导图社区 ACP笔记英文
- 89
- 2
- 1
- 举报
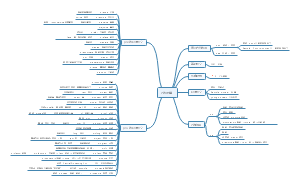
ACP笔记英文
PMI-ACP 笔记, Agile Certified Practitioner。prevent existing customers from stopping use;new product features or services to existing customers。
编辑于2022-07-04 22:50:32- ACP
- CFA Lv2 道德
CFA 2级道德思维导图习题,包含I. Professionalism、II. Integrigy of Capital Markets、III. Duties to Clients、IV. Duties to Employers。
- CFA Lv2 另类
CFA 2级 另类 思维导图 习题,包含M1 Introduction to Commodities and Commodity Derivatives、M2 Overview of Types of Real Estate Investment、M3 Publicly Traded Securities。
- CFA Lv2 衍生品
CFA 2级 衍生品 框架图 习题,包含Key Concepts、M1 Pricing and Valuation of Forward Commitments、M1 Pricing and Valuation of Forward Commitments等。
ACP笔记英文
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- CFA Lv2 道德
CFA 2级道德思维导图习题,包含I. Professionalism、II. Integrigy of Capital Markets、III. Duties to Clients、IV. Duties to Employers。
- CFA Lv2 另类
CFA 2级 另类 思维导图 习题,包含M1 Introduction to Commodities and Commodity Derivatives、M2 Overview of Types of Real Estate Investment、M3 Publicly Traded Securities。
- CFA Lv2 衍生品
CFA 2级 衍生品 框架图 习题,包含Key Concepts、M1 Pricing and Valuation of Forward Commitments、M1 Pricing and Valuation of Forward Commitments等。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
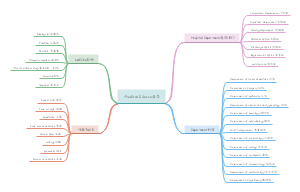
Agile
Manifesto
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
Working software over comprehensive documentation
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
Responding to change over following a plan
Values
Communication
4C
Communicaiton
Coordination
Cooperation
Collaboration
Conflicts
Problem to resolve
Collaboration
Disagreement
Support and Safety
Contest
Accommodate, negotiate, get factual
Crusade
Establish safe structures again
World War
Do whatever is necessary
Simplicity
Feedback
Courage
Humility
Principles
Our highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software
Welcome changing requirements, even late in development. Agile processes harness change for the customer's competitive advantage
Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference to the shorter timescale
Business people and developers must work together daily throughout the project
Build projects around motivated individuals. Give them the environment and support they need, and trust them to get the job done
The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation
Working software is the primary measure of progress
Agile processes promote sustainable development. The sponsors, developers, and users should be able to maintain a constant pace indefinitely
Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design enhances agility
Simplicity — the art of maximizing the amount of work not done — is essential
The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams.
At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly
Triangle
Traditional iron triangle
Scope (not change)
Cost
Schedule
Agile iron triangle
Cost (not change)
Scope
Schedule (not change)
Agile Triangle
Value
Quality
Constraints
Cost
Schedule
Scope
Lifecycle
Characteristics
Phase
Envision
Speculate
Explore
Design, build and test product features
Adapt
Adjustments to dynamics, i.e. handling problems
Close
Agility
Balance flexibility and stability
Product Roadmap
Steps
Identify Requirements
Organize Requirements into categories or themes
Estimate relative work effort
Estimate rough timeframes
Product Road Map
Backlog grooming for project prioritization and selection
High-level representation of the features or themes that are to be delivered in each release
Parking Lot Diagram
Agile Unified Process (AUP) framework
Inception
Elaboration
Construction
Transition
Complex and Adaptive Systems (CAS)
Chaotic
Elevator statement
Process
Tailoring
Adapt the process
Instantiation
Implement the adapted process
Product refinement
no more than 10% of development team's time
multiple scrum team may participate
facilitated by team
Release Planning
Planning Levels
Portfolio
Product
