导图社区 语言学第四章思维导图
- 1.5k
- 57
- 14
- 举报
语言学第四章思维导图
语言学思维导图 第四章思维导图
编辑于2020-04-18 22:15:06- 相似推荐
- 大纲
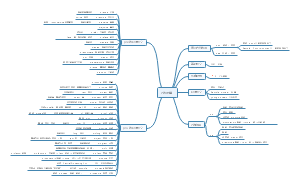
Syntax
Definition
study of rules governing the way words are combined to form sentences in a L;formation of sentences
Syntactic Relations
Positional/word order sequential arrangement of words in a L
-of substitutabllity classes/sets of words substitutable for eac other grammatically in the same sentence
-of co-occurrence different sets/classes may permit/require the occurrence of a word of another set/class
Sentence Formation
Conjoining
the process where one clause coordinated or conjoined with another;conj-and,but,or
E.g. You may come here on friday,or you may do it next month
Embeding
the means by which one clause is included in the sentence(main clause)i syntactic subordination
E.g. Ihave a friend who have a cat
Transisition
2 properties of text
Cohesion
to do with discourse/text;relations of meaning that exist within the text;and define it as a text
Halliday Reference,Substitutable,Ellipsis,Conjunction,Lexical cohesion
Coherence
relationships which link the meanings of utterances in a discourse or of the sentences in a context
Fuctional Approach
Fuctional Sentence Perspective
refers to an analysis of utterances(or texts) in terms of the information they contain
Vilem Mathesius
Theme
the point of departureis equally to the speaker and to the hearer
Rheme
the goal of discourse presents the very info that is to be imparted to the hearer
J.Firbas
Communicative Dynamism extend to which s element contributes to development of communication
Cenerative Approach
Syntactic Category
Types
Lexical- n,v,adj,adv
Phrasal- NP,VP,PP,AP
Syntactic Movement
NP-- relative to two constructions passiv sentence a raising construction
Aux-- have be do may can will shall,could moved to the begining of the sentence
Wh- mostly takesplace in wh-queation,including direct &indirect&indirect wh-question S
Deep/Surface Structure
Deep
abstract/underlying representation of syntactic properties of a construction
E.g. the love of God(surface)-God loves somebody/somebody loves God
Surface
final stage/actual in syntactic derivation of a construction
Move-a Rule
general movement rule which accounts for the syntactic behavior of ary consitltuent movement
Covernment/C-command
Covernment
type of control ove the form of some words by otherswords in certain syntactic constructions
E.g. leave in the autumn-2 G relats;in G t autumn,leave G in t autumn
C-command
constituent command-
a co-command B if a does not dominate B and every r that dominates a also dominates B
Binding theory
An anaphor bound in its governing category
A pronominal free in its governing category
A r-expression must be free abbreviation of "referential expression"
Traditional Approach
Grammatical relation
Subject
major constituent of sentence/clause strcture;"doer" of an action
Predict
expresses actions;processes;and states that relates to the subject
Object
item can become subject in a passive transformation; accusative case-direct-/dative case-indirect-
Category
a group of linguistic items which fufill same/similar function in a particular L such as a S,a n praseor a v
Categories of Noun
Number(N/Pron) Singular&Plural---Dual in Greek&Arabic;Trial in Fijian
Gender(N/Pron) by reference to sex----feminine,masculine,neuter
Case(Noun) nominative,vocative,accusative,genitive,dative,ablative
Categories of Verb
Tense(16/Z) indicate the time of an event etc in relation to the moment of speaking
Aspect(not deictic) distinguish the status of eventset in relation to specific periods of time
Mood distinguish modalitywhich covers both of a kind of act and of the degree of certainty
Categorical relations
Concord/Agreement Notional-& Crammatical- this man,these men He drinks,they drink
Government syntactic relation of another type of control Eg--She gave him a book,She gave a book to him