导图社区 语言学概论 chapter 1
- 345
- 10
- 4
- 举报
语言学概论 chapter 1
这里是胡壮麟版语言学概论读书笔记思维导图,语言学就是要研究人类最核心本能的语言能力,透过对口语、书面语甚至手语进行分析和研究,进而了解人类的本质。
编辑于2022-01-12 13:29:22- 胡壮麟版语言学概论
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
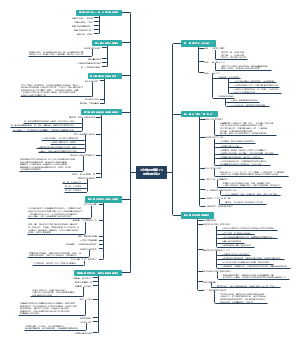
chapter 1 Invitation to Linguistics
Definition of language
Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.This definition has reveealed five essential factors for languae: arbitrary,vocal,symbolic and most importantly human-specific.语言是人类以口头交流的任意的符号系统。该定义揭示了语言的五个要素:系统,任意,口头,符号,人类。
The design features of language
Abitrary 任意性
It is the core feacture of language,which refers to the fact that there is no logical or intrinstic connnection between a particular sound and the meaning it is associated with. It is not entirely arbitrary at all levels. Some words, such as the ones created in the imitation of sounds are motivated in a certain degree.任意性是语言的核心特征,是指符号的形式或者声音与意义之间没有逻辑或者内在的联系。虽然语言从本质上讲是任意的,但也不是完全任意的。一些词语,例如一些拟声词的发音和其意义之间还是有一定联系的。
Duality 二层性
Duality refers to the propety of having tow levels of structures, such that units of the primary level are composed of elements of the secondary level and each tow levels has its own principles of organization. The property of duality only exists in such a system,namely,with both elements (e.g. sounds,letters)and units(e.g. words) 二重性是指拥有两层结构的这种属性,底层结构是上层结构的组成部分,每层都拥有自己的组合规则。二重性只存在于这样的系统之中,既有元素又有他们组合成的单位。
Creactivity 创造性
Creativity means language is resourceful because of its recusivenes,which enables human beings to produce and understand an infinitely large number of sentences in our native language, including the sentences whinch were never heard before.创造性指语言的能产性,它能使人造出和理解无穷的长句,其中很多句子是以前从未听过的。
Displacement 移位性
Displacement means that human languages enable their users to symbolize objects,events and concepts which are not present(in time and space)at the moment of communication.Displacement benefits human beings by giving them the power to handle generalizations and abstractions.移位性是指人类语言可以让使用者在交际时用语言符号代表时间上和空间上并不可及的物体、事件和观点。移位性赋予人们的概括和想象力使人类受益无穷。
Cultural transimission 文化传递性
Language is culturally transmitted. It cannot be transmitted through heredity.语言不是靠遗传,而是通过文化传递的。
Origin of language 语言的起源
The Biblical account 圣经的记载
The bow-wow theory ”汪汪“理论
The pooh-pooh theory “噗噗”理论
The yo-he-ho theory “呦-嘿-吼”理论
The evolution theory 进化理论
Fuctions of language 语言的功能
Informative function 信息功能
Language is used to tell something,to give information ,or to reason things out, functionis regarded as the most important function.Declarative sentences serve this function. 语言用来陈述某件事,提供信息或用作推理。信息功能是语言最重要的功能,一般出现在陈述句中。
Interpersonal function 人际功能
The interpersonal function is considered as the most important sociological use of language, by which people establish and maintian their status in a society. 人际功能是语言最重要的社会功能。人们由此建立和维持他们的身份和社会地位。
Performative function 施为功能
The performative function of language is primarily used to change the social status of persons, such as in marriage ceremonies,the sentencing of criminals, the blessing of children, the naming of a ship at a lauching ceremony,and the cursing of enemies. The kind of language employed in performative verbal acts is usually quite formal and even ritualized.语言的施为功能主要用于改变人的社会地位,例如在结婚仪式,罪犯的量刑,孩子的祝福,在洗礼仪式上命名船只以及诅咒敌人。在施为性言语行为中使用的语言类型通常是相当正式的,甚至是仪式化的。
Emotive function 感情功能
