导图社区 英语语法
- 513
- 32
- 10
- 举报
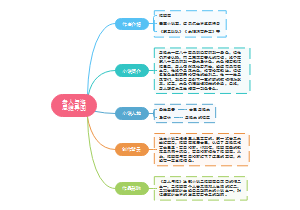
英语语法
初高中,英语语法中的一些常用点,包括词类(名词、代词、形容词、数词、冠词、动词、副词、介词)、句子成分(主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语、宾语补足语)、构词法(合成法、派生法、转换法)等知识点。
编辑于2021-07-18 11:53:32- 相似推荐
- 大纲
英语语法
Article(art.)
Indefinite article:a\an
Uses:Indefinite means "not specific".uses a\an before a singular countable noun.Not use"a"or"an"before a plural countable noun. ---some shirts.Not use "a"or"an"before an uncountable noun. Mark is eating a soup.Mark is eating some soup. 1)first time.2)not important.3)not specific.4)any one member of a group. 5)people's jobs.6)phrases of frequency.---four times a week.7)Exclamations "the"means "specific"---already mentioned the subject. articles only modify nouns.
a:before consonant uh
a European("y"sound,Yuropean) a university
an:before vowel:a,e,i,o,u un
an honour("onour")
EX: 1)Shall we boil an egg? 2)The king needs an heir.
If the noun is uncountable,there is no article.
advice is uncountable
Exceptions in using articles no article
Countries
the USA,the UK,the UAE,the Virgin Islands the country's considered to be a nation state,a collection states, or collection of different countries in one bigger state.
She lives in England. They live in America.
Meals
I don't eat breakfast.--general We didn't like the dinner--specific. breakfast,lunch,dinner,brunch
Jobs
I want to be a politician. 在职业前要用不定冠词
Proper Nouns 专有名词
See you on Monday. He is in London.
Language
He speaks English. French,Russian
Only one
The moon is beautiful. He is always on the internet. the Sun.
Uncountable Nouns
I like bread.--general I like the bread--specific
Abstract Nouns
The information was helpful,--specific Freedom is worth dying for.--general
Nouns
Count nouns or Non-count nouns
Noun-person,place,animal,thing,feeling... Not an action(verb),description(adjective),preposition(on)
Countable
a\an --a dog,an apple
often,can be counted I have a book. I have two books.
need s\es if more than 1 3 sisters some exceptions-fish,moose I have 5 fish
Uncountable
don't use "a"or"an" don't add s\es
often can't count--happiness category-furniture,clothes,money--coins,bills food\drink--milk,musfard,juice--a glass of juice
EX: English--[U] bottle--[C] water--[U]a bottle of water sadness,coffee--[U]
Much--[U] Many,A lot of--[C]--a,an
Pronoun(pron.)
Personal Pronouns: 人称代词
Possessive Pronouns: 物主代词
Reflexive Pronouns: 反身代词
Demonstrative pronouns: 指示代词 This,These,That,Those
This Present
distance
Uses:1)we use"this"to specify an objecy or person in the singular that is near to us. 2)We use "this"+noun to specify an object or person in the singular that is near to us.
EX:This is my bag. This is my sister. This bag is heavy. (This+noun---the specific bag) This computer is expensive.
time
This pizza is delicious(during the meal)
These
Uses:1)we use "these" to specify objects or people in the plural that are near to us. 2)We use "these"+noun to specify an object or person in the plural that are near to us.
EX:These are my children. These flowers are for my wife. These shoes are uncomfortable.
That Pastent
distance
Uses:1)we use"that"to specify an objecy or person in the singular that is far from us. 2)We use "that"+noun to specify an object or person in the singular that is far from us.
EX:That is an amazing view. That aeroplane is very high. That boat is beautiful. (That+noun---the specific boat).
time
That pizza was delicious last night(the next day)
Those
Uses:1)we use "those" to specify objects or people in the plural that are far from us. 2)We use "those"+noun to specify an object or person in the plural that are far from us.
EX:Those are my shoes. Those aeroplanes are very fast.
the text have mentioned,demonstrative noun. action 1 action 2.
Preposition(prep.)
By or With
Similarity:Answer how
By+verbing After "by"we often have a verb when we're explaining how something is done.
