导图社区 爱德思化学U1知识框架
- 123
- 0
- 0
- 举报
爱德思化学U1知识框架
爱德思化学U1不知道怎么复习?这篇笔记帮你快速提炼知识点和考点,构建知识框架。 使用方法:对照笔记中的关键词回忆相关知识点,如果有回忆不起来的,就回去看看教材和笔记。
编辑于2024-08-30 10:13:54- 知识框架
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
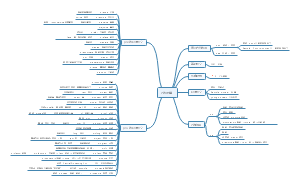
Edexcel AS Chemistry U1
Topic 1 formulae, equations and amount of substance
atoms, elements and molecules
equations
name and formulae
balancing equations
using state symbol
ionic equations
ionic half-equations
reactions
acids
with metals
with metal oxides and insoluble metal hydroxides
with alkalis
with carbonates
with hydrogencarbonates
displacement
involving metals
in aqueous solution
in the solid state
involving halogens
precipitation
chemical tests
carbon dioxide
sulfates
halides
working out chemical equations
equation, ionic equation and observation
calculations
conceptions
relative atomic mass (Ar)
the weighted mean (average) mass of an atom compared to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of C-12
relative molecular mass (Mr)
the weighted mean (average) mass of an molecule compared to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of C-12
relative formula mass (Mr)
molar mass (M)
the Avogadro constant
mole
calculation
mole
n = m/M
amount of particles
using reacting masses
formulae
empirical formula
molecular formula
concentration of solution
c = n/V or c = m/V
molar volume
n = V/24 or V/24000 (at r.t.p)
the ideal gas equation pV = nRT
others
percentage yield
atom economy
ppm (parts per million)
in solution
in gas
Topic 2 atomic structure and the periodic table
atomic structure
conceptions
atomic number
mass number
isotopes
mass spectrometer
process
formation of positive ions
accelerate
deflect
large m/z - deflect less
small m/z - deflect more
analysis
calculate relative atomic mass
ratio
determine relative molecular mass
electronic configuration
quantum shells
quantum shell
sub shell
orbital
predicting electronic configuration
ionisation energy
definition (equation)
successive IE
electronic configuration
trend
across a period
down a group
anomaly
Be and B (Mg and Al)
N and O (P and S)
the periodic table
groups
periods
periodic properties
atomic radii
melting and boiling points
simple
giant
first ionisation energies
Topic 3 bonding and structure
ionic bond
nature
formation: ions
structure: giant lattice
strength
existance of ions
electrolysis of molten NaCl
direct current passing through copper(II) chromate
electron density map
ion radii
trend
polarisation
properties
high melting points
brittle
electrical conductivity
solid
molten or in aq
solubility
covalent bond
nature
formation
σ bond
π (pi) bond
bond length and bond strength
electronegativity
polar
continuum of bonding type
structure
discrete (simple) molecular
bonding
expression
displayed formula
dot and cross diagram
dative covalent bond
shapes of molecule
shapes
bond pair
lone pair
bond angle
polar and non-polar
properties
low melting points
do not conduct electricity
giant lattice
substances
diamond
graphite
graphene
silicon (IV) oxide
properties
hardness
high melting points
electrical conductivity
graphite and graphene
diamond and silicon dioxide
metallic bond
formation
cation and delocalised electrons
structure
giant lattice
properties
high melting points
conduct electricity
conduct heat
delocalised electron
cation
melleability
ductility
Topic 4 introductory organic chemistry and alkanes
introduction
formulae
empirical formula
molecular formula
displayed formula
structural formula
skeletal formula
conceptions
saturated or unsaturated
functional group
homologous series
nomenclature
carbon chain
prefix
suffix
structural isomerism
chain isomerism
position isomerism
alkane and cycloalkane
type of reaction
addition reaction
substitution reaction
oxidation reaction
reduction reaction
polymerisation reaction
chemical hazards
alkanes
crude oil
fractional distillation
cracking
reforming
fuels
complete combustion
incomplete conbustion
oxide of S and N
catalytic converters
alternative fuels
biofuel
hydrogen
substitution reaction
initiation
propagation
termination
further substitution reaction
Topic 5 alkenes
double bond
σ bond
π bond
geometric isomerism
cis-trans naming
E-Z naming
addition reaction
types
hydrogenation (Ni catalyst, heat)
halogenation
hydration (H3PO4 catalyst, heat)
+ hydrogen halide
mechanisms
electrophilic addition
1. form carbocation and anion
2. form product
asymmetrical molecules
primary
secondary
tertiary
equations, conditions and mechanisms
oxidation to diols
+ acidified potassium manganate(VII)