Release
Sprint
Daily
Prediction
Monte Carlo Simulation
Progressive elaboration
Rolling wave planning
next few iterations are planned
Empirical Process Control (EPC)
Transparency / Visibility
Inspection
Adaptation
Share product vision
Revenue
Retained Revenue
prevent existing customers from stopping use
Incremental revenue
new product features or services to existing customers
Quality
Fluid
Define details at capability or feature level
Comparison with Product Roadmap
Risks
Measurement
Qualitative
5 areas
Schedule flaw
Specification breakdown
Scope creep
Personnel loss
Productivity Variation
Risk Exposure
Probability * Size of loss
Risk Analysis
Monte Carlo
eXtreme Programming (XP)
Team
Customer
No Product Owner
Write stories and acceptance tests of each story
Developer
Manager/Tracker
Define rules, schedule plann, track
Coach
Identify XP practices
Onsite customer
40 hours per week
Code refactor
Customer Test
Tool for a customer to verify the business requirements
Continuous Integration
Test Driven Development (TDD)
Add a test
Run all tests
Write code
Run tests and refactor code
Acceptance Test-Driven Development (ATDD)
Acceptance testing
Long term goal
Developed by Kent Beck
Activities
Coding
Testing
Listening
Designing
Other Agile Practice
Lean
Value stream map
Purpose: remove the waste
Steps
1. confirm product
2. confirm process and lead time duration
3. analyze to find out waste
4. provide vision or future product/process
5. refine process to archieve goal
7 wastes (WIDETON)
Waiting
Inventory
Defects
Extra processing
Transportation
Over production
Motion
7 Principles
Eliminate Waste
Buile Quality In
Create Knowledge
Defer Commitment
Deliver Fast
Respect People
Optimize the Whole
Work in Process (WIP)
Material in production but not completed
Last Responsible Moment (LRM)
A strategy of not making a premature decision but instead delaying commitment and keeping important and irreversible decisions open until the cost of not making a decision becomes greater than the cost of making a decision.
Visual Controls
Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM)
Similar to Scrum or XP but time is fixed
Kaizen cycle
Get employees involved
Find problems
Create a solution
Test the solution
Analyze the results
Crystal
Scaling to projects based on size and criticality
Colors
Clear–up to 6 people
Yellow–up to 20 people
Orange–up to 40 people
Red–up to 80 people
Maroon–up to 200 people
Criticality
Comfort (C)
Discretionary Money (D)
Essential Money (E)
Life (L)
Feature Driven Development (FDD)
5 steps
1. Develop an initial model
2. Develop a Feature List
3. Plan by Feature
4. Design by Feature
5. Build by Feature
Swarming
Whole team work to resolve a complex problem
Others
Emotional intelligence
7 components
Self awareness
Emotional resilience
Motivation
Interpersonal sensitivity
Influence
Intuitiveness
Conscientiousness and integrity
Blitz planning
story dependencies and involves using cards to plan a project where timeliness, tasks,and story dependencies are identified and considered
360 assessments
assess project soundness in terms of business value and feasibility
Cohn's square root of the sum of squares
First find the local safety value of all tasks
Next, sum the square of these values
Finally, find the square root of the sum
Tacit knowledge
all knowledge the project team have
Progressive elaboration
Plans and details will inevitably change but become more refined
Scrum
Team
Product Owner (PO)
Development Team
no specific Subject Matter Expert (SME)
T talents
Scrum Master (SM)
Servant Leadership
Characteristics
Promoting self-awareness
Listening
Serving those on the team
Helping people grow
Coaching vs. controlling
Promoting safety, respect, and trust
Promoting the energy and intelligence of others
Types
Do agile
Become agile
Remove impediments
Supported by team and senior management, but not PO
Artifact
Product backlog
DEEP
Detailed Appropriately
Estimable
Emergent
Prioritized
User Story
Front side
a type of user
