导图社区 英语语法词法句法
- 702
- 67
- 7
- 举报
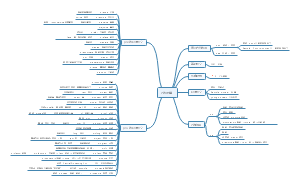
英语语法词法句法
这个思维导图包含基础的语法词法句法,并有一定的列句,如有补充欢迎交流
编辑于2020-06-14 11:47:13- 相似推荐
- 大纲
英语语法
词法
1.实词
1.名词
1.物体、人名、国家、吃的喝的。
2.可数名词
个体名词、集体名词
3.不可数名词
物质名词、抽象名词
2.动词
1.谓语动词,时态,语态(主动/被动),语气(祈使、陈述、感叹、疑问),(真实/虚拟、主谓一致)
1.实义动词,表示动作或状态。
特点
具有完整词汇意义
能够充当谓语
除助动词和情态动词外均为实义动词
及物动词
不及物动词
2.助动词,起到辅助作用
1.特点
不具备词汇意义
不能单独做谓语,须和实义动词连用,帮助构成各种时态,语态,语气,否定和疑问等。
2.三个助动词,也是实义动词。
be
I am a mayor.实义动词
I am studying English.辅助构成进行时态。
do
have
I have two projectors.
I have lived in Beijing for 6 years.
3情态动词
1.用法说明
1.表达说话人的态度与角度,阐述对所描述的情景或事件的态度。
2.本身有一定词义,但不能独立做谓语,只能和行为动词一起构成谓语。
3无人称和数的变化,后面要跟动词原形,否定式为后面加not.
4.注意:个别情态动词有现在式和过去式两种形式。过去式用来表达更加客气委婉的语气,时态性不强,可用于过去、现在或将来。情态动词属于非及物动词,没有被动语态。
2.常用单词
1.can/could
1.能力、可能,could的可能性比can小,一般不好的事用could.
Can you speak a foreign language?Yes,I can.
She could sing well when she was a little girl.
Clint isn't class today.He could be ill.
She can/is able to answer this question.
2.can许可、允许;could请求,用于疑问句,could语气委婉,
Can you teach me how to do it?
Could you teach me how to do it?
You can leave the office as soon as you have finished the work.
You can use my car tomorrow.
3.惊讶、怀疑、不相信等,can的怀疑度更强些
She cannot be you daughter.
Could this be true?
How could you be so stupid?惊讶
2.may/might
1.表请求,可不可以
1.May/Could/Might I…?一般用于第一人称,表示请求对方允许我们做某事。
May I/Could I…?较正式,多用于陌生人之间。May I/Could I have some ice cream?
Can I…?非正式,两人较熟悉。Can I have some ice cream?
Might I…?过于正式,一般不用。
2.表允许,may表一般现在时,might表过去时。
3.表可能,对现在的推测,may(可能)可能性大于might(或许)
Why isn't John in class?He may be sick.He might be sick.
4.表建议,may/might as well,建议换另一种方式做某事,“倒不如,不妨”。
You may as well do the homework.你不如现在就做作业。
You might as well tell the truth.你不如就说出真相吧。
5.表转折,may…but表示让步。
You may have good reasons,but that doesn't make it legal.Although you have good reasons,that doesn't make it legal.
3.must/have to
1.必须,一定要,得。
1.must+动词原形,多用于义务、命令或必要
We must call the doctor.
2.have to多用于肯定句,有时态变化
When I was in school,we had to wear school uniform.
来自外界,不得不。
3.mustn't,必须不能做某事/决不能做某事
That's a factor which we must not neglect.
We must not be complacent about our achievements.
4.don't have to,不必
You don't have to yell;I can hear you.
I don't have to stand such rude behavior.
5.must引导的疑问句,肯定回答用must,否定回答用needn't.
2.推测,通常用于肯定句,具有较大的可能性,常翻译为必定,一定是;否定句/疑问句中,用cannot/can't.
You must be joking.You can't be serious.
一般现在时(实事)>must(必定,很可能)>may(可能)>might/could(或许)
He was sick.
He must have been sick.
He may have been sick.
He might/could have been sick.
4.shall/should,应该
1.征求对方建议,
1.shall用于第一人称的一般疑问句中,表示主动提供帮助、提供建议或请求给与指示,表示提供建议或请求给与指示时,也可以用在第三人称。
Shall I open the window?
Shall we sit here?
How shall we do now?
Shall he come with us?