The emotive function of language is the most powerful uses of language because it is so crucial in changing the emotional status of an audience for or against someone or something.语言的感情功能是语言最有用的功能之一,因为它在改变听者赞成或反对某人、某物的态度上作用非常关键。
Phatic function 寒暄功能
This function refers to rxpressions that help define and maintain interpersonal relations,such as slangs,jokes,jargons,ritualistic exchnages,switches to social and regional dialects.寒暄功能是指那些有助于确立和维持人际关系的表达,例如俚语、玩笑、行话、礼节性的问候、社会方言或地域方言的转用等。
Recreational function 娱乐功能
The recreational function refers to the use of language for the sheer joy of it, such as a baby's babbing or a chanter's chanting. 语言的娱乐功能是指纯粹为了娱乐而使用的语言,例如婴儿的牙牙学语,歌者的吟唱。
Metalingual function 元语言功能
The metalingual function refers to the fact that our language can be used to talk about itself. 语言的元语言功能是指语言可以用来讨论语言本身。
Definition of linguistics 语言学的定义
Linguistics is usually defined as the science of language or, the scientific study of language. It not only focus on a particular language,but is based on the systematic invesigation of linguistic date, conducted with reference to some genteral theory of language structure.The four principles which make linguistic a science are exhaustiveness, consistency,economy and objectivity. 语言学通常被定义为研究科学的语言,或对语言的科学研究。它不仅仅关注某种特定的语言,而是基于一些语言结构的综合理论,对语料进行系统研究。语言学研究的科学性可以归纳为:穷尽性、一致性、简洁性以及客观性。
Branches of linguistics 语言学的分支
Microlinguistics--intra-disciplinary divisions 微观语言学
phonetics 语音学
phonology 音系学
morphology 形态学
syntax 句法学
semantics 语义学
pragmatics 语用学
Macrolinguistics--interdisplinary divisions 宏观语言学
psycholinguistics 心理语言学
sociolinguistics 社会语言学
applied linguistics 应用语言学
computational linguistics 计算语言学
neurolinguistics 神经语言学
Important concepts and their distinctions 重要概念及其区分
Descriptive vs. Prescriptive 描写式与规定式
To say that linguistics is a descriptive (i.e. non-normative)science is to say that the linguist tries to discover and record the rules to which the members of a language community actually conform and does not seek to impose upon them other (i. e. extraneous)把语言说成描述性的科学是说语言学家试图发现和记录同一语言共同体的成员所遵循的规则,并不是强加给它们其他规则或正确标准。规定式的语言学目的在于为正确使用语言定下的各种规则,一劳永逸地解决用法上的争议。它们的主要区别在于前者描述事情怎样而后者规定事情应该如何。
Synchronic vs. Diachronic 共时与历时
Language can be studied at a given point in time or over time. When we study language development through time, it is called diachronic or historical linguistics. Synchronic linguistics focuses on the language at any points in history while diachronic linguistics focuses on the differences in tow or more than tow states of language over decades or centuries.语言研究可以是在一个给定的时间也可以是一段时间。当我们集中在某一点来研究语言时就叫做共时语言学。当我们研究随着时间发展的语言时就叫做历时语言学。共时语言学集中研究历史任何时期点的语言现状,而历时语言学集中研究几十年或几百年的时期内两个或比两个更多的语言状况的差异。
Langue vs. Parole
Saussure distinguished the linguistic competence the speaker and the actual phenomena or data of linguistics ( utterances) as langue and parole. Langue refers to abstract linguistic system shared by all the members of speech community. Parole refers to particular realizations of language.索绪尔用语言和言语来区分说话者的语言能力和言语上(表达的)的实际表现或语料。语言是指一个语言群体的所有成员所共有的抽象的语言系统。言语是指语言的具体实现和运用。
Competence vs. Performance(语言能力和语言应用)
1. Chomsky made the fundamental difference between competence and performance. 乔姆斯基提出了语言能力和语言应用的根本区别。
A language user's underlying knowlege about the system of rules is called his linguistic competence. 一名语言使用者对于语言规则系统潜在认知称为他的语言能力。
Performence refers to the actual use of language in concrete situations. 语言运用是指在具体场景中的语言的实际运用。
浮动主题