导图社区 1. Language and Linguistics
- 165
- 11
- 2
- 举报
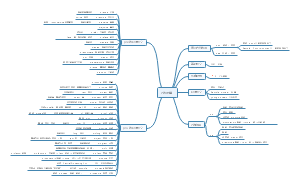
1. Language and Linguistics
A highly condensed version of the textbook LINGUISTICS: A NEW COURSEBOOK FOR STUDENTS OF ENGLISH, which is a good choice for review.
编辑于2021-05-16 19:45:55- Unit4 Syntax
Syntax is a branch of linguistics that studies how words are combined to form sentences and the rules that govern the formation of sentences.
- Unit11 Coginitive Linguistics
The approach that language and language use are based on our bodily experience and the way we conceptualize it is called cognitive Linguistics. CL is not a single theory. It is a collection of approaches to the study of language which include
- Unit9 Language and society
Sociolinguistics is the sub-field of linguistics that studies the relationships between language and society, between the uses of language and the social structures in which the users of language live. It studies how, when, why and in what ways varia
1. Language and Linguistics
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- Unit4 Syntax
Syntax is a branch of linguistics that studies how words are combined to form sentences and the rules that govern the formation of sentences.
- Unit11 Coginitive Linguistics
The approach that language and language use are based on our bodily experience and the way we conceptualize it is called cognitive Linguistics. CL is not a single theory. It is a collection of approaches to the study of language which include
- Unit9 Language and society
Sociolinguistics is the sub-field of linguistics that studies the relationships between language and society, between the uses of language and the social structures in which the users of language live. It studies how, when, why and in what ways varia
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
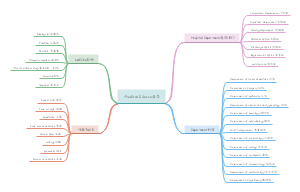
Language and Linguistics
Language
Definitions
Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.
SYSTEM: elements of language are combined according to rules ARBITRARY: no intrinsic connection between a linguistic symbol and what the symbol stands for VOCAL: the primary medium for all languages is sound HUMAN: language is human-specific; very different from the communication systems other forms of life possess
Design Features
Arbitrariness 任意性
no logical or intrinsic connection between a particular sound and the meaning it is associated with
Exceptions:
Onomatopoeic words 象声词:bang, hiss, etc.
Compound words 复合词:pineapple, 土豆, etc.
Displacement 移位性/不受时空限制
Language can be used to refer to and talk about things which are present or not present, which are real or imagined, which are in the past, present, or future.
e.g. I was afraid. (Maybe not now, not the place)
Exception: bees have displacement but in an extremely limited form
Duality 二重性
two levels of structures
Primary level: word, phrase, sentence, text
Secondary level: sound
Units of primary level are composed of elements of the secondary level, and each of the two levels has its own principles of organization
e.g. boy Primary level: distinct and identifiable meaning Secondary level: /b/ /o/ /i/ meaningless
The property of duality only exists in a system with both elements and units.
Animals: 只有基本层次(意义单位),没有第二层次(语音单位)
Productivity/Creativity 能产性/创造性
Novel utterances are continually being created.
Language is resourceful or productive because of its duality and its recursiveness. Language is creative in another sense, that is, its potential to create endless sentences.
Cultural Transmission 文化传递
The fact that the details of the linguistic system must be learned anew by each speaker
The details of the linguistic system cannot be transmitted from generation to generation biologically. Animal systems, on the other hand, are genetically transmitted. People acquire a language in a culture with other speakers and not from parental genes.
Functions
Phatic function/ communion 寒暄功能/交际
e.g. How do you do?
Directive function 指令功能
e.g. Close your book and listen to me carefully!
Informative function 信息功能
e.g. the symbol "Road Closed" on a road
Interrogative function 询问功能
e.g. What time is it now?
Exceptions: rhetorical questions: "If Winter comes, can Spring be far behind?"
Expressive function (reveal speaker's attitudes and feelings) 表情功能
e.g. My God!
Evocative function (create certain feelings in the hearers) 呼唤功能
e.g. jokes, ads, etc.
Performative function (do things or perform acts) 施为功能
e.g. judge's imprisonment sentences, Queen's naming of a ship, chairman says "I declare the meeting open", etc.
Recreational function 娱乐功能
e.g. Chinese verbal dueling (对歌)
Linguistics
Definitions
Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language.
