导图社区 2021年CFA三级 - Behavioral Finance
- 108
- 9
- 1
- 举报
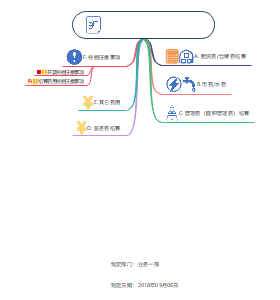
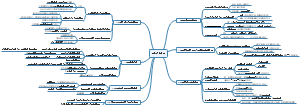
2021年CFA三级 - Behavioral Finance
2021年CFA三级Behavioral Finance思维导图分享,供广大CFA三级备考同学参考,如有差错,请随时指正,谢谢。
编辑于2021-06-01 21:53:23- CFA
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
Behavioral Finance Perspective
Traditional VS Behavioral Finance
TOP 7
4 Axioms
Completeness
Transitivity
Independence
Continuity
REM
Rational Economic Men - perfect rationality
Risk Aversion
risk aversion VS 3 types of risk appetites
Limitations
decision-making is flawed by lack of information or flaws
individuals not process all informtions availabe to them
conflict that prioritize short-term (spending) goals over long-run (saving) goals
lack of perfect knowledge
people not perfectly self-interest
wealth utility not always concave
Utility Theory & Prospect Theory
Utility Theory
Indifference Curve
complex risk functions
Decision Theory
de: make ideal decision when the decision maker is fully informed, mathematically able and rational
Bound Rationality
knowledge capacity limit
remove assumption of perfect information
not fully rational decision-making
not consistent utility maximization
satisficing
Prospect Theory
prospect theory = people view loss and gains differently, thus make decision based on perceived gains -> loss aversion
release risk aversion + impose loss aversion
2 stages
Editing Phase
Codification
assign probability to each possible outcomes
Combination
combine identical values
Segregation
segregate values into both risk-free and risky returns
Cancellation
remove outcomes common to 2 proposal
Similification
apply to very small differences in probability + highly unlikely outcomes
Detection of Dominance
proposal clearly dominant
Isolation Effect
focus on one outcome/factor but ignore others
Evaluation Stage
probability-weighted outcome to determine expected utility
S-shape value function -> disposition effect
Traditional Finance Impact on Market
Efficient Market Hyphothesis
technical analysis features, e.g. resistence level or floor level, are examples of weak-form efficient violation
Behavioral Finance Perspective
Consumptions & Savings
mental accounting + framing bias
wealth = current income + current assets + NPV of future income
less to spend from current assets/future wages + more from current income
Behavioral Asset Pricing
sentiment premium
estimated by the dispersion between different analyst' forecast
是用不同的analyst之间观点的差异程度进行衡量的,而不是预测与实际之间的差异。
Behavioral Portfolio Theory
construct portfolio in layers, with different risk and expectations
Five-factor process
1. allocate each goal into layers based on importance
2. allocate assets into layers
3. number of assets reflect investor's risk aversion
4. concentrated position for information advantage
5. risk averser will hold large cash position
Adaptive Market Hypothesis
investor satisfice to survive in the market, rather than utility maximization
5 conclusions
1. relationship of risk and return is unstable
2. active management can find opportunities to exploit
3. no strategy can work all the time
4. adaptive and innovation are essential to continue
5. survivors change and adapts
Behavioural Finance 2 - The Behavioral Biases of Individuals
Cognitive Bias
TOP 2
Features
Fault reasoning, statistical, information-processing or memory errors
Easy to correct
Categories
Belief perseverance - cling to previous belief irrationally/illogically
1. Conservative Bias
Conserative Bias -> focus on relate new information to old one Anchoring and adjustment Bias -> stick on initial number
Definition
maintain prior forecast/view by inadequately incorporating new information
overweight previous belief + underweight new information
Consequences
maintain/slow to update view/forecast
opt to maintain prior belief due to difficult in processing new information
Mitigations
aware the bias
conduct careful analysis incorporate new information + respond properly
2. Confirmation Bias
Definition
look for/notice what confirms belief + ignore/undervalue what contradicts
Consequences
consider positive information + ignore negative
develop screening criteria + ignore contradicts
under-diversify portfolios
hold disproportionate investment assets in employing company's stock
Mitigations
actively seek information challenges belief
corroborating support for investment decisions
3. Representativeness Bias
Definition
tend to process new information based on past experiences and classification
Types
Base-Rate Neglect
base rate/probability of the categorization is not adequately considred
Sample-Size Neglate
believe small size is representative of populations
Consequences
adopt view/forecast exclusively based on new information/small samples
using simple classification, but not analyze complex data
