导图社区 Chapter6_Organizational Structure and Design
- 31
- 0
- 0
- 举报
Chapter6_Organizational Structure and Design
Chain of CommandThe line of authority extending from upper organizational levels to lower levels, which clarifies who reports to whom.
编辑于2022-12-12 13:17:16 四川省- Chapter6_Organizational Structure and Design
Chain of CommandThe line of authority extending from upper organizational levels to lower levels, which clarifies who reports to whom.
- Chapter5_Foundations of Planning
Defining the organizational purpose and ways to achieve it. Planning includes defining goals, establishing strategy, and developing plans to coordinate activities.
- Chapter4_Foundations of Decision Making
Intuitive decision making can complement both bounded rationality and rational decision making.
Chapter6_Organizational Structure and Design
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- Chapter6_Organizational Structure and Design
Chain of CommandThe line of authority extending from upper organizational levels to lower levels, which clarifies who reports to whom.
- Chapter5_Foundations of Planning
Defining the organizational purpose and ways to achieve it. Planning includes defining goals, establishing strategy, and developing plans to coordinate activities.
- Chapter4_Foundations of Decision Making
Intuitive decision making can complement both bounded rationality and rational decision making.
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
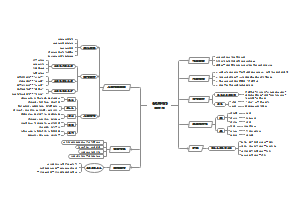
Chapter6 Organizational Structure and Design
Six key elements in organizational design
Work specialization Dividing work activities into separate job tasks; Individual employees “specialize” in doing part of an activity rather than the entire activity in order to increase work output. Also called division of labor
Departmentalization How jobs are grouped together
Functional Departmentalization Grouping activities by functions performed
Product Departmentalization Grouping activities by major product areas
Customer Departmentalization Grouping activities by customer
Geographic Departmentalization Grouping activities on the basis of geography or territory
Process Departmentalization Grouping activities on the basis of work or customer flow
Recent trend
Cross-functional Teams Teams made up of individuals from various departments and that cross traditional departmental lines
Authority、Responsibility and Power
Chain of Command The line of authority extending from upper organizational levels to lower levels, which clarifies who reports to whom
Authority The rights inherent in a managerial position to give orders and expect the orders to be obeyed
Line Authority Authority that entitles a manager to direct the work of an employee
Staff Authority Positions with some authority that have been created to support, assist, and advise those holding line authority
Responsibility An obligation to perform assigned duties
Power refers to an individual’s capacity to influence decisions. Authority is part of the larger concept of power
Coercive power Power based on fear. The power a leader has to punish or control
Reward power The power to give positive rewards. A reward can
Legitimate power The power a leader has as a result of his or her position in the organization.
Formal power
Expert power Power based on expertise, special skills, or knowledge.
Referent power Comes from being trusted and respected because of a person’s desirable resources or personal traits.
Informal power
Span of control The number of employees a manager can efficiently and effectively supervise
determinants
Job complexity
Similarity of subordinate jobs
Physical proximity of subordinates
Abilities of employees
Abilities of the manager
Centralization and Decentralization
Centralization The degree to which decision making takes place at upper levels of the organization
Decentralization The degree to which lower-level managers provide input or actually make decisions
Formalization How standardized an organization’s jobs are and the extent to which employee behavior is guided by rules and procedures
What Contingency Variables Affect Structural Choice?
Mechanistic or Organic organizations
Mechanistic Organization A bureaucratic organization; a structure that’s high in specialization, formalization, and centralization
Organic Organization A structure that’s low in specialization, formalization, and centralization
Four contingency variables
Strategy —>Structure
Size —>Structure
Technology—>Structure Every organization uses some form of technology to convert its inputs into outputs. Joan Woodward divided the firms into three distinct technologies that had increasing levels of complexity and sophistication
Unit Production The production of items in units or small batches (NONROUTINE TEC). Large turbines, ships or repair works and experimental plants
Mass Production Large-batch manufacturing (ROUTINE TEC)
Process Production The production of continuous process products such as oil and chemical refiners (ROUTINE TEC)
Environment —>Structure
What are some common organizational designs?
Traditional organizational designs
simple Structure An organizational design with low departmentalization, wide spans of control, authority centralized in a single person, and little formalization
Functional Structure An organizational design that groups similar or related occupational specialties together
Divisional Structure An organizational structure made up of separate business units or divisions
Contemporary Organizational Structures
Team Structure A structure in which the entire organization is made up of work teams. Employee empowerment is crucial because there is no line of managerial authority from top to bottom
Matrix Structure A structure in which specialists from different functional departments are assigned to work on projects led by a project manager
Project Structure A structure in which employees continuously work on projects, no formal departments where employees return at the completion of a project.
Boundaryless Organization Internal boundaries within the company will be eliminated and external barriers between the company and its customers and suppliers will be broken down.
Virtual Organization An organization that consists of a small core of full-time employees and outside specialists temporarily needed to work on projects.
Network Organization Which is one that uses its own employees to do some work activities and networks of outside suppliers to provide other needed product components or work processes.
What Are Current Organizational Design Challenges?
Keeping employees connected
Managing global structural issues
Building a learning organization Designing flexible work arrangements