导图社区 Chapter3_Integrative Managerial Issues
- 23
- 0
- 0
- 举报
Chapter3_Integrative Managerial Issues
Social responsivenessis characteristic of the business firm that engages in social actions in response to a popular social need.
编辑于2022-12-12 13:14:06 四川省- Chapter6_Organizational Structure and Design
Chain of CommandThe line of authority extending from upper organizational levels to lower levels, which clarifies who reports to whom.
- Chapter5_Foundations of Planning
Defining the organizational purpose and ways to achieve it. Planning includes defining goals, establishing strategy, and developing plans to coordinate activities.
- Chapter4_Foundations of Decision Making
Intuitive decision making can complement both bounded rationality and rational decision making.
Chapter3_Integrative Managerial Issues
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- Chapter6_Organizational Structure and Design
Chain of CommandThe line of authority extending from upper organizational levels to lower levels, which clarifies who reports to whom.
- Chapter5_Foundations of Planning
Defining the organizational purpose and ways to achieve it. Planning includes defining goals, establishing strategy, and developing plans to coordinate activities.
- Chapter4_Foundations of Decision Making
Intuitive decision making can complement both bounded rationality and rational decision making.
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
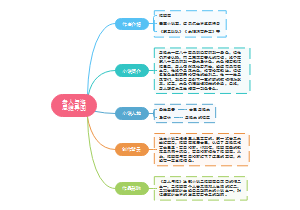
Chapter3 Integrative Managerial Issues
Globalization
Globalization is the process of international integration arising from the interchange of world views, products, ideas and other aspects of culture.
How Does Globalization Affect Organizations? Organizations are considered global if they exchange goods and services with consumers in other countries.
Global organization
Multinational Corporation (MNC) Any type of international company that maintains operations in multiple countries.
Multidomestic Corporation An MNC that decentralizes management and other decisions to the local country where it’s doing business.
Global Corporation An MNC that centralizes management and other decisions in the home country
Transnational (Borderless) Organization A structural arrangement for global organizations that eliminates artificial geographical barriers.
How Do Organizations Go Global?
Global Sourcing Purchasing materials or labor from around the world wherever it is cheapest
Exporting Making products domestically and selling them abroad
Importing Acquiring products made abroad and selling them domestically
Licensing An agreement primarily used by manufacturing businesses in which an organization gives another the right, for a fee, to make or sell its products, using its technology or product specifications- products
Franchising An agreement primarily used by service businesses in which an organization gives another organization the right, for a fee, to use importing its name and operating methods – the entire system
Global Strategic Alliance A partnership between an organization and a foreign company partner(s) in which resources and knowledge are shared in developing new products or building production facilities
Joint Venture A specific type of strategic alliance in which the partners agree to form a separate, independent organization for some business purpose
Foreign Subsidiary A direct investment in a foreign country that involves setting up a separate and independent facility or office
What Do Managers Need to Know About Managing in a Global organization?
Parochialism A narrow focus in which managers see things only through their own eyes and from their own perspective
Hofstede’s Framework
Power Distance
Individualism vs. Collectivism
Achievement vs. Nurturing
Uncertainty Avoidance
Long-term vs. Short-term Orientation
What Dose Society Expect from Organizations and Managers?
Social Responsibility also known as Corporate social responsibility (CSR) refers to a business’s intention, beyond its legal and economic obligations, to do the right things and act in ways that are good for society.
Obeys the law Pursues the economic interest Views a business a moral agent
Social obligation are activities a business engages in to meet certain economic and legal responsibilities.
Social responsiveness is characteristic of the business firm that engages in social actions in response to a popular social need.
Sustainability a company’s ability to achieve its business goals and increase long-term shareholder value by integrating economic, environmental, and social opportunities into its business strategies.
What is today’s workforce like and How does it affect the way organizations are managed?
Workforce diversity the ways in which people in an organization are both different from and similar to one another.
Types of Diversity
Age
Gender
Race and ethnicity
Race: biological heritage Ethnicity: related to race but it refers to social traits, such as one’s cultural background or allegiance
Disability/Abilities
Religion
GLBT-sexual orientation and gender identity
Other types of diversity
How Are Managers Adapting to a Changing Workforce?
Work-life balance programs Benefits that provide a wide range of scheduling options that allow employees more flexibility at work, accommodating their needs for work/life balance
Contingent Workforce Part-time, temporary, and contract workers who are available for hire on an as-needed basis
Generational differences present challenges ranging from appearance to technology and management style