Mitigations
aware statisical mistakes + check whether overlook reality
invest in diverisified portfolios + stick to it
check the probability + always ask questions
备注
此处representative bias和利用historical data做regression中的不同,此处更侧重于利用最近比较easy理解的信息用于判断
4. Illusion of Control
Defintion
people believe they can control/influence outcomes when they actually cannot
Consequences
trade more than prudent
investment in inadequately diversfiied portfolios
e.g. invest in employer's company stock
Mitigations
aware investment cannot be controlled by them
seek contraditory viewpoints
keep records of transactions to remind yourself
keep rational
5. Hindsight Bias
回顾偏差-回顾的时候觉得已经发生的事情是高概率的
Definition
see past events predictable and reasonable to expect
Consequences
overestimate the degree to which they predict investment outcome + false sense of confidence
cause financial decision maker unfairly assess money manager/security performance
Mitigations
aware the bias + ask questions whether honest about self
record and examine investment decisions + avoid make repeated mistakes
remind to assess performance via benchmarks
Processing errors - use information irrationally/illogically in financial decision making
1. Anchoring and Adjustment Bias
Definition
start with a initial default number (anchor) + inadequate adjustment on new information
Consequences
stick to original estimate when new information occurs
Mitigations
aware the bias + ask questions
e.g. whether based on rational analysis or just achor?
remeber past event/price cannot predict future
2. Mental Accounting Bias
Definition
treat same amount of money differently
Consequences
strucutre portolios in layers + make investment in discrete bucket without consider asset correlation
neglect opportunities to reduce risk by combining assets with low correlation
irrationally distinguish return from income and capital appreciation
Migitations
aware the bias - correlation is not taken into account when construct the overall portfolio
go through all summary documents and investment assets to see the true asset allocation
treat income and capital appreciation differently + focus on overall returns
3. Framing Bias
Definition
people answer questions differently based on the way it is asked
Consequences
willingness to accept risk is influenced by how situations are presented/framed
misidentify risk torelance
choose suboptimal investments
focus on short-term price fluctuation -> excessive trading
Mitigations
ask questions whether focus net gain or net loss
be neutral and open-minded when interpreting investment related situations
4. Availability Bias
Definition
people take a rule of thumb/mental shortcut approach to estimate the probability of an outcome based on how easily the outcome comes to mind
Types
Retrievability
choose the first answer come to the mind as correct one
Categorization
people gather information from what they perceive as relevant search set, e.g. familiar category
Narrow Range of Experience
use too narrow a frame of reference based upon that experience when making an esitimate
Resonance
baised by how closely a situation parallels their own personal situtaions
Consequences
make choice based on advertising not analysis
limit investment opportunity set based on familar classfication schemes
fail to diversify -> based on narrow range of experience
fail to achieve an appropriate asset allocation
over-react to recent market conditions
Mitigations
develop appropriate investment policy strategy
carefully research and analyze investment decisions
focus on long-term result
Bias Mitigation
Relative Wealth
the higher the level of wealth -> the more could adapt to client's bias
Standard Living Risk
the higer SLR -> the more client's bias should be moderated
Deviation from Goal-Based Model
Emotional Bias
Features
Reasoning influenced by feelings, impulse, intuition
Recognize and adapt
Categories
1. Loss-Aversion Bias
Definition
strongly prefer avoid loss than achieve gains
Myopic Loss Aversion 短视损失厌恶
Consequences
Disposition Effect
hold loss asset too long + gains asset too fast
limit the upside potential -> via disposition effect
trade excessively for gains + trade less for loss
hold riskier assests than objectives/returns
Mitigations
disciplined approach to investment based on fundamental analysis
consider probability of future losses and gains to make rational decisionss
2. Overconfidence Bias
Definition
demo unwarranted faith in their own intuitive reasoning, judgements, objective ability
Types
Prediction Overconfidence
assign too narrow confidence interval to investment predictions
Certainty Overconfidence
assign too high probability to outcomes when make judgement
Casues
Illusion of Knowledge
Self-attribution
Consequences
underestimate risk + overestimate expected returns