I learn English by watching ENGVID. I learn English with watching ENGVID. I write with a pen. I write by a pen.
similarity:answer the question"how" difference: 1)I turn on the computer by pushing the on button. 2)I keep healthy by exercising.
By+noun
noun:person,place or thing
communication,transportation,other expections/examples
EX: 1)I will contact you by email. 2)I will message you by test. 3)I will go by bus.(a\the)without any article.
With+noun with body parts when we are talking about tools or different instruments
noun:person,place or thing
body parts,tools,instruments.
EX: 1)Italians talk with their hands. 2)I point with my fingers. 3)I cleaned the floor with a map. 4)I ate dinner with folk.
place:at,in,on,under,near,next to,between,in front of,behind direction:along,across,across from,to time\date:at,on,in
At,On,In
Noun:time and place.
At
Specific time
at 5:00 12:30 midnight
Specific name\Exact location
at the supermaket the office her desk starbuck 25 Main Street Jfk Airport
On
1 day\1 date
on Monday January 25
Medium street\Highway
on Main Street Route 66
In
months-----July seasons-----(the)summer years-----2005 decades-----the 1960s centuries-----the 1800s long periods-----the past
floor-----the 6th floor large: city-----Los Angeles state-----California country-----the U.S continent-----North America area
By,Until
By
Before a specific time. A time limit for something to happen. An event must happen before a specific time is reached.action finished. Use:1)by for deadlines. 2)to say when someone will return
EX: 1)Please deliver the parcels by Monday. limit time 2)All job applications must be received by the 15th July. 3)Mark:Where is Jane? David:She is in London.She will be back by Saturday.
By then
by then=before a specific time that we have already mentioned.
EX:Tomorrow is the last day of school. You must finish all the exercises by then.
Until
descibes a continuous action that stops at a specific time. the duration of an action before a specific time.
I'm staying in New York until Friday.
till
is more informal
ftom...until...
Forms: 1)from+specific time =start time 2)until specific time =end time
EX: The shop will be closed from 7pm until 8am tomorrow. start end through(A.E)
When NOT to use"until"
not to descibe numbers or a quality
1)The tram can take until 50 passengers. up to 2)You may take the accounting exam up to 3 times.
like,prep. things,actions similarity,comparing
similar to something else, or happening in the same way.
comparison
like+noun
He looks like a Martian
He,Martian,compared two people,very similar
as+clause
clause:S+V
She is shopping as if there were no tomorrow. unreal situation
As your boss,I forbid you from using FB at work. in the position of
more__than
qualities
__er than
as___as
About
means regarding something,you're talking about something,you're pointing to something
Conjunction(conj.)
Until
I'll be at the office until noon. stay continue continued action. 9:00 a.m-----12:00p.m start continued action state
Until he arrives,she can wait in the lobby. will
FOR and SINCE
time
for:how long, a span of time
It has rained for 3 hours.---a span of time.
since:when begin
It has rained since 9 a.m---specific time.
Still
Uses:a.--calm\quiet conj.---however noun---quiet--stillness verb--to make quiet
EX: 1)The still-a. atmosphere that is in the garden. 2)The sense of stillness--n. that is to be found in these beautiful gardens."
So and neither
Mary has a car.So does John. positive sentence
Mary and John swim everyday.So do Nacy and Mark.
Mary doesn't have a car.Neither does John.
can,could,may,might,shall,should Uses:the same word
correlative conjunctions
Uses:two statement and two ideas together. join words,clauses and phrases,statement,related information.
Signa:for,so,because,and,or
either,or---is a choice Not only...but also--surprise neither,nor---not true,negation both,and---including
EX: 1)They told me to either buy the shoes or put them back.(choice) 2)The dog neither ate nor sleep that night. (negation)didn't eat and sleep,neither thing is true. 3)Mrs. was both funny and modest.("both"means two things.)
During--preposition\While used to refer to activities that are happening while something else is happening for happened.
During+noun
--the movie --the snowstorm --the interview
While+S+V While+Gerund
1)--We were watching. 2)--watching the movie. 3)--it was snowing. 4)--he was being interviewed. --being interviewed.
Adverb(adv.)
Already and Yet
Already--1)something has happened before now 2)surprise,question 3)ad.--before expected.
Yet--1)something hasn't happened before now 2)something has happened--done 3)-ad.-in spite of\but |as of yet--ad.--so far
EX: Are you going to take your medicine? 1)I have already take it. 2)I haven't take it yet.
founctions: 1)Have you cleaned your room yet? 2)Has Dana already finished her homework? 3)I have not yet seen Africa.
