导图社区 5 basic knowledge
- 32
- 0
- 0
- 举报
5 basic knowledge
这是一篇关于Business statistic must know 5 basic points的思维导图,有需要的小伙伴可以收藏起来观看哦。
编辑于2022-06-14 23:34:16- 相似推荐
- 大纲
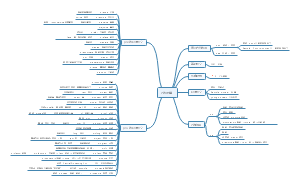
10 basic knowledge
population and sample
population
definition: set of all items of interst
symbol: population size: N
example:all of uoft students
parameter
defintion: number descriping a population
symbol: population mean= μ
sample
defintion: subset of population
symbol: statistic size: n
example: random sampling 1000 uoft students
statistic
defintion: number descriping a sample
symbol: sample mean:¯x¯
statistic
descriptive statistic
describe a sample
inferential statistics
definition: make inference about a population and its parameter using sample data
probability versus statistic
probability
know everything, know population
calculate probability of an event occurs
statistic
unknown population
take sample dataand calculate sample statistic
infer parameter
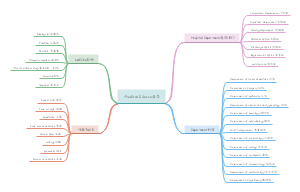
sampling and nonsampling error
Sampling Error
characteristics
it is not a mistake
cause the sample is a random subset of the population
as sample size rizes, sampling error tends to fall
Non-sampling Error
4 categories
biased estimate
definition: systematically higher or lower than the population parameter
reason: sample is too samll
systematic lying
reason: due to poor survey design
example: There is a survey about humanity and some passerbys could give money to homeless dogs under moral pressure if lots of people arrounded him.
non-response bias
reason: low response rate where non-responders differ from responders
example: If students can write report letter to the headmaster email which decide whether teachers leave or stay, it could appear a situation that letters are almost bad letters to teachers.
sampling frame differs from target population
reason: the list from which units are drawn for the sample is wrong.
example: if a investiagator plan to make a survey of meansalary of uoft students, but he asks parents of uoft students. (cause students could lie to their parents.)
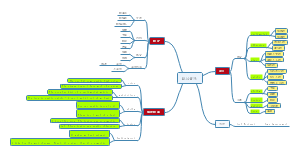
What are data
definition: data are recorded information, whether numbers of labels together with its context
3 types
cross sectional data
definition: same variables in same time period measured for different units
time series data
definition: same variables for same unit measured a different time period
panel
definition: same variables measured for a range of units and time periods.
What is variable
definition: A variable holds information about the data.
Quantitative variable数字变量
definition: a variable in which the numbers are values of measured quantities
Discrete variable
definition: a finite or countable list of values 结果有限
example: number of heads in 4 tosses of a coin
continuous variable
definition: any value possible in an interval(uncountable)结果无限
example: after tax income
categorical variable类别变量
defiinition: a variable that labels the category of the measured unit
discrete variable
4 types
Quantitative variable
Interval
numerical measurements which allow for degree of difference between values
distance is consistent but ratios are meaningless
Does not have a true 0 measure
Ex: dates
Ratio
numerical measurements which allow for degree of difference between values
ratios are meaningful-sensible to carry out multiplication/division
Ex: temperature, length,time duration
Categorical variable
Nominal
categorize units into distinct classes
unordered categories
Ex: gender, program of study, favorite color
Ordinal
ordered categories without natural units / distance metric.
natural ordering to the categories; not just the names of the categories differ
Ex: letter grades, income, professional rank
categorical
units
Ex:
Q:
Q1: Consider data on 257 people who tasted a new snack product at loblaws. Each was asked: how likely is it that you will purchase this product in the future? which kind of data are these: a. Cross sectional data b. Time series c. Panel data
answer: a
Q2: Price of the textbook each year for the past decade and the percent of students that had a copy. which kind of data are these? a. Cross sectional data b. Time series c. Panel data
answer: b