导图社区 罗马
- 286
- 2
- 1
- 举报
罗马
罗马(英语:Rome;意大利语:Roma),是意大利共和国的首都和最大的城市,也是全国政治、经济、文化和交通中心,已有2500余年历史,是世界著名的历史文化名城,古罗马帝国的发祥地,因建城历史悠久而被昵称为“永恒之城”。
编辑于2022-05-08 13:53:40- 地理位置
- 罗马历史
- 文学成就
- 英汉语音对比
英汉语音对比的思维导图,语音是语言的物质外壳,它有多方面的属性:物理属性、生理属性、社会属性,英语和汉语是两种不同的语言,其语音也存在很大的差异。
- 中世纪艺术
The great cathed rals, most of which were dedicated to the Virgin, portrayed her as Mother of God, Bride of Christ, and Queen of Heaven. The image of Mary as a paragon of virtue and chastity constituted an ideal feminine type.
- 罗马
罗马(英语:Rome;意大利语:Roma),是意大利共和国的首都和最大的城市,也是全国政治、经济、文化和交通中心,已有2500余年历史,是世界著名的历史文化名城,古罗马帝国的发祥地,因建城历史悠久而被昵称为“永恒之城”。
罗马
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- 英汉语音对比
英汉语音对比的思维导图,语音是语言的物质外壳,它有多方面的属性:物理属性、生理属性、社会属性,英语和汉语是两种不同的语言,其语音也存在很大的差异。
- 中世纪艺术
The great cathed rals, most of which were dedicated to the Virgin, portrayed her as Mother of God, Bride of Christ, and Queen of Heaven. The image of Mary as a paragon of virtue and chastity constituted an ideal feminine type.
- 罗马
罗马(英语:Rome;意大利语:Roma),是意大利共和国的首都和最大的城市,也是全国政治、经济、文化和交通中心,已有2500余年历史,是世界著名的历史文化名城,古罗马帝国的发祥地,因建城历史悠久而被昵称为“永恒之城”。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
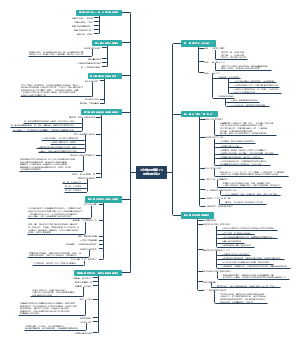
Roman:The Rise to Empire
罗马的崛起和衰落
地理位置
早期历史
Rome's origins are to be found among tribes of Iron Age folk called Latins
Etruscan(伊特鲁利亚人)
起源不明
Established themselves in northwest Italy
For three centuries, Etruscan kings ruled the Latin population
擅长冶金术(metallurgy)、城镇建设、城市规划
罗马所学
城市规划
战车竞赛(chariot racing)
长袍(toga)
青铜与黄金工艺
Arch (the most ingenious structural principle of Mesopotamian architecture)
Romance numerals(数字) were based on an Etruscan system that was borrowed in turn from the Greeks
传说中创建罗马城的双胞胎Romulus and Remus
Greek
colonized the tip of the Italian peninsula (意大利半岛) and Sicily(西西里岛)
the master of philosophy and the arts
罗马所学
a pantheon of god and goddesses
linguistic(语言学的)and literary principles
the aesthetics of the Classical style(古典主义之美)
Phoenician(腓尼基人)
settled on the northern coast of Africa
字母、商业和航海(maritime)技能
王政时期
The Roman Republic(509~133 B.C.E)
崛起
领土扩张
Punic War
Roman(winner) VS Phoenician(腓尼基人)
in 509B.C.E, the Latins overthrew the Etruscans(伊特鲁利亚人)
如何管理
Monarchy(君主政体)gave way to a government "of the people"
Obedience to the Roman state and service in its powerful army were essential to the life of the early Republic.
