导图社区 DNA mutation
- 20
- 0
- 0
- 举报
DNA mutation
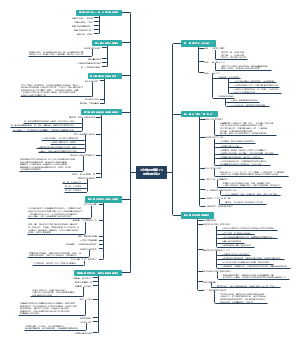
DNA mutation:type of mutations、Type of leisions、Source of Damages、DNA repair.
编辑于2022-06-09 22:52:45- DNA mut…
- Source of…
- leisions
- mutations
- DNA repair
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
DNA mutation
type of mutations
single base/point mutation
Reversion
True reversion
second mutation restores DNA sequence
Suppression
Intragenic
insersion followed by deletion
Intergenic
double mutant between interacting proteins
tRNA suppression
mutation on tRNA gene
stop nonsence mutation
substitusion
fixation
after DNA replications
chemically
transition
purine to purine, pyrimidine to pyrimidine
4 possibillities
transversion
pyrimidine to purine, purine to pyrimidine
8 possibillities
codon sense
silent
same aminoacids' degeneracy codon
missense
change 1 amino acids
neutral
a similar propertie's amino acid
nonsense
stop codon
addition/deletion
codon sence
usually frameshift
other consequences
altered splicing partern
lose exon/ adds intron: frame-shift/ trancate results
genes
duplication
chromosomes
inversion
deletion
translocation
genomes
euploidy
aneuploidy
Type of leisions
mismatch
arrised from keto-enol tautomers escape proof reading+mismatch repair
loopingout
replication
parental/ template strand loops out
results in deletion of the complementary strand
Most readily occurs in a run of identical bases
noncoding
spontaneously debase
depurination
depyridination
produce abasic noncoding site: 100000 per cells per day
Bulky
UV Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (thymine dimers) and 6-4 photoproducts bulky leisions
can block DNA replication and transcription
strand breaks
ionizing radiation: nonreversible deletion result in
Source of Damages
Spontaneous
errors during Replication
Mismatch
arrised from keto-enol tautomers escape proof reading+mismatch repair
loopingout
parental/ template strand loops out
results in deletion of the complementary strand
Most readily occurs in a run of identical bases
spontaneous self modification
deamination
cytosine deamination
C to U
transistion
increased by nitrous acid
5-mec deamination
5-mec to T
debase
depurination
depyridination
produce abasic noncoding site: 100000 per cells per day
cellular damaging agents
Reactive oxygen species
superoxide, hydroxyl radical, peroxide
G to 8-hydroxyguanine
8-hydroxyguanine pair with C/A
cause transversion
S-adenosylmethionine methylates G, T, A
O6-methylguanine
pair with C/T
cause GC to AT transition
Induced
Physical
ionizing radiation
X-rays, γ-rays
Direct — interaction of high energy photons with DNA
Indirect — interaction of e- and ROS (formed by radiolysis of water) with DNA
cause strand breaks
single
double
leads to nonreversible deletion
non-ionizing radiation
UV
Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (thymine dimers) and 6-4 photoproducts
bulky leisions
Chemical
Base analogues
Keto (normal) tautomer of 5-BrU pairs with A
Enol tautomer pairs with G
Causes TA to CG and CG to TA transitions
Base modifying agents
acid promotes C deamination. Resulting U pairs with A.
accelerated deamination processes
Hydroxylamine produces hydroxylaminocytosine — pairs with A
Alkylating agents
Electrophilic compounds that attack nucleophilic centres on DNA
•N-Methyl-N-nitroso-N’-nitroguanidine (MNNG)
•Methyl methanesulphonate (MMS)
•Ethyl methanesulphonate (EMS)
•Nitrosamines
Dietary nitrites can form nitrosamines in stomach
Arylating agents
resulting NON-informational or blocking lesions stop DNA polymerase recognation
Error-prone repair, lesion bypass mechanisms may then operate
Bi-functional alkylating agents can cross-link strands e.g. mitomycin C (from Strep. Sp)
Arylating agents
ex.PAH
• Non-informational, non-coding BULKY ADDUCTS (cf thymine dimers) block replication and transcription • Activated to diol epoxide by liver cytochrome P-450s
Aflatoxin B1
Potent liver carcinogen found in peanut fungus
ptaquiloside
carcinogen in bracken fern
•Reacts with adenine
•Causes strand breaks
Intercalating agents
ethidium bromide, proflavin and acridine orange
Cause frameshift mutations: additions or deletions depending on whether they intercalate into the template or newly synthesised DNA strand.
DNA repair
Direct repair
DNA ligase
repair "Nicks"
form phosphodiester bond between approximated 3'OH and 5' OPO32-
Alkyltransferase
deakylates
O4-alkylthymine
O6-methylguanine
Suicide inactivation
Photoreactivation
Photolyase (flavoprotein) repair UV leision using light as energy source
Excision repair
Methyl-directed Mismatch Repair (MMR)
mismatch targeting
require methylated DNA around to direct repair in e. coli
but not in human
excise by mut H
synthesize by DNApol III
Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER)
bulky leision targeting
excise and synthesized by DNApol I
Base Excision Repair (BER)
specific altered sites recognized by different glycosylases
exice by AP endonuclease
Strand break repair
Single-strand break repair
Double-strand break repair
Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ)
Homologous Recombination (HRR)
Ecoli SOS