导图社区 英语语法
- 98
- 14
- 2
- 举报
英语语法
英语语法,课程在网易公开课上搜索标题就可以找到相应课程,还有彩色版。
编辑于2023-06-14 16:24:40 北京市- 学位英语
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
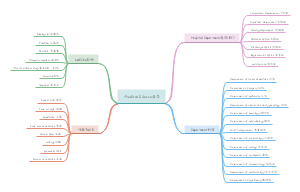
英语语法
1.语序和5种基本句式
英语5种基本句式
基本句式一:S V (主+谓)
the universe remains.
宇宙长存
英语和汉语语序一致
基本句式二:S V P(主+系+表)
the food is delicious
食品好吃
英语和汉语语序一致
基本句式三:S V O(主+谓+宾)
he took his bag and left
他拿着书包离开了
英语和汉语语序一致
基本句式四:S V o O(主+谓+间宾+直宾)
her father bought her a dictionary
她的爸爸给她买了一本词典
英语和汉语语序一致
基本句式五:S V O C(主+谓+宾+宾补)
we made him our monitor
我们选他做我们的班长
英语和汉语语序一致
2.be动词的形式和用法
be动词的形式:be,is,am,are,was,were,being,been
the manis back
theyare (复数)back
一般现在时时态的be动词
hewas back
theywere back
过去时态的be动词
they have been back(他们已经回来了)
be动词的过去分词时态
be动词的用法
后面接名词,形容词,地点副词或短语做补足语
the man isa teacher 补足语
mary's new dressesare colorful 连接的作用,链接前面的主语和后面的补足语
3.be动词的否定,提问,回答
be动词的否定
在am,is,are,was,were 后面加not
缩略式:am not,isn't,aren't,wasn't ,weren't
the man isn't back(现在时)
be动词提问和回答
is he a teacher?
将陈述句的he is,调换位置
yes, he is / no,he isn
4.代词的主格和宾格
主格代词:i,he ,she,it ,you ,we,they
i am a teacher
放在句首
宾格代词:me, him,her,it ,you ,us,them
he likesme
放在句子动词的后面(句尾)
5.名词性、形容词性物主代词
形容词性物主代词:
单数形式:my,your,his/her/its,one's(某人的)
this ismy book
修饰后面的名词book
复数形式:our,your,their
后面必须接名词
名词性物主代词:
单数形式:mine, yours,his/hers/its ,one's
the book isours.
复数形式:ours,yours,theirs
后面不能再接名词了(句尾)
6.反身代词
反身代词:myself,yourself,herself,himself,itself(自己)
yourselves,ourselves,themselves(复数反身代词)
使用方法:
please helpyourself to some fish.
让你自己吃点鱼吧
反身代词可以做宾语和同位语,通常为主语的词性
7.实意动词的特征
实意动词:come,read, go,watch,play,fly
实意动词:动词有实际意义的动词
hecomes from shenyang
动词的单三形式:一般现在时,主语是第三人称单数的时候使用实意动词的单三形式
一般现在时,后面接的介词
she is reading story books
现在进行时
theywent(go的过去式) to America yesterday
过去时
we havewatched the game for three times
现在完成时,动作已经发生,对现在造成了一定影响
my motherwillfly back to china next month
动词的将来时。动词不会变化,在前面加will
实意动词有时态和数量上的变化,数量体现在单数和复数主语连用时
8.实意动词的否定,提问,回答
使用助动词进行否定
在助动词do,does,did后面加not
don dosen didn
idon't(助动词否定形式) go(实意动词) to school by bus.
一般现在时且是非第三人称单数所以用don't
使用助动词进行提问
he oftenplays golf.
Does often play golf?
yes,he does/no,he dosen
9.使用疑问词进行提问和回答
只有who后面不用加助动词,其他都需要将原句中的助动词放在前面,或者加助动词
使用疑问词进行提问:when ,where,who,what ,how
he boughtthree books yesterday
who bought three books yesterday?
what did he buy yesterday?
对原句中的宾语进行提问需要加助动词(did)
when did he buy three books?
对原句中的be动词放在前面,或者加助动词
疑问词放在句首
使用疑问词进行提问:how long ,how far ,how often(多久一次) ,why
they have been in chinafor three years
how long have they been in china?