2.shall用于第二第三人称的陈述句中,表示“命令”说话人的允诺、意愿。
Each competitor shall wear a number.
You shall have the money back next week.
He shall be punished if he disobeys.
3.should表示建议忠告或者规劝,表示强烈的明确的忠告;could表示建议某事的可能性。
A:John doesn't feel good.He has a bad stomachache.B:He should see a doctor.C:He could see a doctor,or he could stay in bed for a day and hope he feels better tomorrow.
4.should表示应该,可以用于不同的人称。
I should write some letter tonight.
You should not be reading a nover.You should be reading a textbook.
2.表示推测
1.should+do表示对将来的推测,肯定程度上较大的推测,should表示说话人一种合理假设,因此它用来对说话人所希望发生的事情进行推断,若不是他所期望的,则不用。
A:What did the weatherman say?B:It should rain tomorrow.It may rain tomorrow.It might/could rain tomorrow.
Let's go to the movie The film should be really good.
2.if引导的虚拟条件句中,在表示与现在或将来实事相反的非真实条件句中,其谓语动词可用should+do.
If she should refuse,they could be greatly disappointed.
3.should have done表示对过去的推测,表示说话人所希望发生的事。
You should have received four letters by now.
4.should特殊用法,表示竟然、万一。用在absurd,amazing,annoying,funny,fidiculous,strange,surprising等形容词后,翻译时带有惊奇的感情色彩,带有竟然的意思。
It is unthinkable that he should be so careless.真不可思议,他竟然如此粗心大意
It is strange that you and I should have the same name.
I can't think why he should have been so angry.
5.should常用在lest,for fear that和in case引导的从句中,表示“万一”
I've bought my umbrella in case it shool rain.
5.will/would
1.表将来
I will call you when I am ready.
He will be here this afternoon.
2.表请求
1.用于肯定句中,表示客气地征求意见提出请求,愿望,看法等。would此时并不表示过去,只是更加委婉。
Will you stay for lunch?
Would you do me a favor?
I would like to have a little talk with you.我想和你谈一会。
2.won't/wouldn't否定式,表示更委婉。
1.Won't you take off your coat?
2.Wouldn't it be better to paint it green?
3.表意愿
1.will表现在的意愿
A:The phone is ringing.B:I will get it.
would表过去的意愿
He wouldn't let the doctor take his blood pressure.(昨天体检的时候)他不肯让医生量他的血压。
4.表拒绝,主语有时可以是物
1.won't用于现在或将来
The door won't shut.
2.wouldn't用于过去。
He wouldn't lend me a penny last night.昨晚上他一便士都不愿借给我。
Jimmy wouldn't drink the milk.
5.will还可以表示决心、许诺、指示、叮嘱等,具体语境来定。
I won't leave you.You can't make me.我绝不离开你,你不能强迫我离开。
We'll pay back your money soon.
You will not go out today;you will stay in and work.今天你不要出去,待在家里干活。
No one will leave the examination room before 12 o'clock.
2.非谓语动词
动词不定式to do——要做、去做
分词
现在分词doing——主动,进行
过去分词done—— 被动,完成
动名词doing
动作的名词
3.动词和动词的组合
V1+to V2
意思:V1去做V2
条件
必须是同一个人做
V1在先,V2在后
V1+V2-ing
意思:V1-V2这件事
V1+V2
常见使役动词,省略to,营造快节奏、紧迫感。
3.形容词
品质,类属,颜色,
4.副词
时间,地点,程度,强调
疑问,连接,关系
5.数词
基数词
序数词
分数词
6.量词
7.代词
人称代词
第一人称
主格I,we
宾格me,us.
第二人称
第三人称
he,she,it主格单数
him,her,it宾格单数
they主格复数
them宾格复数
it
指示代词
this,that,these,those.
2.虚词
冠词
不定冠词a/an
定冠词the
特指
某类人
独一无二
介词
不及物动词+介词+名词
of/at/on接触/off脱离/in/like/since/about/during……
转圈圈
around转圈圈(更具体)
about转圈圈(更抽象)
over,翻转,跨越,强立体感
about,of,on,关于,范围由大到小,over,提纲挈领的关于,总括
to,at(针对),对着冲着朝着
up有时是强化前面动词的原本意思
用法
+代词宾格
+n.
+doing
时间,地点,其他
介词短语
连词
并列and,or,neither,as well as.
转折but,yet
因果for,as,therefore.
引导时间状语从句when,before,after,since.