Instead
Uses:1)in place of,or as an alternative to. 2)on the contrary.rather than=instead of
EX:1)Instead we can buy a new car. stress 2)Used English terms instead of Latin ones. stress
Really vs very
Really
Uses:use to modify verbs,adjectives,adverbs
EX:You're really funny! a. He runs really fast. I'm really tired.
Both add intensify\emphasis
Very
Uses:use to modify adjectives,adverbs used more negative statement.
EX:This sandwich is very good. really You're not very funny. negative He doesn't run very fast. negative They're very rich. a.
Always --forever
Actually=In fact--contrast,correct
EX: A is true.Actually,no.A is not exactly true. Many people think A,but that is actually not true. one-word signa!emphasis. Lisa:Tom would never cheat on me. Clara:Well...actually...transition,change ideas Lisa:What!with who!
Last,latest,at least,the latter,later,lately,
last
最终的或不间断的
The last item on my shopping list this morning was a box of Weetabix.
latest(up to date)
at least(as a minimum)
The latter(2 mentioned)
Later(after more time)
lately(recently)
outlast(live longer)
lastly(finally)
Suddently
ad.突然地
Adjective(adj.)
Some or any
Some\any+noun
Some: positive statement: I need some water. requests: Can I have some time off? offers: Would you like some more?
Any: Negative statement: I don't have any money. question: Do you have any salt?
Phrases
would rather
Uses:describe a preference of one thing compared to another thing. Forms:1)sub+"would rather"+not\b.f+"than"+b.f contracted form:would rather+'d rather 2)sub+"would rather"+differnent sub+negative\past simple I would rather they stayed here. The form is the past simple but we are referring to the present or future.
EX: He would rather watch TV than read a book.
No longer
Uses:was--co.now--wro. distance
I am no longer working as a driver. 我曾经是一个司机。 It's no longer than a couple of miles,no, I can do it easily.No problem. 不会更怎么样。
No quite
-amount -ability
I'm not quite sure what you mean by that. 不能完全确定,更多的是一种能力 Not quite,but I'm trying. 你有20磅"Not qiute"我有19磅
Nearly
-time -amount -ability.
,and so on. etc. ...(ellipses)
and so on:继续同样类型的示例
I like pizza,hamburgers,fish and chips,and so on.
etcetera
句中:...etc.,but...
...pause
Even though
Even--surprising,against expectation
Even though I was late,my boss wasn't angry. Though,Only shows regular contrast
Even if I win the lottery.I won't have enough money to... if:it's a hypothetical,possible
Even when he presented the evidence,no one believed him. after,when shows realistic.
No one thought Tom's joke was funny,not even Kathy.
extre information
Even Superman wouldn't be able to defeat him.
Talk about
Travel
trip
preparation
booking,reservation
restaurant,hotel,accomodation
rent,hire
car
baggage-check in,carry on
boarding-pass,time,gate
via--transit
Depart from--city,country Arrive at airport\in city,country.
Moods,emotions,feelings
Positive
happy,glad,pleased,delighted,thrilled, ecstatic,delirious,elated, in a good mood,over the moon,cheer up on cloud nine,walking on air,a happy bunny.
Negative
sad,unhappy,miserable,melancholy, lonely, in a bad mood,down in the dumps, under a cloud,not a happy bunny.
Physical+Mental health
Working in a charity shop
voluntary---unpaid
verb:look after,care for
benefits:learn the language,work experience, mental health,improve feelings.
donantions:books,clothes,shoes,handbags
Negative agreement
neither,either
I don't like to drive. agree---Me neither.| agtee---I don't either. ---Neither do I.
I can't skate. Me neither. I can't either. Neither can I.
Biography
I was born\pass away,died
Place
in China
Time
at 5:30a.m on Sept.25 in 1975
Manners
Polite
Impolite
talk loudly
Ticket
free
poster 海报---advertisement(ad.) 广告 magazine 杂志
shopping
travel
restaurant
enjoy meals
mainly about
Money,price
Rate(cost\amount) mean the cost of something; or uesd as a verb"what do you think of something"
EX:1)What is your rate for...? 2)Give me your best rate.
Commission(slice of the pizza)
We charge 0% commission.