原句中的be动词放在前面,或者加助动词
10.名词
名词分两类
可数名词
是指数得过来的概念
apple,pencil,student
以元音开头的单词前面加an 以辅音开头的单词前面加a 表示一个 变成复数形式时,去掉前面的a/an
单数
apple
pencil
tomato
复数
apples
pencils
tomatoes
名词变复数规则
不可数名词
无法计算的数量或抽象概念
salt,coffee,water,history,love
不可数名词无复数,只用单数表达
不可数名词前不可加a/an没有复数,但前面可以加量词
11.代词:指示代词和不定代词
指示代词:标识人或事物的代词,用来代替前面已提到过的名词
this-these
that-those
不定代词:指代不确定的人或事物
one
the other
some
any
something
nothing
12.形容词
形容词通常形容人或事物的状态,性质,大小等,通常用在名词前,be动词后
beautiful-thebeatiful girl
the girl is beautiful
the+形容词=复数名词,表示一类,后面的动词使用复数
old-the old
young-the young
the old need more care thanthe young
13.副词
副词可以修饰动词,形容词,其它副词以及其他结构
he runsfast
she is very beautiful
they work very hard
副词的位置
常用的频度副词(always,usually,often,sometimes,never.....)的位置通常放在一般动词前面,be动词后面,助动词和实意动词之间
theyalways come early
samoften writes homework at 7:00
14.不定量的表达法
some,any,most,every ,all
some,any 都表示“一些”
some主要用于肯定句,希望得到肯定回答时,也可以用在疑问句中
any主要用在否定和疑问句中
i'd been expecting some letters the whole morning ,but there weren't any for me
most做形容词时表示"大部分的,大多数",后面接复数名词
most people here are from china
every表示“每一个,所有”后面接单数名词
every one likes the film
all表示“所有”,后面接可数名词复数,不可数名词单数
all the cars are parked in the paking lot
all the coffee is served on time
both表示两者都,可做形容词,代词和副词
both his eyes were severely burned
either是两者之一
一般做主语,后面动词用单数
there are trees oneither side(任何一边) of this street
neither是两者都不
neither answer is correct
many修饰可数名词,表示“许多”
many books
much修饰不可数名词,表示“许多”
much water
a lot of/lots of ,plenty of均可修饰可数和不可数名词
a lot of/lots of books/water
a few ,为肯定含义“几个”,few,为否定含义“没几个”以上两个词均和可数名词连用
a few books are put into the box
few books are put into the box
a little ,为肯定含义“一点儿”,little为否定含义“没多点”以上两个词均可和不可数名词连用
there isa little water in the bottle
there islittle water in the bottle
none 和no one的意思相同,主要做代词,翻译为“一个也不,一点也不”用法稍有区别
none可以接of短语,动词可用单数,也可用复数
none of us have (has) arrived
no one不能接of短语,动词只能用单数
no one knows the answer
15.there/here be 句型
there/here +be根据上下文,有多重翻译方法,可以翻译成 “有”“是”be动词根据后面的名词有单复数变化
不是主语,be动词后面的是主语,决定了be动词的单复数
there is a bllk on the bookshelf
there are some books on the bookshelf
here is the bus stop
here are your books
16.一般现在时和现在进行时
一般现在时,表示通常性,规律性,习惯性的状态或者工作,主语是单数第三人称时,动词有单三的变化,主语是非第三人称单数时,动词为原形
they often get up at7:00
he often get s up at 7:00
一般现在时否定和疑问句用do,does帮助构成
hedoesn't like the car
does he like the car?yes,he does/no ,hedoesn't
一般现在时,动词的单三变化
现在进行时表示现在正在进行或发生的动作,句中通常有now等时间副词呼应,基本构成形式为be+doing
动词的现在分词(ing)
they are watching TV
he <font color="#ff0000" style="">is watching TV
i am watching TV
现在进行时变否定句和疑问句时,将be动词否定或提前
theyaren't watching TVare they watching TV?
