导图社区 Neurological disorders
- 14
- 0
- 0
- 举报
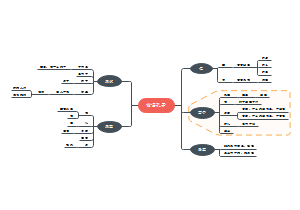
Neurological disorders
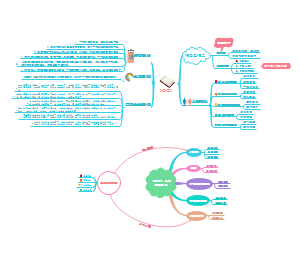
Neurological disorders:inhibits β- secretase or γ-secretase that are essential to the cleavage of APP into Aβ 42 or 40.
编辑于2022-06-08 22:54:33- Neurological disorde
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
Neurological disorders
Alzheimer's diseases(AD)
symptoms
defective in Intelligence, judgement, behavior, memory, and language.
irreverible, progressive.
brain physiological hallmarks
senile plaques
it consinsts of aggregates of amyloid β-peptides(Aβ)
neurofibrillary tangles
early-onset AD
rare
affect 30 to 60
usually running in families
mutation in APP, PS1, and PS2
Sporadic AD
appears after age 65.
mechanisms
AD disrupts neurons communications, neuronal metabolisms and neuronal repairs.
senile plagues(Aβ)
1. β-secretase and γ-secretase cleave amyloid precursor protein (APP) to produce amyloid β-peptides(Aβ)
two iso forms of Aβ
Aβ40 and Aβ42
depends on γ-secretase
Most of aggregates are the longer isoform Aβ42
2. Aβ aggregates outside and around nerve cells to form senile plaques.
neurofibrillary tangles(tau)
1. tau helps stabalize microtubles in neurons. microtubles function as internal structural support in neurons.
2. in AD, tau is hyperphosphorylated, hyperphposphorylated tau aggregates to form neurofibrillary tangles.
tau mutation itself will only leads to neurofibrillary tangles and demental, but not leads to senile plagues.
identified disease causing mutations
within or near the region encoding Aβ
all those mutation enhances production of Aβ42
Mutations in presenilin 1 (PS1) and PS2
cause early-onset familial AD
PSENs are transmembran proteins
it cleaves integral membrane proteins
it cleaves APLP-1, APLP-1 is a homologous of APP
AD linked PSEN mutant also cleaves APP and yields Aβ42
Mutations in Apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4)
cause late-onset AD
it's normally involes in lipoprotein metabolism.
The AD-linked APOE4 isoform binds Aβ and enhance Aβ aggregation.
Mutations in α2 macroglobulin
it shares the similar role with APOE4.
Aβ cascate hypothesis of AD pathogenesis
early onset AD
over-production of Aβ42 directly triggers pathogenic cascade.
Sporadic AD
The clearance of Aβ 42 is too slow due to the massive aggregation, leads to vicious cycle.
immune system might involve
The aggregation factors may involved in these cases.
other possible causes of AD
reactive oxides damage may leads to AD.
increase level of homocyteine may cause AD.
inflammation in certain regions of the brain may casues AD.
strokes may cause AD.
therapy
Durg design
inhibits β- secretase or γ-secretase that are essential to the cleavage of APP into Aβ 42 or 40.
its 40 or 42 depends on γ-secretase, when it cleaves at residue 40 will produce Aβ40, if it cleaves at residue 42 will produce Aβ42
inhibits proteins those are activating β-secretase and γ-secretase.
PSEN knockout mice have 80% reduction in γ-secretase activity.
BACE is a transmembrane protein share same activity with β-secretase.
the drug must be able to path blood brain barrier.
Ginkgo biloba Extract
it may prevent oidative damage caused by amyloid β peptide.
early diagnosis
screen the carrier and prevent
Parkinson's disease(PD)
symptoms
movement disorder, resting termor, and rigidity.
protein deposits in specific neurons
fibrillar cytoplasmic inclusions(Lewy bodies) in dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra.
familial PD
rare
sporadic PD
common
mechanisms
α-synuclein and ubiquitin aggregates to form Lewy bodies.
familial PD is due to Ala30Pro and Ala30Thr mutations in α-synuclein that will enhance the protein aggregation.
Huntington's Disease(HD)
symptoms
progressive neurodegenerative disorder
form incluson bodies and spiny neurons
neuronal cell death, primarily in the cerebral cortex and striatum
leads to psychiatric symptoms, motor impairment and dementia.
autosomal dominant inheritance
mechanisms
Trinucleotide(CAG) repeat expansion disorders elongate the polyQ region on huntingtin, the polyQ elongation on huntingtin enhances protein aggregation to form inclusion bodies.
Trinucleotide repeat expansion
a common mutation
it becomes a disorder when the trinucleotide repeats in certain genes exceeding the normal, stable, threshold, which differs per gene.
increase number of CAG repeats can cause 10 neurological disorders.
When the number of CAG repeats on the huntintin Gene exceeds 35, HD will develops
just 35 repeats have no phenotype
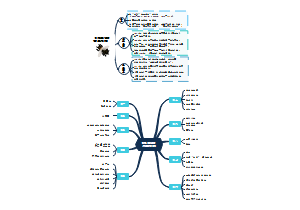
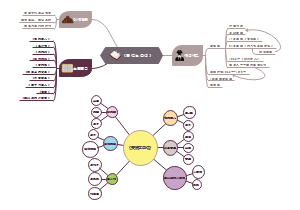
Prion diseases
PrP
structure
PrPc
no beta sheets
40% a-helixes
PrPsc
50% beta sheet
20% a-helixes
PrPc
Informatics
product of one gene
present in brain and many other tissue types
This shown is the processed form, a C terminal yellow ladder sequences is replaced by GPI anchor sequence during the processing.
The GPI anchor sequence will anchor Prc to the outer surface of the plasmamembrane
the PrPc knockout mice is resistence to all associated diseases
not resistent to proteolytic treatment.
Cellular biological function
the knock out mice shows more sensitivity to pressures.
PrPc is concentrated in both pre and post-synaptic membranes.
hypothesis 1
octomeric repeat region can binds 5 Cu2+ at synapses.
Cu2+ can catalysis the conversion of reactive oxygen species. (function like SOD)
hypothesis 2
PrPC bind Zn2+, and mediates Zn2+ transportation.
Zn2+'s location might be very important for the function of the brain.
PrPsc
can aggregates into amyloid fibril: a coil of several fibrils perpendicular to a cylindrical axis.
The proteolytic removal of 60 - 70 aa from the A-terminal can leaves the protein a protease-resistant core.
this is why eating PrPsc can cause vCJD
because PrPsc itself is resist to degestion
shows infectivity
infectivity is neutralized by denaturing agents and anti-PrP antibodies.
Propagation of PrPsc conformation
hypothesis 1: template-assisted conversion
hypothesis 2: Nucleation-polymerisation
Common
all caused by insoluble protein aggregation
beta sheet formation in the protein's conformation is essential for its aggregation, because it will forms a protease-resistant core
may facilitated by
mutation
proteolytic cleavage
binding of chaperones
the protein aggregates may not only contains the disease causing protein, but it may also involves various proteins that are recruited by the protein.