感叹词
Oh,Ah,Well
句法
一、如何正确造句原则
1.抓主干
2.有且只有一个谓语动词
当中文句子中没有实意动词时,就加be动词或感官动词表示
二、五种简单句
1.主谓
1.及物动词和不及物动词
2.按句子语序逐一翻译
2.主谓宾
1.sb/sth做了什么事
2.及物动词
3.把字句,去掉把,调整为正常主谓宾语序翻译
3.主系表,表达主语的一个状态
1.什么东西怎么样、是什么、在哪儿,系动词一般用到be动词,am\is\are\was\were
2.什么东西变得怎么样,become\get\turn\grow\go.
3.什么东西保持/持续怎么样,remain\stay\keep\hold等
4.什么东西闻起来/听起来/看起来/尝起来/摸起来怎么样,look\sound\smell\taste\feel
4.主谓双宾
1.谁给谁干了一件什么事,先去“给”
1.主+谓+物+to+人
2.主+谓+人+物
主谓间宾直宾
5.主谓宾宾补
1.sb觉得/认为sth怎么样,按顺序翻译即可
三、特殊结构句
陈述句
否定句
1.表达中文中“不”、“没有”等否定含义。
2.(助动词/情态动词 not+实义动词)/(be作为实义动词时+not)
He is not a manager.
He hasn't accomplished his homework.
I will not permit you to take part in the party.
3.do及其各种变形+not+实义动词(be除外)
I do not like miracle.
He doesn't like miracle.
He didn't like miracle.
4.am not和may not没有缩写,其他均有。特别的有shan't,can't.
疑问句
一般疑问句(封闭式问题)
1.用Yes或No作答的疑问句叫一般疑问句。是/不是的句子,通常以“……吗?”
2.将陈述句变成一般疑问句的步骤
1.有be动词,助动词,情态动词,将其提到句首,句末打问号即可。
Lucy can speak English well.Can Lucy speak English well?
He has finished his homework.Has he finished his homework?
2.无be动词,助动词,情态动词,则根据谓语动词相应do的形式放在句首。do,does,did.
They go to school by bike.Do they go to shool by bike?
Bill gets up at 6:30 every day.Does Bill get up at 6:30 every day?
The students saw a film yesterday.Did the students see a film yesterday.
3.陈述句变一般疑问句的注意事项。
1.有第一人称时,最好变为第二人称。第二人称则要变为第一人称,第三人称则不需要发生改变。
I support you.Do you support me?
I can hear you.Can you hear me?
My sister is lack of money.Is your sister lack of money?
2.有some时,要变成any.
3.有复合句时,通常只变主句,从句不变。
I know he has separated from his family for 10 years.Do you know he has separated from his family for 10 years?
4.有have时,且表示“有”时。除借do外,也可将其提到句首。I have some friends in America.Have you any friends in America.Do your have some friends in America.
4.回答方式
1.第一个词不是Yes就是No.
2.第二个词,问谁答谁。(如果主语是this,that,回答时用it代替,如果主语是these,those,回答时用they代替。
3.第三个词,用什么问,就用什么答。
特殊疑问
反义疑问句
被动句
强调句
倒装句
多为对状语的强调,倒装即换个方式强调,助词提前,only,seldom,never。
完全倒装
In the house lies a cat.
多用于场地,方位等
部分倒装
I can understand him only in this way.
Only in this way can I understand him.
I have never seen him
Never have I seen him.
删掉It is who/that句子通顺,为强调句。多为对名词的强调。
对助词的强调
祈使句
感叹句
假设句
省略句
四、从句
1.主宾表状、定同从句,从句在句子中为其类型相应成分。
2.定语从句
1.限定性定语从句
合并同类项
who人
whose所有格/whom宾格
whom前面无介词时可以用who替换,有介词时,不能用who替换
which物
从句在后句做状语时
介词+which=where/when/why
I really hate the city in which I met him
I really hate the city where I met him
I cannot see the reason for which he left me
I cannot see the reason why he left me
从句在后句做主语、宾语时
which
2.非限定性定语从句
即为补充说明的插入语,用“,”隔开
不能用that
as,正如,可用在句首。
3.that/省略(口语中)
who/which=that
定语从句中,介词后面不能接that
先行词表示强调时,用that
3.名词从句
主、宾、表、同位。
主语从句
成分不缺,陈述,用空虚无意义的that,不能省略
That you love me is important.
It is important that you love me .It作为形式主语或形式宾语。
是否:whether
Whether you love me or not is important.从句可以不后移
It is important whether you love me or not.