动词现在分词的变化规则
17.一般过去时和过去进行时
一般过去时表示过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态:过去习惯性,经常性的行为
基本结构:主语+动词过去式+其他,一般动词在动词后面加ed,还有一些不规则动词不规则变化
play-played
come-came
heworked very hard last night
theycame here by car
动词一般过去时变化规则
过去进行时表示在过去某一时刻或某一段时间内进行或发生的动作
其形式为was/were +doing
they were waiting for you
he was talking with his friends just now
18.将来时
一般将来时表示将来某一时刻的动作或状态,或将来某一段时间内经常发生的动作或状态,常常和表示将来的时间状语连用
如:tomorrow明天next week 下周in the future 将来
助动词will或shall+动词原形。表示将来发生的事情
theywill go to shanghai by ship tomorrow
we shall leave for shanghai next month
be going to+动词原形,用来表示近期或事先考虑过得将要发生的动作以及已有迹象表明必将发生某事,意为“打算,就要”
theyare going to play football this afternoon
she is going to learn french next year
be doing 表示位置转移的动词,如:go,come,leave start ,arrive,可用现在进行时表示将来时
they are leaving for japan
she is arriving tomorrow
19.完成时
现在完成时(have+动词过去分词)动作过去发生,已经完成,对现在造成的影响或后果,动作可能还会持续,可使用的时间状语为:already(已经)和yet(还)
theyhave alreadyarrived in shanghai
shehas played soccer for 3 hours
shehasn't finished the homework yet
过去完成时(had+动词过去分词)表示句中动作发生在过去之前,即过去的过去,已经完成,对过去造成了一定的影响或后果
theyhad arrived in shanghai
shehad played soccer for 3 hours
they hadn't finished the work yet
20.动词用法
动词根据功能分为四类:
实意动词
系动词
助动词
情态动词
动词有数量和时态的变化,时态通常有三大时态:现在,过去,将来时
根据动作进行的状态可分为:一般时,进行时,完成时
使用动词时通常将时态和状态结合使用,例如:一般进行时,过去进行时。。。。。
动词形态变化总结:
21.情态动词can/could/may/might
can/could表示能力,用be able to代替
can/could现在/过去的能力
可以翻译成,能,可能,可以。。。。
he can/could /is able to swim
he can/could come tomorrow
can/could i stay here?
客观可能性(can的可能性大)
表示请求和允许
may/might表示可能性,may的可能性大“请求,允许”might更委婉
口语中常用的回答
yes,please
no,you can't/mustn't(禁止,不准)
he may/might come here by bus
may/might i join you?yes,please/no,you can't/no,you mustn't
22.情态动词should /ought to /must(have to)
must/have to表示“必须,必要”(must表示主观多一些,而have to则表示客观多一些)
have to 有时态和数量的变化
must和have to 二者的否定意义大不相同
如:you mustn't go 你不准去
you don't have to go 你不必去
you must get up early
it's going to rain,i have to go home now
should 表示劝告,建议,命令,其同义词是ought to,should 强调主观看法,而ought to 强调客观要求。在疑问句中,通常用should代替ought to
youshould/ought to do the job right now?
should they stay here now?
23.情态动词need/don't have to
need"需要”
情态动词
he need come here early
he needn come here early
need he come here early?yes,he need/no ,he needn't
实意动词,有第三人称单数和时态的变化,后面可加带 to 的不定时
heneeds to come here early
hedoesn't need to come here early
does he need to come here early?yes,he does/no,he doesn't
回答must和have to 的提问句时,否定式使用needn't,don't have to 等回答方式(不需要,不必)
must i come here early tomorrow?no,you needn't/don't have to
24.情态动词had better/would rather
had better 表示“最好做某事”had虽然是过去式,但不表征过去,better后面接动词原形
hehad better eat more
you'dbetter finish it right now
would rather表示“宁愿,宁可,最好,还是....为好”语感上比“had better ”要轻
you would ratherdeal with it now
否定形式分别为:
had bettr not +动词原形
he had better not eat more
would rather not+动词原形
you would rather not deal with now
25.情态动词used to+动词/would+动词
used to ,would 表示过去习惯性动作,可翻译为“过去常常......”
used to 可指过去的状态或情况,would则不能
the novel used to be popular
would表示反复发生的动作,如果某一动作没有反复性,就不能用would,只能用used to
hewould practise english every week
iused to live in beijing
used to 表示过去经常性或习惯性的动作或状态现在已经结束,would则表示有可能在发生
people used to believe that the earth was flat
he would go to the park as soon as he was free
26.情态动词否定和疑问形式
情态动词的否定,情态动词+not+动词原形
he can't sing an english song
hemay not know her他可能不知道她
he mustn't go there
hedoesn't have to go there
使用情态动词进行提问,情态动词+主语+动词原形
can he sing an english song?yes,he can/no,he can't
must he go there?yes,he must/no,he needn't
does he have to go there?yes ,he does/no,he doesn't
27.情态动词+have+动词过去分词(完成时)
情态动词+have+动词过去分词(完成时):可能.....