Charge(n+v)\Free(n)
payment
Cost\price(amount)
So the overall cost.
Transfer(change)n+v
Cut(something taken off)
I have just had a cut in...
Cutback(reduce)
I'll need to cutback on
Coupon(discount voucher)
I'll use the coupn to...
spent+doing,pay for,cost accept,refuse
Praise or criticize
praise:to say sb. is good at sth.
[n]flatter(can be negative) [v]applaud,compliment,congratulate---approvement glorify
criticize:to say sb. is bad at sth.
[n]critic. pessimist. backseat driver. [v]criticize disparage.
Meals
cook n.厨师v.烹饪,烧,煮 make meals 做饭
expensive a.昂贵的 enjoy v.享受...的乐趣,喜爱 taste v.品尝
Healthy lifestyles
bike,bicycle,ride
It is healthy,fun and good for the environment. without pollute,prevent heart diseases,control your weight,more relaxed and self-confident. popular a.流行的
Heard\Said
Don't get stressed out
modern life
stresses,strains,pressure and traumatic
I can't take the stress of this
comfort zone
going outside stepping staying inside
pushing the envelope--try new things
Some people thrive on stress,other people can't cope with stress
types of stress--time,situation(control status) anticipation(future),encounter(meeting people)
Time
9:00a.m--------------------------------------12:00p.m --------------------------------------leave(until) end --------------------------------------arrive(by) end\start by--at\on or before (finite action) until to (continued action state) by,until all tenses except perfects.
finite means a limit time
EX: 1)I'll be--stay at the office until noon. 2)I'll be--arrive at the office by noon. 3)I'll have completed my tasks by 5.future perf. 4)By the time he arrives,She had already left.
Grammer
1)Too much,Too many,A lot of
Bad vs Good with nouns
too much--uncountable-s
negative or you don't like
too much homework
too many--countable-s
too many people
a lot of--uncontable and contable
2)Time
Days\Months
ago(past)--now--from now(future)
EX: 1)IF today is Sunday,3days from now(future) ,it will be(future) Wednesday. 3days ago(past) ,it was(past) Wednesday.
Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Sunday
Tenses时态
Past Progressive 过去进行时
was\were +ving
1)about an event in progress at some points in the past,before now. 2)two events happened in the same time.
1)Jane was washing the dishes yesterday
2)They were singing very loudly.
3)While he was swimming,I was reading.
Future Progressive 将来进行时
Use:to say that something will be happening at a specific time in the future. Form:will be +ving Question:Will Sb be working?
Questions: 1)Request:Will you finish your homework tonight? 2)Want decision:Are you going to finish your homework tonight? 3)Ask Plans:Will you be finishing your homework tonight?
A possible or probable situation in the future 将来可能发生的情况 条件状语从句
Use:first condition,this happen,would do that Form:If+simple present+simple future If rains I will stay at home will be replaced by shall,can,may
EG:you'll speak better English, if you watch all my Youtu videos. Now:Haven't watched. Fut:Depends on an action.
I will survive,as I know to love. I've got all my love to give.I'll survive.
unless(如果不....;除非)
We will go there next Saturday unless it rains.
Present Perfect 现在完成时
somthing that current now,but looking back to past. tell us situation about now. Past simple is completed action. Structure:has\have +past participle(verb+ed) Contracted form(affirmative):'ve + p.p negative have not +p.p=haven't +p.p question :1)have+subject+(verb)p.p 2)What\Why\Where+have+subject+(verb)p.p?
Bruce is looking for his helmet.He can't find it. He has lost his helmet.=now past pres future recent
Past Simple: past=He lost his helmet,but now he has found it! completed action and finished in the past.
EX: Dad,I have cleaned my bedroom.Can I go to the park? OK,good.See you later!
Present perfect continuous 现在完成进行时
--links past+present --started in past,continuous present. --------------*----------*----------- present
I have been working hard all day,so I'm tired. something happened in the past,and the result is now.
Form: subject+have\has been+Ving
Past prefect continuous 过去完成进行时
--links past+past --started in past,continued in past. -------*-----*--------/------- past past present
I had been working hard all day,so I was tired. happened in the past,and the result is past.
