导图社区 Unit4 Syntax
- 473
- 15
- 2
- 举报
Unit4 Syntax
Syntax is a branch of linguistics that studies how words are combined to form sentences and the rules that govern the formation of sentences.
编辑于2021-06-10 18:26:05- Unit4 Syntax
Syntax is a branch of linguistics that studies how words are combined to form sentences and the rules that govern the formation of sentences.
- Unit11 Coginitive Linguistics
The approach that language and language use are based on our bodily experience and the way we conceptualize it is called cognitive Linguistics. CL is not a single theory. It is a collection of approaches to the study of language which include
- Unit9 Language and society
Sociolinguistics is the sub-field of linguistics that studies the relationships between language and society, between the uses of language and the social structures in which the users of language live. It studies how, when, why and in what ways varia
Unit4 Syntax
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- Unit4 Syntax
Syntax is a branch of linguistics that studies how words are combined to form sentences and the rules that govern the formation of sentences.
- Unit11 Coginitive Linguistics
The approach that language and language use are based on our bodily experience and the way we conceptualize it is called cognitive Linguistics. CL is not a single theory. It is a collection of approaches to the study of language which include
- Unit9 Language and society
Sociolinguistics is the sub-field of linguistics that studies the relationships between language and society, between the uses of language and the social structures in which the users of language live. It studies how, when, why and in what ways varia
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
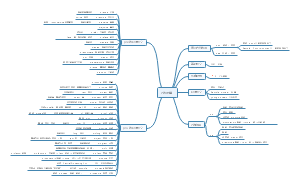
Syntax 句法学
What is syntax?
Syntax is a branch of linguistics that studies how words are combined to form sentences and the rules that govern the formation of sentences.
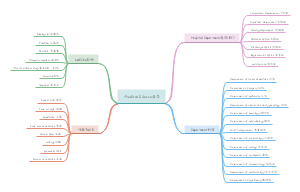
The structural approach 句子分析的结构主义方法
Started by Saussure in the beginning of the twentieth century.
Syntagmatic and paragidmatic relations (横)组合关系/(纵)聚合关系
Saussure
The syntagmatic relation is is a relation between one item and others in a sequence, or between elements which are all present. There are syntactic and semantic conditions the words in a syntagmatic relation must meet.
The sequence which a sign forms with those it is in a syntagmatic relation is sometimes called a structure, to use the word in a more restricted sense. The syntagmatic relation is nowadays also referred to as the horizontal relation, or chain relation.
The paradigmatic relation, Saussure originally called associative联想关系, is a relation holding between elements replaceable with each other at a particular place in a structure, or between one element present and the others absent. e.g. The ___ is smiling. man/boy/girl/... (These words are in a praradigmatic relation)
The class of signs which are in a paradigmatic relation are sometimes called a system, with “system” also used in a restricted sense. The paradigmatic relation is also known as the vertical relation, or choice relation.
Saussure argues that all linguistic units are systematically related to other units by both kinds of relations.
Immediate constituent analysis (IC analysis) 直接成分分析法
Leonard Bloomfield
Definition
Immediate constituent analysis is the analysis of a sentence in terms of its immediate constituents — word groups (or phrases), which are in turn analyzed into the immediate constituents of their own, and the process goes on until the ultimate constituents are reached.
Advantages
Through IC analysis, the internal hierarchical structure of a sentence may be demonstrated clearly, and ambiguities歧义, if any, will be revealed.
* tree diagram * labeled tree diagram 加标记的树形图: Adding labels标记 like noun, verb, determiner, adjective, preposition, or noun phrase, verb phrase etc. to the nodes节点.
Problems
1. At the beginning, some advocators insisted on binary divisions. Any construction, at any level, will be cut into two parts. But this is not always possible.
2. Constructions with discontinuous constituents will pose technical problems for tree diagrams in IC analysis.
3. The most serious problem is that there are structural ambiguities which cannot be revealed by IC analysis.
Endocentric and exocentric constructions (内向)向心结构/(外向)离心结构
Endocentric construction: An endocentric construction is one whose distribution is functionally equivalent, or approaching equivalence, to one of its constituents, which serves as the centre, or head, of the whole. Hence an endocentric construction is also known as a headed construction. e.g. three small children
Two sub-types
Subordinate constructions: Those in which there is only one head, with the head being dominant and the other constituents dependent, are subordinate constructions.
Coordinate constructions: In the coordinate construction, there are more than one head, e.g. boys and girls, coffee or tea, the city Rome, in which the two content constituents, boys and girls, coffee and tea, the city and Rome, are of equal syntactic status, and no one is dependent on the other.
Exocentric construction: The exocentric construction, opposite to the first type, is defined negatively as a construction whose distribution is not functionally equivalent to any of its constituents. There is no noticeable centre, or head, in it. e.g. on the shelf
The functional approach 句子分析的功能方法
Functional sentence perspective 功能句子观(从功能的角度分析句子结构)
Theme主位 and Rheme述位 Theme refers to that which is known or at least obvious in the given situation and from which the speaker proceeds. Rheme refers to what the speaker states about, or in regard to, the starting point of the utterance.
The analysis of a sentence in terms of theme and rheme is also referred to the functional sentence perspective.
Systemic-Functional grammar 系统功能语法
Systemic-Functional grammar means language elements form into systems.The use of language involves a network of systems of choices. The items in a system are in a choice relation with each other.
Halliday argues that there are three general functions of language: ideational概念功能, interlersonal人际功能 and textual语篇功能. And they are related to three grammatical systems: transitivity及物性, mood语气 and theme主位.
The ideational (which is subdivided into experiential and logical) function is to organize the speaker or writer's experience of the real or imaginary world. It correspongs closely to the descriptive function of language, i.e. the function to convey factual information, which can be asserted or denied, and in some cases even verified, but it is broader because it also includes the expression of the speaker's attitude, evalution, his feelings and emotions.
Language serves to establish and maintain social relations: for the expression of social roles, which include the communication roles created by language itself — for example the roles of questioner or respondent, which we take on by asking or answering a question; and also for getting things done, by means of the interaction between one person and another. We refer this function to as interpersonal.
Language has mechanisms to make any stretch of spoken or written discourse into voherent and unified text and make a living passage different from a random list of sentences. This is the textual function of language.