导图社区 刘润清 新编语言学
- 1.3k
- 42
- 17
- 举报
刘润清 新编语言学
刘润清 新编语言学教程 第二章语音 思维导图
编辑于2020-04-08 21:26:16- 相似推荐
- 大纲
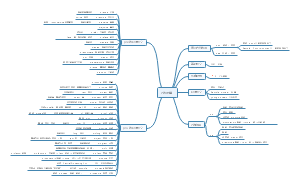
chapter 2 The sound of language
Introduction
phonetics and phonology is hard to learn but it is very important for language learning.
Phonetics
Phonetics
Defination
The study of speech sound that occur in all human languages. The study of phonetics can be divided into three main branches:articulatory phonetics,acoustic phonetics and auditory phonetics.
Classificaton
Articulatory phonetics
how speech sound are produced or articulated.
Acoustic phonetics
deal with the transmission of speech sounds through the air
Auditory phonetics
how the speech sounds are percieved bu the listener.
Articulators and their functions
articulators=organs of speech:the diferent part of vocal tract
seven major articulators
lips
teeth
alveolar ridge/alveolum
齿龈
velum/soft palate
软腭
hard palate
硬腭
tongue
tip
blade
front
back
root
pharynx
1. 咽喉
Voiced and voiceless sounds
voiced
the vocal cords are drawn together,the airstream forces its way through and cause them to vibrate.
[b] 、[d]、[g]、[v]、[z]、[ð]
voiceless
the vocal cords are spread apart,the airstream form the lung is not obstructed at the space between vocal cords and pass freely.
p]、[t]、[k]、[f]、[s]、[θ]
Nasal and oral sounds
nasal sounds
the velum is lowerd,air escapes though the nose as well as the mouth.
[m]、[n]、[ŋ]
oral sounds
the velum is raised all the all to touch the back of the throat,the passage through the nose is cut off.
[p]、[b] 、[t]、[d]、[k]、[g]、[f]、[v]、[s]、[z]、[θ]、[ð]......
Classification of English sounds
English Vowels
defination
a major catagory of the sound segment,produced without obstruction of the vocal tract so that air escapes in a relativly unimpeded way through the mouth or the nose.
20个
which part of the tongue is the highest
front vowels
speech sounds produced by holding the tongue toewards the front of the mouth.
/i:/、 /ɪ/、/e/ 、/æ/
central vowels
speech sounds produced by holding the central part of the tongue highest
/ə/ 、/ɜ:/
back vowels
speech sound produced by moving the tongue towards the back of the mouth
/u:/ 、/ʊ/、/ɔ:/、 /ɒ/ 、/ɑ:/
how wide the mouth is opened in the production
open(低)
/ɒ/ 、/ɑ:/、/æ/、/ɑ/
semi-open、close(中高、中低)
/ə/、/e/、/ɔ:/、/ɜ:/
close(高)
/i:/、 /ɪ/、/u:/ 、/ʊ/
whether the lips are rounded
In English all the front and the central vowels are unrounded vowels and all the back vowels except /ɑ:/are rounded
Rounded vowels
/u:/ 、/ʊ/、/ɔ:/、 /ɒ/
Unrounded vowels
/i:/、 /ɪ/、/e/ 、/æ/、/ɑ:/
the length of the vowels
long vowels
/ɑ:/ /ɔ:/ /ɜ:/ /i:/ /u:/
short vowels
/ʌ/ /ɒ/ /ə/ /ɪ/ /ʊ/ /e/ /æ/
number
12monophthongs
/ɑ:/ /ɔ:/ /ɜ:/ /i:/ /u:/ /ʌ/ /ɒ/ /ə/ /ɪ/ /ʊ/ /e/ /æ/
8diphthongs
/eɪ/ /aɪ/ /ɔɪ/ /əʊ/ /aʊ/ /ɪə/ /eə/ /ʊə/
English consonants
defination
a major catagory of the sound segment,produced by a closure in the vocal tract,or by a narrowing which is so marked that air cannot escape without producing audible friction.
28
the place of articulation
defination
the involement of articulators in the production of a particular consonant(where the airstream is most obstructed.)
classification
Bilabials
Both lips are the articulators
/p/ 、/b/、/m/ 、/w/
Labiodentals
Produced with upper teeth and lower lips
/f/、 /v/
Dentals
Peoduced with the tip of the tongue between the upper and lower teeth.
/θ/、 /ð/
Alveolars
Produced with the front part of tongue on the alveolar ridge.
