导图社区 连词
- 214
- 4
- 1
- 举报
连词
这是一个关于连词的思维导图,主要内容有连词概述(conjunction)、并列连词(coordinators)、从属连词(subordinators)。
编辑于2022-08-06 18:23:20 广东- 连词
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
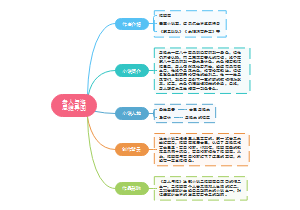
连词
连词概述(conjunction)
什么是连词
连词是连接单词、短语或从句的词类。它是一个虚词,本身没有语义内容,主要是增加语法功能,揭示句子的结构关系。
eg.office and facilities(连接单词),rode in the truck and walked the routes and interviewed people(连接短语),I was very angry,and I was deeply confused.(连接从句)
连词的分类(classification of conjunction)
从语法上来讲,连词分为两类:并列连词(coordinating conjunction)and,but,or,nor,for,yet,so...,从属连词(subordinating conjunction)although,because,since,unless...
从构词法来讲,连词分为两类:单词连词(one-word conjunction)and,but,or,nor,yet,for,so...,多词连词(multiple-word conjunction)neither...nor,as well as,as though...)
并列连词(coordinators)
表示转折关系(But-group coordinators)
表转折关系的并列连词:but,yet,while,whereas,not...but,only,表示转折关系的连接副词:nevertheless,however,still,on the contrary,on the other hand,表示对立或者变成另外一个意思
eg.It never rains but it pours.,I have failed,yet I shall try again.,Jane is slender,while/whereas Mary is stout.,This coat is not mine but yours.,He very much wanted to buy the house,only he could not afford it.
有些连接副词例如:however,furthermore,nevertheless,consequently,therefore,accordingly...,就像连词一样,连接两个用分号分隔的主句或两个单独的句子。eg.It's raining hard,but I think we should go out.,It's raining hard;however,I think we should go out.,It's raining hard.However,I think we should go out.
but和however的用法区别
but是连词,可放在句首、句中连接平行结构(but后没有逗号)
eg.But what else can we do?,He is young but experienced.,He worked hard,but he failed at first.
however是副词,可放在句首、句中、句末(however后有逗号)
eg.He worked hard.However,he failed at first.,He worked hard;however,he failed at first.,He worked hard;he failed at first,however.
but和yet的用法(都是连词)
but自然轻松转折;yet强烈意外转折 eg.He didn't go shopping but go back home.,He is rich,yet he is not happy.
but不能与although连用,yet可以 eg.Although he is rich,but(×) he is not happy.,Although he is rich,yet (√)he is not happy.
but和yet都可以位于句首 eg.But what else can we do?,Yet the house was cheerful.
yet和but或and连用,构成习语 eg.He has a good job,(but/and)yet he never.,Seems to have any money.
while和whereas的用法(都是连词),表转折时,while=whereas,但whereas语气更强,更正式,强调两者间的对比,往往连接内容和结构对称的句子
eg.I love strong tea while/whereas my father loves coffee.,Some men are rich while/whereas others are poor.
while的用法
表示让步的用法,其意为“虽然,尽管” eg.While the work was difficult,it was interesting.,While I understand what you say,I can't agree with you.
表示时间的用法,其意为“当.......的时候” eg.We must strike while the iron is hot.,Stand still while I take your photograph.
表示对比的用法,其意为“而”“但” eg.Michael's very good at science while his sister Tian is good at arts.
省略用法,即主句与从句主语相同,且从句谓语动词含有动词be时,通常可省略从句主语和动词be eg.While (she was) in prison,she wrote her first novel.,He had sstrayed from home while still a boy.
表示并列关系(And-group coordinators)
表示并列关系的并列连词:and,both...and...,not only...but(also)...,not...nor,neither...nor...,表并列关系的连接副词:also,besides,furthermore,moreover,in addition
通常用来表补充(addition)或引申(extension),在积极或消极的方向。and可以有其他意义:顺序(temporal sequence),结果(result),条件(condition),对比(contrast),评注(attitudinal disjunct)
and的用法
eg.I like English and French.(补充),Alice is smart and Jim is dull.(对比),He closed the window,turned off the light and left the room.(顺序),I miss breakfast and I'm starving.(结果),Think it over again and you'll find a way out.(条件,结果),He has a somewhat swelled head,and I don't like it.(评注)
both...and...,neither...nor...,not only...but also...的用法
both...and...
连接相同结构 eg.Both teaching and research are making great strides.,We are going to fly both to Chicago and to Miami. (不可说成We are going to fly both to Chicago and Miami.)
不能连接两个分句 eg.Both Jane wanted to study French,and her husband wanted to study French too.(×),Both Jane and her husband wanted to study French.(√)
neither...nor...
可连接相同结构,可连接两个分句 eg.Neither the Kansas coach nor the players were(就近原则) confident of victory.,Neither does he smoke nor does he drink.
nor后既可带主动词也可不带;nor可引导整个分句 eg.He neither likes fiction nor(likes)poetry.,He neither likes fiction,nor does he like poetry.
not only...but also...
