导图社区 Chapter 2 Culture in Ancient Rome
- 225
- 2
- 1
- 举报
Chapter 2 Culture in Ancient Rome
第二章:古罗马文化,罗马,文化,包括The Historical Development of Ancient Rome,The RomanSocial andEconomic Conditions,Other aspects(myth,religion,literature,architecture,law)等内容。
编辑于2022-11-04 13:34:31 新疆- 古罗马,古罗马文化,文化
- Chapter 2 Culture in Ancient Rome
第二章:古罗马文化,罗马,文化,包括The Historical Development of Ancient Rome,The RomanSocial andEconomic Conditions,Other aspects(myth,religion,literature,architecture,law)等内容。
- Chapter1 Culture in Ancient Greece
这是一个关于Chapter1 Culture in Ancient Greece的思维导图,主要内容有The historical development of Greek civilization、Greek mythology (religion)、Greek philosophy等。
Chapter 2 Culture in Ancient Rome
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- Chapter 2 Culture in Ancient Rome
第二章:古罗马文化,罗马,文化,包括The Historical Development of Ancient Rome,The RomanSocial andEconomic Conditions,Other aspects(myth,religion,literature,architecture,law)等内容。
- Chapter1 Culture in Ancient Greece
这是一个关于Chapter1 Culture in Ancient Greece的思维导图,主要内容有The historical development of Greek civilization、Greek mythology (religion)、Greek philosophy等。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
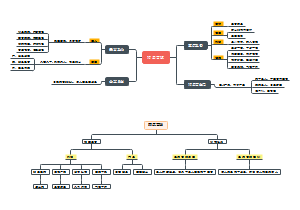
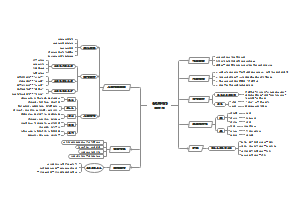
Chapter 2 Culture in Ancient Rome
1.The Historical Development of Ancient Rome
Origin : a small villages in central Italy
Seven-Hill Ally(During 700 BC -800 BC,it took shape and cities and tribes came into being.)
The early development: 753 BC--509 BC 王政时期(the rule of seven kings ,two consuls(archons)anad a senate.
became arepublic(509 BC)
Octavius took supreme power as emperor with the title of Augustus(27 BC)
During the 4th century BC, Rome unified Italy by military conquest.
From about 264 BC, Rome came into the hundred years’ conflict with Carthage and defeated Carthage in 146 BC.
Overseas expansion: Rome conquered such Mediterranean countries as Greece and Macedon and built up overseas provinces. (frequent wars) --ambition, violence, ruthlessness.
In 59 BC, Julius Caesar with other two formed the alliance of the first Triumvirate (knights, common people and the army) to fight against aristocrats until his death.
the Pax romana lasted for two centurie
divided into East(the Byzantine Roman)and West(395 AD)
the West Rome ended(476 AD)
the East Rome collapsed(1453 AD)
2.The RomanSocial andEconomic Conditions
Social structure and Tendencies
hierarchy --legal distinction between
the ruling class <--->the ruled
the rich <-->the poor
aristocracy <-->the ordinary people
the citizen <-->the noncitizen
Diparties between city and countryside
politics is a combination of democratic forms and oligarchic dominance
Family Life and Customs
Military service
Male-domination inherent
Name assigned way
males had three names
Forename
middle name
last or family name
Roman women,only have one name
Slave
Physical labour
Farming
mining
Manual labour
Bookkeeping
teaching
music -playing
housework
Leisure time
games
religious rituals
carefree conversation
Building of Houses and Towns
Every section of the city had its function
water supply was at an advanced level of engineering
Roman Law
Justinian Law code
3.Other aspects(myth,religion,literature,architecture,law)
Myth and religion
influenced by Greek culture and myth ,the Etruscans and Greek migrants brought Greek myths in modified form
Three important gods
jupiter: a god of lightning -->a Chief god like Zeus
Juno :-->Hera
Minerva : -->Athena in charge of arts,science and wisdom
Literature
Roman poetry
Virgil(70-19 BC)
Aeneid
Eclogues
Horace (65-8 BC)
Book of satires
The odes
compact pomes on universal subjects such as love,pleasure and the brevity of life
Epistles
Ovid(43 BC-AD17)
Works
the metamorphoses
Philomon and Baucis
Ceyx and Halcyone
style -not just the expression of strong feeling but to amuse
Roman Drama
Tius Maccius Plautus (254-184 BC)
The Boastful Armyman
A pot of Gold
The Twin Brothers
Terence(195 or 185-159 BC)
Style -clear,simple and finished
works
the Mother -in-law
Two Brothers
Prose writers
Gaius Julis Caesar (102-44BC)
Commentaries on the Gallic War
The Civil war
Cicero (106-43 BC)
Works
speech
Brutus
orator
Ethical writings
On friendship
On old Age
rhetoric writings
an abstract of the topica of Aristotle
A perfect to lost translations of the speeches of Aeschion and Demosthenes,on the crown and de otimo Genere oratorum.
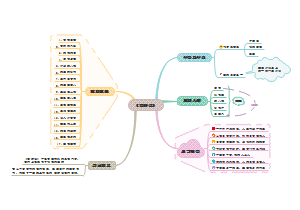
Philosophy(2)
Roman philosophy was greatly influenced by the Greek philosophers, especially by the Stoic and Epicurean schools. They also provide practical explanation and application of philosophical principles. There are two philosophers famous for their contribution to the interpretation of Greek philosophy, namely Lucretius and Seneca.
Lucretius
Epicureanism
Roman Law
The Law of Twelve Tables
Law of the Twelve Tables 十二铜表法:The law of the Twelve Tables was the oldest oral law made by ten magistrates called decimvir, which was inscribed on the bronze and wooden tablets in 450 BC. The original tables were destroyed in 390 BC. They are a series of articles about various private rights and the strict penalties. The code is the basis of Roman laws, existing for almost 1000 years.
The law abolished the system of slavery and banned the intermarriage of aristocrats and common people.
Justinian Law
Roman Architecture
features
unusual use of the arch
innovation
reproduced
the channels of Rome
the Baths of Caracalla
the Baths of Diocletian
the pantheon
Rome
the Basilicas
the Colosseum
Art
augustan art was in a fusion of the prevailing attic and Hellenistic models with Italian naturalism
Sculpture
Venus of Cyrene
Torso valentini
head of hypnos
boxer resting
Discobolos of castel porziano
maiden of Anzio
Discobolos of castel Porziano
alter from ostia
Head of Vespasian