Rome's highly disciplined army was the backbone of the Empire
consisted of citizens who served two-year terms
by the first century C.E, 军队是一种职业,(自由人,服25 or more years)非罗马人可以通过这种方式让自己和自己的孩子成为罗马人。
militray service is a means of Romanizing foreginers
Josephus(a Jewish historian) 描述者witness the Roman destruction of Jerusalem.(耶路撒冷)
the nature of that "perfect discipline" and dedication to duty that characterized the Roman ethos and Roman culture in general
政体和阶层
the agricultural population of ancient Roman consisted of a powerful class of large landowners,the patricians(贵族),and a more populous class of farmers and small landowners called plebeians(平民).
ps:imperium(帝权)
行政、军事、司法
鹰头节杖和束棒(又称法西斯)即一把周围绑着笞棒的斧头
崩溃(Collapse)
军事
元老院管军务且势力越来越大
the new class wealthy Roman entrepreneurs(equestrians骑士)填补了省级政府的职位
经济
Patrician landowners,whose farms soon become large-scale(latifundia)大型种植园
The disappearance of the small farmer signaled the decline of the Republic
原因
腐败成为普遍
贫富差距拉大
改革失败,政局动荡
军事独裁,内战频频
Gaius Julius Caesar
spent 9 years conquering(征服)Gaul(France and Belgium比利时)
his prose Commenaries on the Gallic War高卢战记
远征埃及与埃及艳后Cleopatra诞下一子
Veni,vidi,vici(I came,I saw,I conquered)
改革
改法律
规范税收
减少债务
安排大量失业的无产阶级去往海外殖民地
授予非意大利人公民身份
改革西方历法
365天12个月 July(named after by himself)
修建公共项目
He laid out Rome's first urban center: The Forum,a public meeting place that combined the functions of government,law,commerce,and religion,would be enlarged and embellished by his imperial followers.
a group of his senatorial opponents,led by Marcus Junius Brutus assassinated him
The Roman Empire(30 B.C.E~180 C.E.)
崛起
Octavian
his navy routed the combined forces of Mark Anthony and Queen Cleopatra
Although he called himself "first citizen"(princeps),his title of Emperor betrayed the reality that he was first and foremost Rome's army general(imperator),the Senate,however,bestowed on him the title Augustus("the Revered One"受人尊敬的)
和参议院分享立法权,并保留否决立法的权力
statue
a Pax Romana
peace and stability
与中国和印度等国积极进行贸易往来
试图阻止道德沦丧
通过法律制止通奸行为,单身汉接受遗产(最终失败)
artistic and literary productivity
启动了很多新的公共工程(3 aqueducts渡槽 and 500 fountains喷泉)警察和消防局之类的市政服务
a new religion,Christianity.
Government by and for the people had been the hallmark of Rome's early history,but the enterprise of immperialism ultimate
Roman Law(the Latin jus means both "law" and "justice")
the development of a system of law was one of Rome's most original and influential achievements.
习惯法到成文法
Twelve Tables of Law
praetors (magistrates who administered justice) and jurisconsults (experts in the law) interpreted the laws, bringing commonsense resolutions to private disputes.
Case Law 判例法
公民法到万民法
Early in Roman history, the law of the land (jus civile) applied only to Roman citizens, but as Roman citizenship was extended to the provinces, so too was the law. Law that embraced a wider range of peoples and customs, the law of the people (jus gentium), assumed an international quality that acknowledged compromises between conflicting customs and traditions. The law of the people was, in effect, a law based on universal principles, that is, the law of nature (jus naturale).
The full body of Roman law came to incorporate the decisions of the jurists, the acts passed by Roman legislative assemblies, and the edicts of Roman emperors.
Corpus Juris Civilis(查士丁尼民法大全)
The Roman system of law influenced the development of codified law in all European countries with the exception of England.
衰落
The emperors Diocletian (245-316) and Constantine (ca. 274-337) tried, but failed, to arrest the decline. Finally, in 476, a-Germanic army- commander led a successful attack on Rome and deposed the reigning Roman emperor, Romulus Augustulus. The great Empire had fallen.
戴克里先,改革暂时制止了西方帝国的衰落,颁布4条敕令对基督教徒进行最后一次大规模迫害
君士坦丁大帝,第一位承认基督教的罗马皇帝,迁都拜占庭改名君士坦丁堡,推动基督教成长为世界性宗教
文学成就
Roman Philosophic Thought
more practical 学希腊
代表
Epicureanism(伊壁鸠鲁)
The Latin poet Lucretius
唯物主义
所有东西都是由原子(atoms)构成
only work
On the Nature of Things
Stoics(斯多葛学派)
The commonsense tenets of Stoicism encouraged the Roman sense of duty. At the same time, the Stoic belief in the equality of all people had a humanizing effect on Roman jurisprudence and anticipated the all-embracing direction of Early Christian thought
Lucius Annaeus Seneca(塞内卡)
On Tranquility of Mind
the emperor Marcus Aurelius
五贤帝
沉思录
Latin Prose Literature
Roman gave the West its first geographies and encyclopedias(百科全书) , as well as some of its finest biographies, histories , and manuals of instruction.