Form: subject+had been+Ving
The Subjunctive 虚拟语气
used to emphasize urgency or importance
common for advice used\not used
1)She suggested (that)I leave early! 2)I recommend (that) you study hard. 3)It's important that he come on time.
advise,command,demand,desire,insist, propose,recommend,request,suggest,urge
IF
If I had known...,I would have... Barry didn't know Form:If+subject+had+p.p Use:something that happened in the past,we would have done differently if we have known more something at that time.\used to talk about how a decision would have been differently in the past. 3.-----past2.-----1.pres 4----
EX: seen,caught,gone,invited, moved,been,spoken,decided, done,taken.
Zero conditonals
Uses:descibe facts or things very likely to happen. The result is certain. The condition always has the same result. Form:If+condition+result,result +if+condition. Verbs tenses1):The present simple describes facts. 2)For regular events from the past,we use the past simple.
EX: 1)If you heat ice cream,it melts. condition is true result 2)If you heat ice cream,it melts. There is a comma after the condition. Ice creams melts if you heat it. no comma. 3)If I was naughty,my parents punished me.
when
when often replaces "if"for zero conditional sentences: use"when"because the result always happens when the condition is true.
First conditionals
Uses:describe real future events that are very possible. The first condition describes a specific future event. Although the form of the condition is the present simple, the meaning is the future. Not descibe a fact or regular action. Forms: If+condition+result,result +if+condition. Verbs tenses:The condition takes the present simple. The result takes the future simple.
EX: Andrew:"I'm going to a party in London tonight." Mark:"Hurry up,the bus leaves soon." Andrew:"If I miss the bus,I'll take the train". condition result 1)If I miss the bus,I will take the train. 2)If I'm late,I'll call you.
present simple+"going to" "going to"is slightly stronger than the future simple.describes a strong intention or plan for the future. present simple+modal=result If you do your homework,you may watch television. may--formal,can--informal,should--advice.
EX: 1.If I see her,I'm going to invite her to the party.
Second conditionals
Uses:describes an imaginary,impossible or unlikely situation in the present or future. The situation is hypothetical.It is not real. Verbs tenses:The past simple.subjunctive mood.------ I\you\it\we\they+were. The structure of the result is:subject+"would"+base from of verb Contracted form:I'd go=I would go If I had lots of money,I would go to London. The past tense is inidicating a distance from reality. It is not indicating past time.
EX: 1)If I had a lot of money,I would buy an expensive car. In reality,I do not have a lot of money.
Model
If you played tennis together,he would win. unlikely situation would--- but I'm certain that he would win. might---not certain,Maybe,he would win/ could---be able ton
Third conditionals
Uses:describes hypothetical situations in the past. We are imagining the result of something that did not happen. We are imagining a different past.| Verbs tenses:If+subject+past perfect.The structure of the result is: subject+"would have"+past participle.
EX: 1)If I had won the lottery,I would have bought a house. In reality,I did NOT win the lottery. The condition is impossible because it's in the past. We cannot change the past.
If not--negative conditional 如果不---unless,除非 as long as
Forms : If+s+not pres.v,s+will not unless+s+positive pres v. as long as+s+not v./pos v.
EX: 1)If you don't quilt smoking,you will feel bad. 2)Unless you quit smoking,you will feel bad. 除非你戒烟,否则你会感觉不好。
Conditionals 主将从现
If+ past simple
Missed sotuation 过去准备要做什么, 但是有其他事情发生了, 最后你不得不停止你想做的事情
1)was going to 本来打算做
I was going to go shopping,but I got a phone call which lasted nearly an hour,and by the time the call ended the shops were all shut.
2)was all set to 已经安排好了所有事
I was all set to go on holiday,but then my car broke down,and I had to spend the money on repairs instead.
3)would have intention,reason
I would have called you yesterday,but my phone wasn't work.
4)had every intention 计划好了,也准备去做
I had every intention of returning the book to the library last week,but I have a friend staying,and she's been reading it.
5)had it all arranged to 做了安排
I had it all arranged to give my friend a surprise party,but then she found out about my plan,and she said she didn't want one!
6)If only...wouldn't have...as it is 希望有做某事。 as it is:我做了,产生的结果
If only I'd listened to your advice,then I wouldn't have invested with that bank.As it is,I've lost a lot of money.
Clauses从句 S+V--dependent
Noun Clauses
A noun clause modifies or acts as a specific function to something in the independent clause. It could be the subject,it could be the object of the verb,a complement. basically four\five uses the subject comes before the verb.