疑问:Where you are from is important .从句跟陈述形式,从句可以不后移。
宾语从句引导词
成分不缺,陈述,空虚无意义的that,只有在宾语中可以省略。
是否:whether,能用if.
I don't care whether you like me.
疑问句做从句:问什么用什么
I want to know where you are from.从句跟陈述形式。
宾语从句的反问句
称正常情况,第二第三人反问主语
She thinks (that)Tom is wrong,doesn't she?
特殊情况主语是第一人称,只能反问宾语。
I think Tom is wrong,isn't he?
表语从句
成分不缺,陈述,空虚无意义的that,不能省略
是否:whether
疑问:My question is where you are from.从句跟陈述形式。
同位语从句
同位语从句,说的是完全一件事
The message that Kaidi is dating someone is fake.
定语从句,只是限定范围
The maessage which/that you received from Mr Zhong is fake.
是否:whether
The question whether you love me or not is important.
疑问句做从句:问什么用什么
The question where you are from is important.
词或短语,就用“,”隔开,是从句就要用引导词。
成分不缺,句意完整
4.状语从句
1.特点,与原句是断开的。
2.时间状语,when,while
3.地点状语where
4.原因状语,because,for,as,due to.
Because I am young,I can do it.
5.目的状语,inorder,so that
6.条件状语,if,unless,as/so,long as
7.结果状语,so,so that
8.让步状语as if,although,though
9.方式状语,by way of,by means of
10.比较状语,than as as,not as as,no sooner than.
11.关联词,但常省略
5.独立结果
1.如果你再看我,你就死定了
If you look at me again,you will die!
Looking at me, you will die!
2.去关联词,去从句主语,从句谓语改成分词(主动用ing,被动用ed)。
If I am poor,I will take care of myself.
Being poor,I will take care of myself.
United,we stand;Divied,we fall.
I being a boy,my father taught me to swim.
3.完整句子关联词不能省略;省略的话主动being,被动been,分词可视情况省。
五、中英差异
1.中文感性,英文形式逻辑,英文从句倒叙逻辑
2.中文常省略主语,系动词,关联词,被动语态
不作死不会死
他很好
山无棱天地合,乃敢与君绝。
我的英语是体育老师传授的
3.陈述句结构英中
R1andR2
R1, 变序
R2,并列不变序。
并列and,while
转折but,yet,while
选择or
递进from…to
多主多谓多宾
It引导形式主句,主语从句放后面
英文后重原则
口语多词组,书面多动词
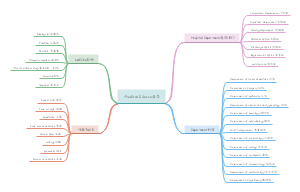
三、时态
1.中文的态—着、了、过、将,时—昨天、今天、明天。
1.英语句子是有时间状态
2.所谓时态都是谓语动词而已
3.通过动词变形体现
2.十六种时态,先时后态原则
1.时态的含义
1.时——关注的是动作发生的时间,过去、现在、将来。
2.态——关注的是动作是固定不变的还是动态变化的,是完成了的还是在延续的。动作持续时间是很短的还是很长的等。
2.时态是针对谓语动词而言,所以是通过动词的变形实现。
3.一般态
1.一般现在时
1.一般现在时单三形式
1.句式标准。He eats fish
2.第三人称单数
1.人称代词,he/she/it。She likes musie
2.单个人人名、地名或称谓。Beijing is big
3.单数可数名词“this/that/the+单数可数名词。That car is red.
4.不定代词someone,sth,sb,nobody,everyting等指示代词this,that.Somebody sings over there.
5.不可数名词。The milk is in the bottle.
6.数字或者字母。"6" is a lucky number.
3.一般现在时中,第三人称单数做主语时,谓语动词一定要用单三形式
4.单三变形规则
1.一般动词直接加-s
2.以s,x,ch,sh结尾的词,后面加-es.
3.辅音字母+o结尾,一般加-es.如does,goes.
4.辅音字母+y结尾,变y为i再加-es.Tom studies Chinese,English,and Art at school.
2.一般现在时四种常用用法
指一般现在都这样的情况,过去、现在、未来基本上都是这个情况
1.表示经常或习惯的动作,或习惯性的状态。often,always,never,from time to time.
1.Usually I every day read books.
2.I usually read books every day.
3.She usually reads books every day.
4.My mom never stays up late.
2.表示客观规律和永恒真理。
当一个动作不受时间限制,始终都是这样
1.The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
2.Knowledge is power
3.Great minds think alike.
4.Trees turn green in spring.