表达过去事实
he can/could have arrived
hemay/might have arrived
he must have arrived
推测的含义(但助动词should例外)
should+have+动词过去分词:本应该.......
heshould have arrived
they should have finished the work
needn't have+动词过去分词:本不需要.....
you needn't have done so
must have动词过去分词:准是已经......
he must have arrived
can't have 动词过去分词:不可能已经.....
hecan't have arrived
28.被动语态-被动态的构成和含义
如果主语是动作的承受者,则用动词的被动语态做谓语
被动语态的构成:be+动词的过去分词....by sb.
heis taken to america by his mother(sb)他是被妈妈带到了美国
被动语态有各种时态
the informationis needed by us
the bookwas being read by him
过去进行时的被动语态
the computerhas been used by her
the roomwill be cleaned
the computercould have been used by them
情态动词+完成时
29.被动语态-被动态和情态动词结合
被动语态也可以和情态动词结合:can/could+be+动词过去分词
may/might must /have to should/ought to had better/would rather used to /would need+doing/to be+动词过去分词
和情态动词结合的形式
the foodcould be taken away
the foodmight be taken away
the foodmust be taken away
the foodshould be taken away
the food needs taking away
the foodhad better be taken away
booksused to be returned<font color="#000000"> in two days
30.被动语态-(by+行为者)可省略
动作的行为者不分明,或不重要,或上下文中提到了行为者时,“by+行为者”可以省略
the information is needed
the book is being read
the door was opened
31.被动语态-被动语态的疑问句
被动语态的一般疑问句:助动词+主语+(其他助动词)+动词过去分词~?
is the information needed by him?yes ,it is/ no ,it isn't
has the computer been used by her?yes,it has/no it hasn't
will the room be cleaned?yes,it will/no it won't
被动语态的特殊疑问句:疑问词+助动词+主语+(其他助动词)+动词过去分词~?
the information is needed by the themwhat is needed by them?
the girl is taken to shanghaiwhere is the girl taken?
the book has been read three timeshow many times has the book been read?
32.非谓语动词-to+动词原形/动词原形+ing
动词不定式:由to+动词原形构成,可以做主语,宾语,宾补,定语,表语和状语
主语:to get there by bike will take us an hour
宾语:the driver failedto see the car in time
宾补:we believe himto be guilty
定语:the next train to arrive is from seoul
表语和状语:
my suggestion isto put off the meeting
i come here onlyto say goodbye to you
动词原形+ing,可做动名词用,具有动词的特征和变化形式,但在句子中的用法及功能类同名词:在句子可以做主语,宾语,表语,定语。他也可以被副词修饰或者支配宾语
reading is an art
they went onwalking and never stoppedtalking
your task is quicklycleaning the windows
this is areading room
33.非谓语动词-假主语/真主语,不定式/动名词的否定式
to不定式或动名词可以在主语的位置上,但一般用it代替它做形式主语,这种情况it叫形式主语
it's a great honorto be invited
it is no use crying over spilt milk
在宾语的位置上,用it代替它做形式宾语,这种情况it叫形式宾语
we thinkit important to learn english
i foundit pleasantwalking in the park
对动名词或不定式进行否定时,在不定式或动名词前加not 否定就可以了
he pretendednot to see her
34.非谓语动词-to不定式表示目的
in order to +动词表示目的
由 in order to 引导的目的状语,置于句首,句尾均可
i've written it down in order to remember it
so as to +动词 表示目的
so as to 引导的目的状语,只能置于句尾
he shouted and wavedso as to be noticed
他们的否定形式分别再to前加not
35.非谓语动词-常见的不定式和动名词句型
包含不定式和动名词的一些固定结构
too~to...:太....以至于不能.....
the room is too small to live
enough +名词+to+动词/形容词+enough +to +名词:足够...可以...
there isenough food to eat
the box isbig enough to contain six apples
on -ing:~一.....就....
on seeing the snake,the girl was very frightende
there is no hope of~ing:没希望.....
there is no hope of seeing him
feel like - ing:想要~
i feel like eating ice cream now
have a hard time -ing:做~艰难
they have a hard timesolving the problem themselves
36.非谓语动词-现在分词/过去分词,分词句
动词+ing可称之为动名词,也可称之为现在分词
writing books is his job
动名词,现在分词不能做主语
he is writing a book.
动词的过去分词形式可称之为动词的过去分词,用在完成时和被动语态当中
he has written the homework
the homework is written
分词句时包含现在分词和过去分词的分句
the students went out of the classroom ,laughing and talking
accompanied by his friend ,he went to the railway station
37.原形不定式-使役动词
使役动词,表示“使/让.....”have,make ,let 做使役动词,构成形式为:have/make/let+宾语+动词
hemade me laugh
ilet him go
pleasehave him come <font color="#000000">here
get 和help 都做使役动词,get的使役动词为get+宾语+to+动词,help的使役动词句尾help +宾语+(to)+动词
i can't get anyone to do the work properly
i helped him (to) repair the car
以上的使役动词+宾语+过去分词,表示“让某物/人被别人......”