What she wore to the party really turned some heads. Whoever wants to know should ask me. object,or subject complement. Please ask mom what we're having for dinner. i.o ask--object Do you know if she's coming? Paul isn't what is generally considered handsome. the subject complement --object--prep. Sarah should not be held responsible for what her bother does. --adjective complement.needs more information I am happy that you've decided to come.
an object answers the question what or whom about the verb. A subject complement answers what or whom about the subject. i.o,indirect object. In a question,the verb will come before the subject. "be"verb as your main verb or any copular or linking verb,like: "seem,appear,looks like"系动词或联系动词。 They're just situation verbs,these are not action verbs. A complete idea 概念的完整--more information
Adjective Clauses
The adjective clause-excuse me-always modifies or identifies a noun in the sentence,in the clause,etc.It means that it's giving you some information about a noun somewhere. They all begin with a relative pronoun. Now,some of these can be also the subject of the clause,which means it will agree with the verb,some of them cannot.---"that,which,who" can be both the conjuction and the subject. "that,which"when the noun is a thing."which"can modify the entire clause before it. "whom,whose,when,where,why"cannot be the subject of the clause,only the relative pronoun,only the conjunction of the clause.All must have a seperate subject to go with the verb in the clause. "whose"means possession,it doesn't have to be about a person,a thing can also possess something. The adjective clauses must always come right after the noun it's modifying.
a defining adjective clause,which means that it's basically poing to the noun and tell you something necessary about the noun. Without the adjective clauses, the noun is incomplete.I don't know what it is,I don't know| it is doing,etc. For defining adjective clauses,no comma.
the second adjective clause is the modifying, means it is not necessary but we put it in to give a little bit of extra information about the noun. So it's like an adjective that gives you a little bit more description about the noun. For modifying,like the extra information,the ones that you could actually take out and the sentence is still okey,use a comma.
EX: 1)The man lives next door. --The man who lives next door is a doctor. "who"can be a subkect,"whom"can only be an object. --Dr.Smith,who lives next door,is a retired surgeon. 2)The car whose front door is scratched is going to be repaired next week. the door belongs to the car. 3)Jerry went to the same store where Jennifer brought her couch. a particular place 3)Many students in Mrs.Reynold's Class, who went on the field trip,are homesick with the flu that's going around. A)have a prepositional phrase. 4)Larry failed his test,which means he'll have to go summer school. 5)The eccentric billionaire,about whom the public knows little about,donated millions to charity.
Conjunctions: (that),which,who,whom, whose,what,if,whether, when,where,how,why, who\m,when,where,what,which-ever
Aderbial Clauses 状语从句 relationship
The adverb clause shows a relationship.Because the subordinate conjunctions,the words that join the clause to the nidependent clause has a very specific function.The two clauses,the independent clause and the subordinate clause have a very distinct relationship.
reason
because,since
because means reason.So,I did something because I had to do it.
since:1)the begining of something,since a time 2)because
contrast there's a difference
although\though,whereas
although: 1)yes\no,positive\negative 2)It could be one idea and then a contrasting idea. 3)One expectation,one completely different result.
condition one thing must be true for something else to be true. 一件事是真实的,那么某事也必须是真实的。
if,as long as
time
when,while
purpose
so that
comparison
as --er than
I love pizza,I rarely eat it,It's unhealthy.
Although I love pizza,I rarely eat it because it 's unhealthy.
Object Clauses 宾语从句
Direct\Reported Speech
Direct speech
uses present
Billy said,"I'm feeling sick"
Reported speech
past+
Belly said that he was feeling sick.
am,is--was are--were do,does--did have,has--had will--would can--could regular=+ed want--wanted
EX: Tell:know who taking to Say:Don't know who talking to Verbs for reporting speach: informed,said,answered,reported, replied,responded,suggested,persuaded
Verb
Auxiliary Verbs 助动词
they're helper verbs,but they're important so we know what tense it is. don't need directly translate
EX 1)She is my boss. 2)He is sleeping,They have been talking. 3)I've got a car.They had gone home. 4)I do not like pizza.We didn't go. 5)I will be here.You will be like this. 6)I would do that.
Function 1)linking verb--joining subject to object 2)continuous tenses 3)perfect tense 4)questions 5)future\certainty 6)hypothetical\imagined--future or past.