3.表示现在的状态,目前当下的状态。
1.She is beautiful.
2.She is five years old.
3.My brother is short.
4.What beautiful flowers they are.(感叹句式)
4.一般现在时表示过去的动作。
1.某人说某话,名人名言,一定能够经得起时间检验的。
1.Descartes says:"Reading is important."
2.Francis Bacon says:"Reading makes a full man,conference a ready man, and writing an exact man."
2.引用报纸、通知、告示的内容。
1.The newspaper reads,"The solution is useless".
2.The sign on the washing machine says,"Out of order."
2.一般过去时
1.变形规则
1.大多数动词后面+ed
1,双辅音结尾动词——repesented,worked,presentde,ascended
2,元音+y结尾动词——played,stayed,delayed.
3,两个元音+一个辅音——rained,trained,cooked
2.不发音e结尾的动词+d——hoped,smiled,leasde.
3.元音字母+辅音字母的重读闭音节结尾,双写末尾的辅音字母+ed.——stopped,planned,starred.
4.辅音+y结尾的动词,变y为i+ed.——worried,studied,buried,varied.
5.常见不规则——begin-began,sing-sang,drive-drove,grow-grew,are-were,break-broke,speak-spoke,let-let,sell-sold,stand-stood,bring-brought,come-came.
2.三个主要用法
1.过去某个特定时间发生的动作,存在的状态
1.上个周五孩子们展现了自己的画作。Children represented their pictures last Friday.
2.在1986年,火山爆发了。The volcano erupted in 1986.
3.他两天前没有来学校。He was absent from school two days ago.
4.ago与before的区别
1.Ago——一段时间+ago,表示一段时间以前,用于过去时。
1.二十年前—20 years ago.
2.五千年前—5 thousand years ago.
2.Before——Before+时间点或某个事件,表示一个时间点或者一个事件以前,用于多种时态
1.两点以前—before 2 o' clock.
2.在她生气以前—before she got upset.
2.表示过去的习惯性或经常性发生的动作。
常与表示频度的时间状语连用,比如often,always,once a week等。
1.她上学时,经常打断别人的话——She often interrupted other's conversation.
2.我在乡下时,经常在河边散步——I often walked by the riverside.
3.在我小的时候,妈妈每天都给我讲故事——Mom told me a story every day.
4.常与表示频度的时间状语连用,比如often,always,once a week等。
3.讲述一个具体的故事。
1.在1998年之前,Mike都是在一家超市工作.但是在1998年那一年,Mike失业了,与此同时,他创立了自己的公司,Mike说:创立公司是2一件令人兴奋的事情。Before 1998,Mike worked in a supermarket all the time.However,in 1998,Mike lost his job,At the same time,he launched his company.He said it was an exciting thing.
一般现在时与一般过去时的区别
1.日常口语中,一些情况下应该用过去时而非一般现在时。之前/以前,我的想法是一种情况,而现在/此刻,我的想法是另外一种情况。
1.I didn't know you are her mather.
2.I didn't realize.
3.I forgot to bring it.
4.I thought you disliked them.
2.一般过去时所表示的时间都与现在时间不发生关系。一般过去时表示的动作或状态都已经成为过去,现在已不复存在。
It is nice to meet you.It was nice meeting you.
3.一般将来时
1.变形规则,谓语动词不需要改变,在前面加表将来的词语。
will,shall,be going to,be about to
2.五种主要句型
1.will+动词原形。
1.表示对未来的猜测。
Will women still need man in the future?
Will we live on Mars?
Will we live to be 100 years old?
2.无计划、无准备下,表意愿,当机立断的决定。
A:The phone is ringing. B:I will get it.
A:Excuse me,I cannot understand the sentence.Cloud you help me?B:OK,I will explain it for you.
2.be going to+动词原形。
1.表示对较近的未来的预测。
It is going to rain.
2.表示打算、计划。
1.I am going to travel around.
2.I am going to the cinema tonight.
will与be going to 的区别。
1.be going to表示近期、眼下就要发生的事;will表示较远的将来。
1.He is going to write a letter tonight.
2.He will write a letter.
3.A:Our manager will go to Japan.B:Yes,he is going to Japan tonight.
2.be going to表示根据目前某种迹象主观判断将来要发生的事情;will表示客观上将来势必发生的事情。
1.He is seriously ill.He is going to die.
2.Everyone will die.
3.He will be 20 years old next month.