连接相同结构 eg.He likes not only the girl,but also the family.,Not only you but also Mary is(就近原则) to blame for this accident.
可连接两个分句 eg.Sports not only keeps a man healthy,but they also give him team spirit.,Not only did he likes fiction,but he also likes poetry.
表示选择关系(Or-group coordinators)
表选择关系的连词:or(或者、还是、否则),either...or...(不是...就是...),neither...nor...(既不...也不...) 表选择关系的副词:otherwise(要不然),通常表交替(alternation),and和either...or也表消极状态(negative condition)
eg.Would you prefer tea of coffee?(交替),Seize the chance,or you'll regret it.(消极),Either you or I must go there.(交替),You'll either behave yourself,or you'll never go out with me?(消极)
or的用法
表示选择,意为“或”、“还是” eg.Is the radio off or on?,Would you prefer tea or coffee?
表示一种否定的条件,意为“否则” eg.Dress warmly,or else you'll catch cold.,Be careful,or you'll break that vase!
可表示“要不就是” eg.He must be joking,or else he's mad.,The book must be here,or else you're lost it.
用于否定句中代替and eg.He was not clever or good-looking.
用于习语 eg.The work is more or less finished.
表示因果关系(For-group coordinators)
表因果关系的并列连词:so,for,表因果关系的连接副词:then,therefore,hence,thus,according,consequently,通常表示原因和影响(cause and effect)
eg.He told me to do it ,so I did it.,The door was looked,so we couldn't get in.,He shook his head,for he thought differently.,The days were short,for it was now December.
for的用法(不能放在句首,也不能单独使用)
for用于加以解释表示推断原因
for所连接的分句只能位于句尾;前面用逗号隔开
for不能用于回答问题
for引导的从句不能位于它所解释的动词之前
for引导的从句不能位于not,but或任何连词之后
so的用法
so用作连词,主要用于表达结果,意为“所以” eg.It's very cold,so wear a heavy coat.
有时可与并列连词and连用,构成习语and so(相当so) eg.He worked hard and so he succeeded.
从属连词(subordinators)
连接时间状语从句的从属连词
表示“当......的时候”或“每当”的时间连词,主要有when,while,as,whenever。 eg.Don't talk while you're eating.,Vegetables are best when they are fresh.,He came just as I was leaving.
表示“在......之前(或之后)”的时间连词,主要有before,after。 eg.Try to finish your work before you leave.,After we have finished tea,we will sit on the grass.
表示“自从”或“直到”的时间连词,主要有since,until,till。 eg.She's been playing tennis since she was eight.,Hold on until I fetch help.,Never trouble trouble till trouble troubles you.不要无事惹事。
表示“一......就”的时间连词,主要有as soon as,the moment,the minute,the second,the instant,immediately,directly,instantly,once,no sooner...than,hardly...when。 eg.I'll let you know as soon as I hear from her.,The moment I have finished I'll give you a call.,I came immediately I heard the news.
表示“上次”“下次”"每次“等的时间连词,主要有every time(每次),each time(每次),(the)next time(下次),any time(随时),(the)last time(上次),the first time(第一次) eg.I′ll tell him about it (the)next time I see him.,You can call me any time you want to. 注意:every time,each time,any time前不用冠词,(the)next time,(the)last time中的冠词可以省略,而the first time中的冠词通常不能省略。
as作为从属连词
表示伴随,意为“随着” eg.As time passed,things seemed to get worse. 若其后不接从句,而接名词,则用介词with“随着”。 eg.With the development of modern agriculture and industry,more and more waste produced.
表示让步,意为”虽然“”尽管“,要用于倒装句(相当于though,但语气稍弱) eg.Boy as he was,he behaved like a girl.,Much as I like you,I couldn't live with you.
表示时间,意为“当......时候” eg.He dropped the glass as he stood up. 注意:as引导时间状语从句时,其谓语动词通常只能是动作动词,而不能是静态或状态动词。
表示原因,引导原因状语从句时,其谓语动词可以是动作动词,也可以是状态动词 eg.As you weren't there I left a message.,另外,引导原因状语从句,可用以下这样的倒装语序。 eg.Tired as she was,I decided to disturb her.
引导条件状语从句的从属连词
主要有:if,unless,as/so long as,in case,only if(只要),if only(但愿......就好了) ,provided/providing that/suppose/supposing that(假如),on condition that(条件是...) Do you mind if I open the window?
if和whether都可以表示“是否”,两者在表示“是否"时的用法区别
互换的场合。引导宾语从句表示“是否”时,两者常可互换 eg.He asked if(whether)we wanted a drink.,He didn′t tell me if(whether)he would come. 如果引导条件状语从句,则只能用if(意为“如果”)
通常用if的场合。当引导一个否定的宾语从句时,通常用if而不用whether。 eg.I don't care if it doesn't rain.,在个别词语(如wonder,not sure等)后的从句否定式有时也可能用whether来引导。 eg.I wonder if(whether)he isn't mistaken.