Auxiliary 1)be present\past simple 2)be present continuous 3)have perfect tense(perf.) 4)do negative\pres.,past simple 5)will future\certainty 6)would
Finding the main verb
1.After is\was\were--pres.\past continuous I was eating pizza.They were singing.
2.After have\has pres.perf,had past.perf. We have got a dog.we had fun.
3.After have \has been&had been---perfect cont. They have been lying.
Transitive and intransitive verbs 及物动词即不及物动词
Transitive verbs
A sentence with a transitive verb has a subject, a verb and a direct object.A direct object is the person (or thing)that is acted upon by the suject.
EX: Mark is writing a letter. David is eating a sandwich.
A transitive verb has a direct object.
EX: Jane is drinking a cup of coffee. I have made a sandwich. Mark is playing football.
Ditransitive verbs can have 2 objects--a direct object and indirect object. An indirect object indicates the person or thing that receives the direct object.-----action receiver. Common ditransitive verbs:bring,buy,give,make,offer,pass,sell,show,wish
EX: Jane is giving me an apple. indirect direct
How to find a direct object: 1)Say the subject and berb followed by the question "what"or"whom?" 2)The answer is the direct object.----The verb is transitive. 3)If there is no answer,there is no direct object.----The verb is intransitive.
EX:1)David is eating a sandwich. 1)David is eating what or whom? 2)"sandwich"is the direct object. Therefore "eating"is transitive. 2)Mark is sleeping. 1)Mark is sleeping what or whom? 2)No answer.There is no direct object. Therefore "sleeping"is intransitive.
Intransitive verbs
1)A sentence with an intransitive verb only has a subject and a verb.The subject is the person(or thing) that is doing the action. 2)Intransitive verbs often describe physical behaviour or movement. 3)Prepositional phrases(or adverbial phrases)are often after an intransitive verb.
EX: 1)Jane is smiling. Mark is sleeping. 2)Jane is laughing. Sarah is walking. The door opened. 3)Sarah is walking to the office. where not direct object. The door opened slowly. how
Common examples of intransitive verbs Only exist as intransitive verbs: arrive,die,fall,go,laugh,sleep,smile,stay Also exist as transitive verbs: close,eat,open,play,run,sit,stand,walk
EX: Intransitive:I'm eating. Transitive verbs:I'm eating sandwich.
TO BE
TO BE Uses:Be expresses a state\condition At base level,it refers to existence(to be or not to be) Linking verb connects subject to other information your body's position,location Common in,at,with----you need to be at the office. I want to be with family this weekend.
Present Tense
Forms:Subject+be(is,am,are)
Past Tense
Forms:Subject+be(was,were)
EX: 1)I want her to be my boss. 2)Please tell him to be on time. 3)Did they tell you to be here at 8:00?
BEING Uses:continuous\drogressive express a temporary state. My computer wasn't being cooperative today.
Model Verbs 情态动词
Have
Present Tense
Basic Verb
Possession
1)what somebody has/owns
2)somebody's features,qualities or characteristics
3)relationships that people have
Actions
shower,dinner,meetings
Helping Verbs
have done
Positive I,We,You,They:have He,She,It:has
Negative don't have doesn't have
Question Do subject have? Does subject have?
Past Tense
Positive I,We,You,They,He,She,It:had(with every subject)
Negative didn't have
Question Did subject have?
Stopped:Infinitive or Gerund?
Infinnitive I stopped to talk. S V1 to V2. action:walk-stop-talk.
Gerund I stopped talking. S V1 V2 1) no to,2)Ving action:no talking.
EX: 1)I stopped to smoke. Action 1:walk. Action 2:stop walking. Action 3:smoke. 2)I stopped smoking. Action 1:smoking. Action 2:stop smoking.
Try to do or Try doing
Try to_v2_ v1
attempt difficult action tried one's best,fail
EX: 1)Maria tried to climb Mt Everest 2)Deepak tried to study,but he was to tired.
Try Ving v1
experiment,not difficult what happens:unknown
EX: 1)Try adding salt to your potatos. 2)If you can't reach me by email,try calling me.
