导图社区 Overview of Cancer signalings(tmp)
- 17
- 0
- 0
- 举报
Overview of Cancer signalings(tmp)
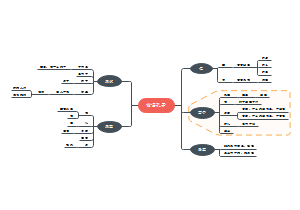
Overview of Cancer signalings(tmp):pRb A molecular checkpoint for the cell cycle restriction point;It also contains a design of positive feed back loop。
编辑于2022-06-08 22:41:10- Cancer
- circuits
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
Overview of Cancer signalings(tmp)
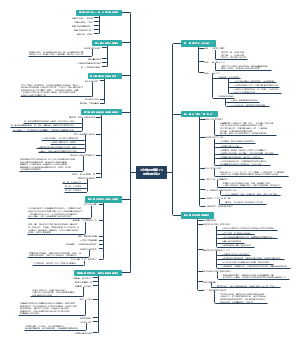
7 main families of mammalian cell surface receptors
1. GPCR
The downstream signalings of GPCR
You can see phospholopase C-β can be activated by both Gq and βγ
2. Cytokine receptors
3. RTK
4. TGFβ receptors
5. Hedgehog(Hh) receptors
6. Wnt receptors
7. Notch receptor
Diagram
Functional modules of cellular signaling circuits
Motility Circuits
Cell adhersion receptors(receptors that are physically attched with extracellular matrix components)
Integrins
hetero dimeric structural organization
α plus β subunit。
Outside in signaling
When ectodomains bind to specific components in EM, intermediary proteins will link the cytoplasmic domain of beta subunit to the cytoskeleton(actin fibires). at the same time, the cytoplasmic domains of beta subunit can attract variaty of signaling molecules.
The signaling adaptors of integrins
FAK(focal adhesion kinase)
It can activates most pathways activated by growth factor receptors.
inside out signaling
cytoplasmic signals can control the binding affinities of integrins for their ECM ligands.
this may lead to the breaking existing contacts and forging new ones in their place.
roles in cell motility
inside out signalings induce integrin to forge new linkages with the ECM.
When cell needs to loosen its tehers at the front, signalings will cause release contact with the substratum.
E-cadherin
Intermediate proteins link cadherin's intracellular domain with cytoskeleton(actin filament).
3 Intermediate proteins are involved, their spacial interactions are indicated above.
p120
β-catenin
The accumulation of β-catenin is very common in cancer.
It may promotes cell proliferation by its transcriptional factor activity.
How it is regulated
axin -> GSK-3β(glycogen synthase kinase-3β) +p-|(targets it for degredation) β-catenin
Apc (Adenomatous polyposis coli) here is part of the protein complex: {axin][GSK-3β][APC][β-catenin][Wtx}
it is critical for the successfuly capture of β-catenin, that is then phosphorylated and targeted to degredation by β-catenin.
Wnt -> Frizzled -> Dishevelled - axin -| inactive SK-3β ---|-> β-catenin
this finally promotes cell prolifereation
Onco-proteins in and around β-catenin
Constitutively activated β-catenin.
APC mtants(fail to bind and down regulates β-catenin levels).
α-catenin
Proliferation Circuits
growth factors, RTK and Ras
Viability Circuits
Bcl2
cytokines
survival factors
deathfactors
Cytostasis and Differentiation Circuits
tumour suppressor/onco proteins around cell cycle regulations
pRb
pRb A molecular checkpoint for the cell cycle restriction point
pRb -| E2F -o-> Proteins to path restriction points
It is phosphorylated by CDKs
Cyclin D-CDK4/6 +p pRb -|-> E2F -o-> DNA polymerase and other proteins for DNA synthesis
interpretation: pRb is the checkpoint to certain stage of cell cycle, because it normally inhibits cell cycle, and it needs to be induced by CDK2-CyclinE.
It also contains a design of positive feed back loop
E2F -o-> Clyclin E, CDK-2, E2F
CyclinE-CDK-2 +p pRb -|-> E2F -o-> ~~~~
So we call it a positive feed back loop
The phosphorylation of pRb becomes CyclinD independent.
Pictures
in cancer, pRb is often inactivated by lose of function mutations.
TGFβ
TGFβ is the receptor for antigrowth signals, TGFβ activation inhibits the cell cycle progression
Type I TGFβ signaling
TGFβ -> SMADs --o-> p15, p21
p15 -| CyclinD-CDK4-6 --> path of restriction point
p21 -| CyclinE-CDK2 --> path of restriction point
TGFβ -> SMAD --| Myc-Miz --> p15, p21
Myc-Miz -o-| p15ink4b, p21zip -| p15, p21
Type II TGFβ signaling
in cancer, TGFβ is often inactibated by lose of function mutations.
SMADs(the protein adaptors at down stream of TGFβ) is often inactivated by lose of function mutations.
smad2- in colon cancer
smad4- in pancrease cancer
c-Myc
cMyc is another cell cycle check point protein, it is a transcroptional factor that can either inhibits or activates cell cycle progression depends on its interacting partners
c-Myc can dimerizes with
c-Myc(form homodimer)
Max
Myc-Max is a transcriptional activator
Myc-Max -o-> Cyclin D2, E2F1, 2,3 , CDK4
results: cell will path G1 checkpoint
Miz
Myc-Miz can be thought as a transcriptional repressor
Miz is a transcriptional activator, and Myc binds and inhibits Miz.
Myc -| Miz -o-> p15ink4b, p21zip
Myc-Miz -o-| p15ink4b, p21zip -| p15, p21
results: cell will not path restriction point
anti-growth factors.
signals around Cyclin D1
Actually all the four modules can finally converge at cyclin D1.
Diagram
Ps. The regulation through gene expressions would not be completely express or completely not, they only some extend up or down regulates the gene product, so the oncogenicities depend on the lose of balance between a positive regulation hubnodes(such as MYC) and negative regulation hubnodes(such as TGF-β).