/t/、 /d/、/s/ 、/z/、/n/、/r/、/l/
Palatals
Produced with the back of the tongue at the hard palate
/ʃ/ 、/ʒ/ 、/tʃ/ 、/dʒ/、/j/
Velars
Produced with the back of the tongue against the soft palate or velum.
/g/、/k/、 /ŋ/
Glottal
Produced without the active use of the tongue and other parts of the mouth.
/h/
the manner of articulation
defination
the type of stricture involved in the production of a consonant(the particular way the airstream is obstructed.)
classification
Stops
speech sounds produced by some form of complete stopping of the airstream(very briefly) and then letting it go abruptly.
/p/ 、/b/、/t/、 /d/、/k/、 /g/
Fricatives
speech sounds produced by blocking the airstream,and having the air push through the narrow opening in the mouth with friction.
/f/、 /v/、/s/ 、/z/、/ʃ/ 、/ʒ/ 、/θ/、 /ð/、/h/
Affricates
speech sound produced by stopping the airstream,and then slowly releasing it with feiction.
/tʃ/ 、/dʒ/、/tr/、 /dr/、/ts/ 、/dz/
Liquids
speech sounds produced when there is some obstruction of airstream in the mouth,but now enough to cause any real friction
/r/、/l/
Nasals
speech sounds produced when the velum is lowered and airstream is allowed to flow out through the nose.
/m/ 、/n/、 /ŋ/
Glides
speech sound with little or no obstruction of the airstream in the mouth.
/w/ 、/j/
Variations of sounds
Liasion
A phenomenon of the linking of words in speech,in particular when the second word begins with a vowal.
Here\there(r) are an egg
Elision
Under certain ciecumstances the loss of a sound or sounds
suppose\factory
Assimilation同化
sounds belong to one word or one syllable can cause changes in sounds belonging to neighboring words or syllables.
/s/——/z/
phonology
Phnology:phnology is the discription of the systems and pattern of speech sounds in a language.
Phonemes:the phonological units of sound
Phonemes is a basic unit of phonological study,and it's an abstract element of a sound which can distinguish meaning.
Konwing a language implies konwing the set of words that comprise the vocabulary of that language.
Minimal pairs and set
minimal piars are toe words which are identical in every way except for one sound segment that occurs in the same place in the string.
e.g. ban and bin, bet and bat......
seek and soup are not minimal pairs because they differ form two words.
Free variation
Two or more sounds occur in the same position with any apparent change of meaning.
Distinctive features
difination
A feature distinguish one phoneme form anohther
branches
voice
place of articuation
manner of articulation
E.g./b/、/d/、/g/
Syllables and consonant clusters(音节和辅音连缀)
We cannot just put a group of sounds together to get a word.
syllables
syllables refers to the phonological units that is composed of one or more phonemes.These unit,which are often longer than one sound and smaller than a whole word.
syllables can be defined both phonetically and phonologically
phonetically
consisting of a center which has little or no airflow and which sounds comparatively loud.the center is usually a vowel.
phonologically
the way in which consonates combine to form various sequences.vowels can form a syllable on their own or they can be the center of a syllable.
elements
syllables
open syllables
have an onset and a nuckeus,but no coda
me、by、no
closed syllables
a syllable consist of a coda is called closed syllable.
up、cup、at
Consonant cluster
In English, some words may contain a sequence of two or more than two consonants in one syllable,/spl/in splendid.Sequences of consonants like this called consonant clusters.
classification
initial cluster
/spl/in splash
medial cluster
/st/in test
final cluster
/str/in pastry
Suprasemental feartures
Stress
word level
difination
when a word has more than one syllable, one of them will be pronounced with more prominence than others,this speech sound phenomenon called stress.
when the word import is pronunced with the second syllable sounding stronger than the first,the word is heard as a verb.
when the word import is pronunced with the first syllable sounding stronger than the second,the word is heard as a noun.
sentence level
the lexical meaning of words is not affected,but the ohonetic form if a word stress may be modified to show which part of the sentence is focus,or which word should receive special emphasis.
Intonation
difinition
when pitch,stress and sound length are tied to the sentence rather than word in isolation,they are collectibely kown as intonation.
Intonation is an important aspect in sproken language, it clearly indicates that an utterance is a question or a statement or a command or a request.
E.g. We say “The chairman may resign” as a statement with a falling pitch or tone, but as a question with a rising pitch or tone at the end of the sentence. Intonation is also indicative of the speaker`s attitude. Sometimes it conveys come information that we cannot generally find in the words used by the speaker.
From all this we can see that although phonetics and phnologu begin at the level of individual soud segments, they also study large units like syllables,words and combinations of words,and eventuallt the various ways in which we use stress and pitch patters to express various meaings in utterance,