3.be going to“计划、准备”的意思,之前安排好/打算要去做的事情。will无计划,无准备,说话人当即做的未来的意愿或决定。
1.A:Kate is in hospital.B:Yes,I know,I am going to see her this afternoon.
2.A:Kate is in hospital.B:Oh,really?I didn't know,I will go and see her.
3.现在进行时表将来,已经定下来和准备好实施的计划。
1.I'm flying to Beijing next week.我下周要飞去北京。I'm going to fly to Beijing next week.我打算下周飞去北京。
2.I'm taking my holiday next month.我下月要休假。
4.be about to do表立马、将要发生。
1.The train is about to leave.Please get on!
2.Sally has her hand on the doorknob.She is about to open the door.
5.be on the point/brink/verge/eve of doing表下一秒、瞬间就要发生。
1.I was on the point of crying.我差一点就要哭出来了。
2.I am on the verge of finishing this paper.眼瞅着我就要做完卷子了。
4.进行态
1.现在进行时
1.变形规则或结构,系动词be(am/is/are)+v-ing形式。
1.通常在动词原形词尾直接加-ing构成。going,answering,studying.
2.与e相关
1.以不发音的e结尾的动词,一般去掉e再加-ing。writing,hoping,caring,saving,producing.
2.如果e发音则保留e。seeing,fleeing,freeing,agreeing.eyeing.
3.以ie结尾的,先去掉e,将i变成y然后加-ing。die-dying,tie-tying,lie-lying.
3.重读闭音节,双写最后字母,再加-ing。running,stopping,planning,starring.辅音字母x直接加-ing。taxing,relaxing.
2.五种主要用法。
1.表示说话时正在进行的动作。
They are playing basketball now.
2.The girl is crying.
2.在目前一段时间内持续的一种活动。目前一段时间内或一个阶段内一直在进行,正在进行的活动,常与these days,this week,this month等时间状语连用。
1.时间点
2.时间段
例句
1.These days we are helping the farmers work on the farm.
2.These days I am accompanying ma family on a trip.
3.They're prepariring the paper this week.
3.表示逐渐变化,“越来越……,日渐……,日益……”
1.Our city getting crowed.
4.现在进行时表将来。I'm flying to Beijing next week.
5.强调感情色彩,用来强调说话人的某种感情。(赞叹、厌烦、埋怨等)。The kid is constantly lying.
现在进行时与一般现在时的区别
1.现在进行时强调目前正在进行的动作,而一般现在时强调经常性或习惯性的动作。
1.I am reading a story now.我现在正在看一个故事。I read stories in my spare time.我有空时看故事
1.Angela is pretty.Angela很漂亮!Angela is being pretty.Angela 正在漂亮!
2.过去进行时
1.变形规则或结构,was/were+v-ing.ing变形同理。
2.三种基本用法
1.表示过去某个时间正在进行的动作。
1.Last night this time,I was recording my CD.
2.I was processing chicken when you called me yesterday morning.
2.渲染故事背景,使表达形象生动,多见于文学作品。
The fire was burning and a cat sleeping in front of it. The girl was playing the piano and singing softly to herself.Then there was someone knocking at the door.炉火正在燃烧着,一只猫正在前面睡觉,女孩一边谈着琴一边轻声的哼唱,突然传来了敲门声
3.表示温婉的请求或提建议,表示态度的词wonder,hope,think等
1.A:Excuse me,Professor Liu.I was wondering if I could talk to you about my paper.B:I have a class in a few minutes.Why don't you come and see me during office hours tomorrow?A:打扰一下刘教授,我想和您讨论一下我的论文。B:我几分钟后有课,明天办公时间你过来找我行吗?
进行时的特点
1.事件具有持续性和未完成行。在讲到的时候,这个事情仍未结束。
My grandma was living in Beijing during the seventies.
2.事件具有时效性。
1.永恒的用一般现在时,The earth moves around the sun.
2.She was sleeping when somebody was knocking at the door.
3.描述具体次数时,不能用进行时。次数将动作分割了,不再是一个持续的动作。
1.He wrote six letters.
2.Tom rang the bell 8 times.
5.完成态
1.现在完成时
1.变形规则或结构,have/has+done(过去分词)
1.大多数动词后面+ed
1.双辅音结尾的动词,represent,worked,presented
2.元音+y结尾的动词,played,stayed,delayed
3.两个元音+一个辅音,rained,tained,cooked,looked
2.不发音字母e结尾的动词+d,hoped,smiled,leased,resolved
3.元音字母+辅音字母的重读闭音节,双写末尾辅音+ed,stopped,planned,starred
4.辅音字母+y结尾的,变y为i再+ed,worried,studied,buried,varied.