hold poorly diversified portfolios
trade excessively
experience lower return than market
Mitigations
keep transaction record + analyze investment returns -> to acknowledge losers
be objective when make investments
conduct post-investment analysis on successful/unsuccessful investments
3. Self-control Bias
Definition
people fail to act in pursuit of their long-term, overarching goals, due to lack of self-control
Consequences
save insufficiently
accept too much risk to pursue higher returns
imbalance asset allocation
Mitigations
proper investment plan
have personal budget
4. Status Quo Bias
安于现状
Definition
unwilling to change + do nothing
Consequences
unknowlingly maintain portfolios with inappropriate risk characteristices
fail to explore other opportunities
Mitigations
education
quantify benefits of diversificiation/proper asset allocation
5. Endowment Bias
Definition
people value the asset more when they hold it
Consequences
fail to sell and replace certain assets
maintain inappropriate asset allocation
continue to hold familar assest
e.g. inherent assets
Mitigations
review other unfamiliar assets and accept them
ask self whether the same amount of money can achieve better return in other investment
6. Regret-Aversion Bias
Definition
avoid to make decisions will result in action out of fear + decision will turn out to be poor
Types
Error of Commission
regret for taking action
Error of Omssion
regret for not taking action
Consequences
too conservative due to past poor returns on risky investment
herding behaviour
Mitigations
education
quantify benefits of diversificiation/proper asset allocation
Behavioral Finance and Investment Processes
understand impact and implication of BF on all aspects of investment
Behavioral Models
TOP 1
Barnewall two-way behavioral model
passive investor
de: not risk own capital to gain wealth
risk averse + need more security
active investor
de: risk own capital to gain wealth + take active role in investment
less risk averse
gather large amount of information to obtain control -> easy lead to overconfidence
BB&K five-way model
confidence
methods of action
Pompain model
4-step process to go through investors' BIT
BIT - Behavioral Investment Types
closer efficient frontier -> other common sense benefits
limitations
inappropriate to classify investors via emotional/cognitive -> as they are the same
traits of more than one behavioral investment types
behavioral may change
same BIT should be treated as the same, due to unique personal circumstance
investor act irrationally at unpredicatable times
Advisor-Client Relationship
Goal
to construct a portfolio for client comfortable to stay in the long run
Measurement of successful relationship
advisor understand long-term financial goals of client
advisor maintain a consistent approach with client
advisor acts as client expects
both advisor and client benefit from relationship
Limitations of Risk Tolerance Questionnair
answer may vary from times due to current circumstance
questions are not structured to measure behavioral biases
affected by framing of the questions
need to update annually/regularly
advisor interpret too literally, should act as an indicator of client's risk attitude and required returns
Portfolio Construction
Biases
Status Que Bias
Target Date Fund
auto change asset allocation on target day - glide path
Naive Diversification (conditional)
e.g. concentration in employer stock
familirity + overconfidence + loyalty effect
Excessive Trading
disposition effect
Home Bias
Behavioral Portfolio Theory
Pyramid Structure
Analyst Forecast
Overconfidence
主要是总结overconfidence如何影响analyst作出错误的forecast判断,结合chapter 2的课本后练习题
Self-Calibration
prompt, well-structured, systematic feedback
develop explicit and unambiguous conclusions
document decision/forecast for reasoning
systematic review process
apprasial by colleagues and supervisors
only include comparable data in reasearch to reduce overconfidence
Influence by company management
Framing
Anchoring and Adjustment
interprete infomation in systematice and disciplined approach
Avalibility
Biased Research
Causes
Confirmation Bias
Gamblers' Fallacy
认为一件事情在之前down了之后,之后up的概率会比理论上的概率高
Mitigations
focus on objective data
collect informaiton in systematic way
structured research process + clear way of incorporate evidence
seek contrary facts and opinions
prompt feedback
timely document for review
Investment Committees
Social Proof Bias
Mitigations
diverse background and culture
people not afraid to speak up
committe chair to encourage others to speak up
mutual respect for all members of group
collect views before meeting discussion
Market Behaviors
Momentum Effect
herding + trend-chasing effect + disposition effect
Financial Bubbles and Crashes
overconfidence + irrational
Value VS Growth
halo effect -> representative bias
Home Bias