achieve a goal
what value it can bring
Back side
Definition of Done (DoD)
Defined/responsible by Team
Confirmed/accepted by PO
Given, When, Then
INVEST
Independent
Negotiable
Valuable
Estimable
Small
Testable
User expectations are captured in acceptance tests
3C
Card
Conversation
Confirmation
Story Points Estimate
Algorithmic
Planning Poker
Fibonacci Sequence
0,0.5,1,2,3,5,8,13
T-shirt Size
Size Range
S, M, L
Dot Vote
Affinity Estimation
for large product backlogs
Non-Algorithmic
Delphi
Domain knowledge is required for the team
Persona -> Epic -> User Story
Persona
Extreme character persona
Identify user stories may be missed
MMF vs MVP
MVP: Minimum Viable Product
MMF: Minimum Marketable Feature
Formed by MVPs
Smallest amount of functionally that adds value to the market
Refine gradually and estimate in iteration plan
Prioritization
Kano
Review both positive and negative aspects
MoSCoW
Must
Should
Could
Would not
Based on Pareto rule (80/20)
Value/Risk Matrix
1. High Risk, High Value
2. Low Risk, High Value
3. Low Risk, Low Value
4. High Risk, Low Value (Avoid)
Sprint backlog
Increments
Events
Sprint
Metrics
Burn Up/Down Diagram
Burn Down
Burn Up
Velocity
Burndown Bar Graph
Lower the top of the bar when tasks are completed
Lower the bottom of the bar (below the baseline) when tasks are added to the initial set
Raise the bottom of the bar when tasks are removed from the original set
Raise or lower the top of the bar when the amount of work involved in a task changes
Risk-Adjusted Burn-up Chart
Kanban
Cumulative Flow Diagram (CFD)
Practices in sequence
1. Visualize the workflow
2. Limit WIP
3. Manage the flow
4. Make the process policies explicit
5. Implement feedback loops
6. Improve collaboratively
Kanba Katas
Daily Kata
Daily standup meeting
Improvement Kata
Improve process
Coaching Kata
Operations review
Timebox
Special Sprint
Sprint 0: preparation
Sprint H (Hardening): Integration
Sprint planning
1st day of sprint
< 8 hrs
Decomposition
User requirements -> functions
Functions -> user stories / features
User stories / features -> tasks
Task estimated during both iteration planning and iteration itself
PO defines the sprint goal first
Daily scrum
<15 mins
Contents
What I did yesterday
Plan today
Impediment
Benefits
Peer pressure
Fine grain co-ordination
Focus on the few
Daily commitment
Raise impediments
Sprint review
< 4 hrs
IKIWISI (I'll Know It When I See It)
for stakeholders but not PO
Scope Verification
1. Review
2. Test
3. Accept
Sprint retrospective
< 3 hrs
RCA: 5Y
Feedback
Dynamic process
Past information
Future behavior
Values
Courage
Focus
Commitment
Respect
Openness
Dictionary
Acclaim: 赞同 Advocate: 主张 Affinity: 亲密关系 Antagonistic: 对抗的 Anxiety: 焦虑 Alleviate: 减轻 Appose: 添加 Apprise: 通知 Arbitrarily: 任意的 Artifact:工件 Assume: 承担 Aspirational: 有抱负的 Attrition:人员损耗 Coherence: 一致 Colocation: 集中办公 Complementary: 互补的 Compromise: 妥协 Confront: 对抗 Consensus: 一致 Continent: 大州 Contradictory: 矛盾的 Contusion: 撞击 Conjunction: 结合 Convey: 传达 Chunk: 量 Crucial: 关键的 Delphi: 德尔菲 Decomposition: 解聚 Disciplined: 遵守纪律的 Disaggregation: 解聚 Dissuade: 劝阻 Distill: 提炼 Dysfunction: 功能障碍 Eliminate: 消除 Elevator: 电梯的 Elevate: 提升 Empirical: 经验主义的 Envision: 构想 Encapsulate: 封入,压缩 Expedience: 便利 Evolve: 进化 Fluctuation: 波动 Fibonacci: 斐波那契 Foster: 促进 Fractional: 微不足道的 Flaw: 缺陷 Hesitant: 迟疑的 Hinders: 打扰 Hypothetical: 假设的 Hardening: 淬火 Illustrate: 说明 Impediments: 阻碍 Inadequate: 不合适的 Inevitable: 不可避免的 Instantiation: 实例化 Intrinsic: 内在的 Ishikawa: 石川 Iterative: 迭代的 Jeopardize: 危害 Lean:精益 Likelihood: 可能性 Notable: 著名的 Mandate: 要求 Mandated: 规定的 Manifesto: 宣言 Metrics: 度量 Morale: 士气 Obstacle: 障碍 Osmotic: 渗透 Pareto: 帕累托 Petition: 请求 Pile: 堆积 Pillar: 支柱 Procrastinates: 拖延 Qualitative: 定性的 Quantitative: 定量的 Radiator: 发射源 Refactoring: 重构 Refrain: 避免 Replenishment: 补充 Retrospective: 回顾的 Servant:仆人 Silo:孤岛 Slack: 松弛 Sophisticated: 复杂的 Speculate: 探索 Subtract: 减少 Tailor: 剪裁 Triangulation: 三角测量法 Vague: 不明确的 Vague: 不确定的 Velocity: 速度 Viable: 可行的 Vocabulary:词汇表