Do and Make
Do
actions\activities\chores
actions
exercise,jumping,jacks etc
activities
a crossword,sudo etc
chores
homework,laundry,dishes,etc
expressions
well,badly,your best me a favour your nails,your hair
Make
constructing\building\creating
a dress a cup of coffee breakfast,lunch,dinner
expressions
arrangments,a plan a decision,an excuse a fool of yourself a phone call make or earn money
When not to use
1.a boyfriend\girlfriend--get 2.exercise--do 3.a year older--turn 4. homework\a test--do 5.my luggage--pack
When to use
Make a choice\decision\mistake\friends a commitment\your bed\food a presentation
Would've\Could've\Should've sound"of"--ve
modals+infinite\base I could eat chocolate.
I would have picked you up,but I ran out of gas.
I could have done better on my exam,if I had studied.
I shouldn't have eaten your chocolate.
-ing verbs
Uses of the- ing verb form
All progressive tenses
Present progressive(I am walking) Past progressive (they were driving) Future progressive(we will be arriving soon)
Gerunds(verbs used as a noun)
I hate cleaning. Watching films is my favorite hobby.
As an adjective
I have a long working day.
Forms: 1)Regular:most verbs add -ing. ex:carry--carrying sing--singing drink--drinking 2)Verbs ending in silent-e: delete the -e and add-ing write--writing observe---observing explode---exploding 3)Verbs ending in-ie: change the -ie to -y and add -ing die---dying tie---tying 4)Verbs ending in -ee:add-ing. see---seeing free--freeing Verbs ending in a single vowel and a single consonant(except-w,-x,-y) for 1 syllable verbs: double the consonant and add-ing run---running sit---sitting cut---cutting for 2 syllable verbs:If the 2nd syllable is stressed: double the consonant and add--ing ad,mit---admitting com,mit---committing If the 2nd syllable is not stressed: target---targeting visit---visiting EXCEPTION for verbs ending in -l: In British English,for verbs ending in -l: double the -l and add -ing: cancel---cancelling travel---travelling American English,for verbs ending in-l: same rules as above(no exception) cancel--canceling travel--traveling Verbs ending in-c:add -king to infinitive panic--panicking mimic---mimicking
Listen and hear when to use them
listen--active
listen to something(radio,CD) Your never listen to me! Will you listen out for the phone?
hear--passive
Did you hear that strange phone? Could you speak up,please,I can't hear you. I don't want to hear about that. Have you heard from your sister recently?
Questions
1.What's the passage mainly about? =What's the best title for the passage?
Not or true?细节匹配 Which of the following is TRUE\Not according to the passage?
The underlined word"it"refers to____?
How much should they pay?
Participles分词
Active___ing(present) Passive__ed\irregular(past)
gerund动名词,noun,a part of the continuous verb,so"be going", adjectives and adverbs
1)adjective participles---an adjective clause modifies a noun,it gives you extra information about it or identifies it. they are reduced adjective clauses,it's meant to modify a noun. It identifies it or gives extra information about a noun. A particple is that adjective clause minus the subjecy and the verb. 减去主语和动词。 (Who was)Dressed in his class-A uniform,the marine looked like a recruitment poster. The marine who was dressed in his class-A uniform looked like a recruitment poster.the entire village. Standing near the window,Marie could see the key when you're using particples at the begining of sentence, you must make sure the implied or the understood subject,which is not there but it is understood:who was,who is the marine.And then the subject of the independent clause must be the same subject. 在句子开头使用分词的关键在于,分词短语在句子开头时.你必须确保主语虽然 不在这里,但是你能理解:who was,who is. The jazz musician,known for his tendency to daydream,got into a zone and played for an hour straight. a little bit more information about the musician.not identifying--use commas.非修饰性形容词从句,时态没关系。 The woman(who is)taking to Jeff is his sister. 我正在修饰这个女人,所以这里没有逗号,因为它是一个修饰性的形容词从句。 The station chief was fired,(which means)meaning there's an open position. ,meaning关于整个独立分句。 The broken window was fixed.----The window (that was broken) 在简化后只有这一个单词时,那么就把它当成一般形容词,放在名词前。
2)an adverb clause shows you are a relationship betweeen the adverb clause itself and the independent clause. adverb participle 副词性短语是一个简化的从句 (If they werer)Given the choice,most people would probably choose good health over good fortune. relationship,would--hypothetical,implied Realizing that the police were on to him,Bernie quickly moved his millions off shore. add conjunction While delivering his speech to the council,Frank had a heart attack.
Passive___ed\irregular(past)