费+修理费+其他费用
税金
一般属于财务现金流出
设备更新分析
设备磨损与补偿
设备磨损的类型
有形磨损(物质磨损)
无形磨损(第一种、再生价值降低,贬值;第二种,出现新设备,原设备相对落后,效益降低)
综合磨损
设备磨损的补偿方式
局部补偿 大修理(有形磨损);现代化改装(第二种无形磨碎)
完全补偿 更新
设备更新方案的比选原则
1、客观立场,旧设备市场价值作为购买支出
2、不考虑沉没成本,沉没成本=设备账面价值-当前市场价值 或=(设备原值-历年折旧费)-当前市场价值
3、逐年滚动比较
设备更新时机
设备寿命
自然寿命、技术寿命、经济寿命
设备经济寿命的计算
设备的年平均使用成本=设备的年资产消耗成本+设备的年运行成本 设备从开始使用到期年平均使用成本最小 的使用年限为设备的经济寿命
设备租赁与购买方案的比选分析
设备租赁
融资租赁(租期长、不得任意中止和取消,贵重设备)
经营租赁(租期短,可以随时取消,临时设备)
设备租赁费用:租赁保证金、租金、担保费
租金的计算 ⭐⭐⭐
附加率法
年金法
价值工程在工程建设中的应用
提高价值的途径
V=F/C,对象的比较价值,最低的寿命周期成本,可靠地实现使用者所需功能
价值工程特点
目标,最低地寿命周期成本,使产品具备它所必须具备地功能。 产品功能与成本关系图
核心,对产品进行功能分析
将产品价值、功能和成本作为整体同时考虑
强调不断改革和创新
功能定量化
集体智慧开展的有计划、有组织、有领导的管理活动
价值提升的途径
双向型:提升产品功能同时,降低产品成本
改进型:产品成本不变,功能提高
节约型:产品功能不变,成本降低
投资型:产品功能有较大提高,成本较少较高
牺牲型:产品功能略有下降,成本大幅下降
价值工程在工程建设实施步骤
工作程序
价值工程工作程序表P71
准备阶段
分析阶段
功能定义
功能重要性:基本功能、辅助功能
功能性质:使用功能、美学功能
用户需求:必要功能(基本功能、辅助功能、使用功能、美学功能)、 不必要功能(多余功能、重复功能、过剩功能)
量化标准:过剩功能、不足功能
总体与局部:总体功能、局部功能
功能逻辑关系:并列功能、上下位功能
功能整理
功能评价
评价程序
目标成本、实际成本;功能价值(两者比值)、改善期望值(两者差值)
功能成本法:Vi=Fi/Ci
V=1 功能评价值等于现实成本,无须改进
V<1功能现实成本大于功能评价值,需要改进
V>1功能现实成本低于功能评价值,分类讨论
V=0
改进范围
Fi/Ci低的功能、▲Ci=(Ci-Fi)值大的功能、复杂、问题多
新技术、新工艺和新材料应用方案的技术经济分析
应用方案的选择原则
技术上先进、可靠、安全、适用
综合效益上合理(方案经济性、效益综合性)
应用方案的技术分析
分析分类
新技术应用方案的技术分析
技术特性(内部)
条件指标(外部)
经济分析★★★
增量投资收益法:增量投资所带来的经营成本(或生产成本)上的节约与增量投资之比 R(2-1)=(C1-C2)/(I2-I1)×100%
折算费用法:当方案的有用成果相同时,比较费用的大小 Zj=Cj+Pj·Rc
技术经济综合分析
简单评分法:加总平均
加权评分法:加权求和