38.原型不定时-感官动词
感官动词see/watch/observe/notice/hear/smell/taste/feel+宾语+动词原形/现在分词
+动词原形,表示动作的真实性
isaw himwork in the garden yesterday
+现在分词,表示动作的连续性,进行性
isaw himworking in the garden yesterday
和使役动词相似,感官动词后可接过去分词“感官动词+宾语+过去分词”
John saw the manknocked down by the car
39.假设-只表示单纯条件的假设
条件状语从句。用“if”引导条件状语从句,从句为现在时,通常译作“如果.....”
if you get up early,you will catch up with the train
if 引导的条件状语从句,可以放在句首,也可以放在句尾
if you ask him ,he will help you
she will be upset if you fail the exam
40.假设-与现在事实相反的虚拟语气
if从句是一种虚拟的条件或假设,和现在事实相反的,主从句时态具体如下:
从句:动词过去是(be用were)
if iwere you , iwould join them
主句:would/could/should/miight+动词原形
shewould come with you if you invited her
41.假设-与过去事实相反的虚拟语气
if从句是一种虚拟的条件或假设,和过去事实相反的
主从句的时态具体如下:
从句:had+动词过去分词
if had got there earlier, ishould have met her
主句:would/could/should/mitht+have+动词过去分词
if thehad taken my advice ,hewould not have made such a mistake
42.假设-wish/as if +过去时/过去完成时
wish后面的从句,译为:希望....就好了,是不可能实现的假设
与现在事实相反愿望
i wish i were as tall as you(一般过去时)
与过去事实相反愿望
he wished he hadn't said that(过去完成时)
将来不大可能实现的愿望
i wish it would rain tomorrow(would/should/could+动词原形)
as if 翻译为:看起来好像....
如果从句表示与现在事实相反
you look as if you didn care
从句表示与过去事实相反
he talks about rome as if he had be there before
从句表示与将来事实相反
he opened his mouth as if he would say something
43.定语从句-关系代词that,who,which,whom,whose
定语从句:在句中做定语,修饰一个名词或代词,被修饰的名词,叫先行词。其后的从句就是定语从句,由关系词(关系代词过关系副词)引出
关系代词,在从句中做一定的成分,代替先行词,起到链接先行词和从句的作用。常用关系代词:that,who,which,whom,whose
the girlwhom/that i spoke to is my cousin
先行词是人的话用that/who/whom/whose来引导定语从句
whom 在从句中做宾语
they are the peoplethar/who were seen yesterday
who 和that 在从句中既可以做主语又可以做宾语
they are the peoplewhom/that/who i saw yesterday
they ae the peoplewhose wallets were lost yesterday
先行词是动物/事物的话,用which,that,whose来引导定语从句
which,that在从句中可做主语和宾语,做宾语时可以省略
he came back for the bookwhich/that he had fogetten.
he came back for the bookwhich/that was on the desk
this is the chairwhose legs were broken
44.定语从句-关系副词when,where ,why
why:用于修饰表示原因的名词(eg.the reason)
we don't know the reason why he didn't show up
when:修饰表示时间的名词(eg. next week)
we'll put off the picnic until next week,when the weather may be better
where:修饰表示地点的名词(eg. the place)
whe don't knowthe place where he lives
45.宾语从句-连词
宾语从句:在句子中起宾语作用的从句
从属连词:thar,if whether
he said that he was there yesterday
连接代词:who, whom,whose,what
do you konw who has won the game?
连接副词:when,where,why,how
he wants to knowwhen the party is
he told me (that)he would go to college the next year
46.比较级&最高级
通常在形容词和副词后面加“er”(比较级)或“est”(最高级,前面加the)
hard-harder-the hardest
词尾是不发音的单音节e时,加“r”“st”
nice-nicer-the nicest
词尾是辅音+y 的双音节时,去掉“y”加“ier”"iest"
dry - drier- the driest
以一个辅音结尾的重读闭音节时,双写最后一个字母,加“er”“est”
hot-hotter-the hottest
多音节和双音节,在形容词和副词前加
程度加强:“more”“the most”
程度减弱:“less”"the least"
interesting-mote/less interesting -the most/the least interesting
不规则变化:
good-better-the best
many-more-the most
形容词或副词的比较级:表示“比较........”
he istaller than his brother
形容词的最高级:表示“最.......”
he isthe tallest in his class