通常用whether的场合
引导主语从句且放在句首 eg.Whether he will come is still a question.,若在句首使用形式主语it,而将主语从句放在句末,则有时也可用if来引导 eg.It was not known whether(if) he would come.
引导表语从句 eg.The question is whether we should go on with the work. 引导表语从句偶尔也用if(很不正式),但远不如用whether常见。
引导宾语从句且放在句首时 eg.Whether he is single I don't know.
引导让步状语从句时 eg.Whether he agrees or not,I shall do that.
与or连用分别引导两个从句时 eg.I don't know whether he is wrong or she is wrong.
用于不定式之前时 eg.I'm not sure whether to stay or leave.
用于介词之后时 eg.It depends on whether the letter arrives in time.
直接与or not连用时 eg.I will write to you whether or not I can come.
在某些动词后(如discuss等)通常只用whether eg.We discussed whether we should hold a meeting.
引导目的状语从句的从属连词
主要有:in other that,so that,in case,for fear等 eg.He raised his voice so that everyone could hear.,Take your umbrella(just)in case it rains.
in case用作连词时的用法
表示条件,意为“如果”“万一” eg.In case it rains,do not expect me.
表示目的,意为“以防”“生怕” eg.I'm shy of buying shares in case I lose money.,Take warm clothes in case the weather is cold. 有时中间的谓语由should构成,强调偶然性,可译为“万一” eg.I wrote down her address in case I should forget it.,I always slept by the phone in case he should ring during the night.
引导结果状语从句的从属连词
主要有:so that,so...that,such...that等 eg.I went to the lecture early so that I got a good seat.,I had so many falls that I was black and blue all over.
引导原因状语从句
主要有because,as,since,seeing(that),now(that),considering(that) eg.He distrusted me because I was new.,As you are sorry,I′ll forgive you.,Since we′re no money,we can′t buy it.
because除经常用于引导原因状语从句外,还可引出表语从句或用于强调句等。 eg.It is because you're eating too much.,It was because I wanted to buy a dictionary that I went to town yesterday.
用于构成复合介词because of,其后可接名词、代词、动名词、what从句(但不能是that从句或没有引导词的从句) eg.He is here because of you(that).,We said nothing about it,because of his wife's being there.
because,since,as,for的用法区别
关于because:语气最强,表示直接原因,可用于回答why提出的问题、引导表语从句、用于强调句等,而其余三者均不行 eg.——Why didn′t he come?——Because he was ill.
关于since与as:两者所表示的原因都是人们已知的,即对已知事实提供理由,而不是表示直接原因。since比as语气稍强,且比as略为正式,它们引导的从句通常放在主句之前,有时也放在主句之后 eg.As you weren't there,I left a massage.,Since you are wrong,you should apologize. since可用于省略句,而其他三者不行 eg.Since so, I have nothing to say.
关于for:是并列连词(其余三者属于从属连词),它有时可表示因果关系(通常要放在主句之后,且可与because换用;有时不表示因果关系,而是对前面分句内容的解释或推断(也要放在主句之后,但不能与because换用) eg.The ground is wet,for(=because)it rained last night.
in that引导从句的用法,如果用in that引导分句,则它是一个习语,意思是“因为,由于”,与从属连词because意思相同 eg.She was fortunate in that she had friends to help her.,The situation is rather complicated in that we have two managing directors.
引导让步状语从句的从属连词
主要有:although,though,even though,even if,while,however,whatever,whoever,whenever,wherever等 eg.I like her even though she can be annoying.,You won't move that stone,however strong you are.
although与though用法区别
用作连词,表示“虽然”,两者大致同义,可换用,只是although比though更为正式。 eg.Though(Although)they're expensive,people buy them.
although一般不用作副词,而though可用作副词,表示“可是”“不过” eg.I expect you're right-I'll ask him,though. 这一例子中用的though通常位于句末,但有时位于句首的though也有这样的意思。
在as though(好像,仿佛),even though(即使,纵然)等固定短语中,不能用although代替though eg.She treats me as though I were a stranger.,He's the best teacher even though he has the least experience.
当though用于倒装形式时,它不能换成although,但可换成as eg.Successful though/as he is,he is not proud.,Much though/as I like you,I couldn't live with you. 在某些特定的语境中,although与but连用的句子是可能的,且在although从句之前 eg.He wanted to go abroad,but although he had some money he couldn't afford it.
引导方式状语从句的从属连词
主要有:as,as if,as though,the way等 eg.Why didn't you catch the last bus as I told you to?,He bent the iron bar as if it had been made of rubber?,She spat out the food as though it was poison.
引导地点状语从句的从属连词
主要是:where,wherever,everwhere,anywhere等 eg.The church was built where there had once been a Roman temple.,I'll take you anywhere you like.
引导比较状语从句的从属连词
主要有:than和as...as... eg.She was now happier than she had ever been.,I glanced at my watch.It was earlier than I thought.,He doesn't work as hard as she does.