5.不规则变化
1.第一类:AAA
2.第二类:AAB
3.第三类:ABA
4.第四类:ABB
5.第五类:ABC
2.两种用法
1.表示过去的动作延续或重复到现在(延续动词),通常有since,up until now,in the past few years,during the last two months,through centuries…等时间状语。
1.He has suffered from the headache for a long time.到目前为止,他遭受头痛好久了。
2.She has prepared the big chirstmas party for several months.到目前为止,她已经为圣诞舞会筹备了几个月。
3.Up until now,we have failed to attract customers.到目前为止,我们未能吸引消费者的注意力。
2.表示过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果(点动词),瞬间动词。
1.I washed my car yesterday.我昨天洗车了。I have washed my car. so we can drive it around.我已经洗过车了,现在我们可以开着它去四处转了。
2.I had my breakfast at home.我在家里吃了早餐。I have had my breakfast at home,so I feel full.我已经在家吃过早餐了,所以我现在感觉很饱。
3.补充性知识点
1.点动词转化为状态词有两个转化技巧
1.将点动词转化为能表达相同含义的延续性动词。go-be,buy-have,
2.讲点动词转化为能够表达相同含义的形容词,用主系表的形式表达。marry-be marry,die-be dead.
2.完成时中,当点动词用于否定时,可以与持续的时间状语连用且出现不确定的时间状语,常用点动词的完成时态。
3.特殊句型
1.This/That/It is+序数词+名词+that+现在完成时
2.This/That/It is+最高级或only修饰名词+现在完成时
2.过去完成时
1.变形或结构,“had+done过去分词”(had没有人称或数的变化)。
1.是一个想对的时态,以过去时间为基点,所表示的动作强调发生在" 过去的过去“
2.连用的时间状语有三种
1.by+过去的时间点
I had finished reading the novel by nine o'clock last night.昨晚九点前我就把这本小说读完了。
2.by the end of+过去的时间点
We had abandoned that idea by the end of last term.到上学期期末结束时,我们已经放弃那种想法了。
3.before+过去的时间点
They had inquired his salary before last Wednesday.
3.常用于并列句中,一个并列句用的是过去式,另一个早于这一句动作的话,需用过去完成时,不一定要用时间状语来提示。
She was very excited.She had never flown before.
We were not hungry,We had just had lunch.
The room was dirty.I had not cleaned it for weeks.
2.两种用法
1.点动词,过去的过去。表示动作在时间基点前就已结束。
1.They had conquered their conflicts before the beginning of the party.在派对开始之前,他们已经消除了彼此间的分歧了。
2.By 9 o'clock last night,we had got notice from the spaceship.昨晚9点之前,我们已经收到飞船发来的通知。
3.She had notified them of the tragedy before 9 o'clock last night.昨晚9点之前,她已经告知他们这一灾难了。
2.延续性动词+段时间,过去某时刻前发生的动作或状态持续到过去某个时间,或继续延续下去,常与for连用。
1.He had worked in that factory for 30 years before last month.截止到上个月,他已经在那个工厂工作了30年。
2.By the time I left the school,he had taught the class for 3 years.到我毕业时,他已经教那个班三年了。
3.When he arrived at the bus stop,the bus had been away for 20 minutes.
3.主从复合句中的过去完成时。
1.状语从句的主从复合句。
When I woke up,it had already stopped raining.我醒来时,雨已经停了。
After he had finished his homework,he went to bed.
We had got to the station before the train left.火车开出之前,我们就已经到了车站。
当主从句谓语动词先后关系十分明确,接连发生或前一动作导致后一动作,两者均用一般过去时。
When the meeting was over,we left the hall.
When I opened the window,the cat jumped in.
2.宾语从句的主从复合句。
She said she had been a doctor.她说她曾当过医生。
I heard that he had got the Nobel Prize.我听说他获诺贝尔奖了。
I knew that you had passed the exam.
3.定语从句中的主从复合句。
I returned the book that I had borrowed.我已归还了我借的书。
She found the key that she had lost.
I lost the book which I had owned for a long time.
6.完成进行态
现在完成进行时
1.规则或结构,have/has been doing已经一直干某事,被描述的事始于过去,持续到现在,且将会继续持续下去。
2.基础用法
1.加延续性动词,表示从过去某时开始一直持续到现在的动作。
1.长期延续的事件,过去到现在相当长时期内持续的一般性活动。
The Chinese have been making paper for two thousand years.
