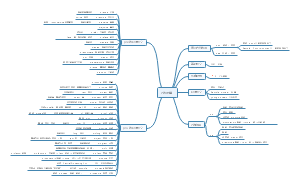
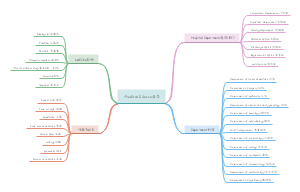
导图社区 improved urban heat island mitigation using bio climatic redevelopment along an
improved urban heat island mitigation using bio climatic redevelopment along an
这是一篇关于improved urban heat island mitigation using bio climatic redevelopment along an的思维导图
编辑于2022-06-01 23:12:02- UHI、wat…