Scope
The study of language as a whole is often called general linguistics(普通语言学).
Phonetics 语音学:the study of sounds used in linguistic communication.
Phonology 音系学:how sounds are put together and used to convey meaning in communication
Morphology 形态学:the study of the way in which symbols, which represent the sounds used in linguistic communication, are arranged and combined to form words
Syntax 句法学:the study of rules which govern the combination of words to form gramatically permissible sentences in languages
Semantics 语义学:the study of meaning conveyed by language
Pragmatics 语用学:When the study of meaning is conducted in the context, in which language communication always occurs, it becomes pragmatics.
The study of all these aspects of language form the core of linguistics.
Sociolinguistics 社会语言学:Language and society are closely connected. The language a person uses often reveals his social background, and there exist so¬cial norms that determine the type of language to be used on a certain occasion; and language changes are often caused by social changes. The stufy of all these social aspects of language and its relation with society form the core of sociolinguistics.
Psycholinguistics 心理语言学:relates the study of language to psychology. Aim to answer such questions as: 1. how the human mind works when we use language; 2. how we as infants acquire our mother tongue; 3. how we memorize; 4. how we process the information we receive in the course of communication.
Cognitive Linguistics 认知语言学: relates language and language use to human experiences of the world and the way they perceive and conceptualize the world.
Applied linguistics 应用语言学:Findings in linguistic studies can often be applied to the solution of such practical problems as the recovery of speech ability. The study of such applications is generally known as applied linguistics.
Some Important Distinctions in Linguistics
Prescriptive vs. Descriptive 语言的规定性研究 vs. 语言的描写性研究
prescriptive 规定性研究:the study which aims to lay down rules for "correct and standard" behavior in using language, i.e. to tell people what they should say and what they should not say
Descriptive 描写性研究:the study which aims to describe and analyze the language people actually use Modern linguistics is mostly descriptive.
Synchronic vs. Diachronic (语言的)共时研究 vs. 历时研究
Synchronic 共时研究:the description of a language at some point of time in history Modern linguistics seems give priority to synchronic approach.
Diachronic 历时研究:the description of a language as it changes through time
Speech and Writing 言语和文字
Speech and writing are the two major media of linguistic communication.
Modern linguistics regards the spoken language as the natural or the primary medium of human language for some obvious reasons:
1. Linguistic evolution: speech is prior to writing. There are still many languages that can only be spoken in the world today.
2. Everyday communication: speech plays a greater role in terms of the amount of information conveyed.
3. Speech is always the way in which every native speaker acquires his mother tongue, and writing is learned and taught later when he goes to school.
4. Modern linguistics: spoken language reveals many true features of human speech, while written language is only the "revised" record of speech.
Langue and Parole 语言和言语 F. de Saussure
Langue 语言 refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all the members of a speech community.
Parole 言语 refers to the realization of langue in actual use.
Contrast: 1. Langue is the set of conventions and rules which language users all have to abide by. Parole is the concrete use of the conventions and the application of the rules. 2. Langue is abstract; it is not the language people actually use. Parole is concrete; it refers to the naturally occuring language events. 3. Langue is relatively stable; it does not change frequently. Parole varies from person to person, and from situation to situation.
Competence and Performance 语言能力和语言运用 N. Chomsky
Competence 语言能力 is defined as the ideal user's knowledge of the rules of his language.
Performance 语言运用 is defined as the actual realization of this knowledge in linguistic communication.
1. Similarity: Saussure thinks that what linguists should study is the langue, and Chomsky--competence. 2. Difference: Saussure took a sociological view of language and his notion of langue is a matter of social conventions; while Chomsky looks at language from a psychological point of view and to him competence is a property of the mind of each individual.
Traditional Grammar and Modern Linguistics 传统语法和当代语言学(规定性研究和描写性研究)
Modern linguistics differs from traditional grammar in several basic ways.
1. Linguistics is descriptive while traditional grammar is perspective. A linguist is interested in what is said, not in what he thinks out to be said.
2. Modern linguistics regards the spoken language as primary, not the written. Traditional grammarians, on the other hand, tended to emphasize, maybe over-emphasize, the importance of the written word, partly because of its permanence.
3. Mdern linguistics differs from traditional grammar also in that it does not force languages into a Latin-based framework语法框架.