雄辩,演说,书信
Titus Livius
写了罗马八世纪的历史
Marcus Tullius Cicero
Clarity and eloquence are the hallmarks of his prose style,which Renaissance(文艺复兴) humanists hailed as the model for literary excellence.
On Duty
沉思录
As Cicero suggests, Roman education emphasized civic duty. It aimed at training the young for active roles in civic life.
P. Cornelius Tacitus
For careers in law and political administration, the art of public speaking was essential. Indeed, in the provinces, where people of many languages mingled, oratory was the ultimate form of political influence. Since the art of public speaking was the distinctive mark of the educated Roman, the practical skills of grammar and rhetoric held an important place in Roman education.
One of the greatest spokesmen for the significance of oratory in public affairs
Tacitus 'Dialogue on Oratory describes the role of public speaking in ancient Roman life. It bemoans the passing of a time when "eloquence not only led to great rewards, but was also a sheer necessity."
Roman Epic Poetry
Under the Octavian, Rome enjoyed a golden age of rature whose most notable
Virgil
The Aeneid
Rome's foremost poet-publicist, Virgil wrote the semilegendary epic that immortalized Rome's destiny as world ruler.
The Aeneid was not the product of an oral tradition, as were the Homeric epics; rather, it is a literary epic, undertaken as a work that might rival the epics of Homer.
Roman Lyric Poetry
代表人物
Virgil
eclogue(牧歌 田园诗)
glorify the natural landscape and its rustic inhabitants.
Virgil's Eclogues found inspiration in the pastoral sketches of Theocritus(田园诗创始人)
Catullus
Many Classicists looked to Hellenic prototypes
深受Sappho的影响
friendship, love, and sex
Ovid
Metamorphoses(变形记)
神话传说之大成
The Art of Love
Horace
Octavian‘s poet laureate
Satire(讽刺)
思考现实与哲学理想之间的矛盾
To Be Quite Frank
Juvenal
Rome's most famous satirist
His sixth satire,“Against Women”is one of the most bitter antifemale diatribes in the history of western literature.
Roman Drama
模仿希腊
以道德和说教为意图
以希腊和罗马的历史为主题
娱乐形式,与作为主要公民节日标志的公共游戏一起提供(ludi)
悲剧
Seneca
其戏剧莎士比亚提供灵感
喜剧
Plautus
Terence
艺术成就
Architecture
Rome's architectural and engineering projects engaged the inventive use of the arch and the techniques of concrete and brick construction.
The Romans adapted this structural principle inventively: they placed arches back to back to form a barrel vault, at right angles to each other to form a cross or groined vault, and around a central point to form a dome
The Romans contributed domed and stone-vaulted types of construction that enclose vast areas of interior space.
Rome's monumental building projects were visual imperial propaganda.
代表建筑
Pont du Gard
输送淡水
万神庙(pantheon)
斗兽场(colosseum)
柱式发展
混合柱式
塔司干柱式
君士坦丁凯旋门(triumphal arch)
Sculpture
主要内容
肖像雕塑
王政时期
遗容蜡像
逼真、死板
共和国
学希腊(复制)
写实与美化结合
奥古斯都像
帝国
注重表现人物的内心和品质
浮雕
记录重大事件、歌颂王权和战绩
his victory over Dacia
提图斯(Titus)凯旋门
与希腊雕塑的区别
Painting
视幻觉法(欺骗眼)trompe l'oeil("fool the eye")
Pictorial Realism also dominates the frescoes with which the Romans decorated their meeting halls, baths, and country villas.
Among the finest examples of Roman frescoes are those found in and around Pompeii and Herculaneum, two southern Italian cities that attracted a population of wealthy Romans.
Music
Passages from the writings of Roman historians suggest that Roman music theory was adopted from the Greeks, as were most Roman instruments.
In drama, musical interludes replaced the Greek choral odes-a change that suggests the growing distance between drama and its ancient ritual function.
Music was, however, essential to most forms of public entertainment and also played an important role in military life; for the latter, the Romans developed brass instruments, such as trumpets and horns(铜管乐器,如号角与战鼓), and drums for military processions.
罗马女人
和黄金时代的雅典女性相比,也没有更多的公民权
不能投票,也不能担任公职
没有从男性那里占据独立的家庭住所
可以拥有独立的财产
自由管理自己的法律事务
可以接受教育,担任各种职务
the emperor Septimiuss Severus banned female combat, finding it an atfront to 3(侮辱) military dignity.