2.近期在延续的事件,最近一段时期内正在持续的一般活动。Cynthia has been working hard on her term paper.
3.在说话的时刻仍在延续的事件,说活之前一段时间内延续的活动,并仍在延续。We have been waiting for you for half an hour.
4.在说话时刻之前在延续的事件,刚刚在延续,但到说话时已经结束的活动。The little boy is dirty from head to foot because he has been playing in the mud.
2.短暂性动词(即点动词)表示动作不能延续,只是一瞬间就结束的动作,但表示一直以来有重复发生的动作。
1.come,go,arrive,reach,see,hear,close,open,leave,begin,start,lose,buy,fall,join,die,become,borrow,get up等
2.I have been coming to Beijing for 14 years.在过去的14年中,我一直不断的来北京。
3.Koreans have been marrying U.S.soldies stationed here since 1950s.The peak years were during the 1970s,when more than 4,000 Koreans married U.S. soleiers each year.自20世纪50年代以来,就有韩国人一直不断嫁给当地的美国驻军,70年代达到了高峰,每年都有超过4000韩国人嫁给美国大兵。
4.Over the past few years,many towns in the United States have been joining with neighboring communities to share the costs of government. 在近几年中,美国的许多城镇不断合并,以降低政府的费用支出。
3.不能使用现在完成进行时的情况
1.不能用来谈某个动作的具体次数或具体几件事情。
1.今天下午我一直喝了5杯咖啡。错误示范:I have been drinking five cups of coffee this afternoon.正确示范:I have drunk five cups of coffee this afternoon.I have been drinking coffee this afternoon.
2.今天上午我一直写了三封信。错误示范:I have been writing three letters this morning.正确示范:I have writen three letters this morning. I have been writting letters this morning.
完成时和完成进行时的根本区别
1.结果与过程延续的区别
1.完成时重在“完成”,强调动作的结果或成就。现在完成时强调的是动作产生的结果或取得的成就,而不是动作本身。
2.完成进行时重在“进行”,即未完成,强调动作持续的过程。现在完成进行时强调的是在一段时期内某项活动的持续性,强调的是动作本身。
2.完成与未完成的区别
3.完成进行时强调未完成,完成时强调已完成。
1.我一直在北京住了20年了,我不知道要搬到其他什么地方去。I have been living in Bejing for 20 years,and I don't know where elso to live.
2.我已经在北京住了20年了,明天要搬走了。I have lived in Bejing for 20 years,and I will move out tomorrow.
3.我一直在看这本书,等我看完之后,有一些问题要和你讨论。I have been reading this book.After I finish it,I'll discuss some questions with you.
4.我看过这本书了,现在有问题要问你。I have read this book,and I have questions to ask you.
4.完成进行时强调动作延续,完成时强调动作结果。
1.I have been learning English for 10 years.我学习英语有10年了。I have learned 3000 English words.我已经学会了3000个英文单词。
3.完成进行时有强烈的感情色彩,完成时较为平铺直叙,缺乏明显的感情色彩。
1.你怎么来得这么晚啊?我在这里一直等了有一个多小时了!Why are you so late?I have been waiting here for more than an hour.
2.我已经等了一个多小时。I have waited for more than an hour.
4.强调时间长度时,用完成进行时。
1.I've been coughing all night.我咳了一整夜。
2.All these years we have been trying to get in touch with him.这些年来我们一直在设法和他联系。
过去完成进行时
had been doing
将来完成进行时
will have been doing
7.例文
1.A:In 1912,the"unsinkable" luxury ship Titanic hit an iceberg and sank to the bottom of the sea.Its final resting place remained a mystery for more than 70 years.You probably already know that tragic story.But do you know the whole story?Do you know who finally discovered the wreck of the Titanic.B:Robert Ballard,of course.He's an exploer who has seen more of the ocean floor than anyone in history.He has been exploring under the ocean waves for more than 30years!
8.例外
逻辑大于规则
1.主将从现,主语将来,从句用现在。从句是条件,不是结果时。
9.虚拟subjunctive mood,主观情绪
1.If,均用were,If…were…,…would…
2.对现状虚拟
3.对过去虚拟
4.对将来的虚拟
If should……,……would
5.混合
过去将来
If you had worked hard enough,You would pass it tomorrow.
虚拟多用过去式
建议要求命令
I suggest that she should(常省略缓和语气) go now.
If only,Would rather,As if,Lest,But for,It is time.
前句过去分词,后句+would/could/might
虚拟前句,用倒装形式