导图社区 生物第九章 气体交换及吸烟 知识结构图
- 474
- 3
- 0
- 举报
生物第九章 气体交换及吸烟 知识结构图
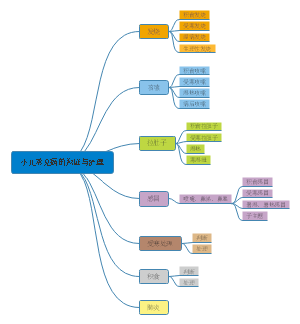
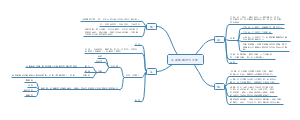
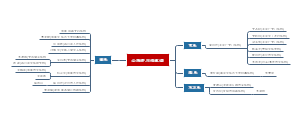
第九章知识结构图。内容包含气体交换、肺及气管结构、吸烟以及吸烟引起的疾病等。气体交换指肺泡和血液之间,以及血液和组织之间的气体交换。是物理性的扩散过程,气体从分压高的一侧向低的一侧扩散。
编辑于2021-06-10 08:53:40- 相似推荐
- 大纲
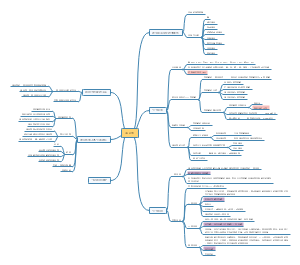
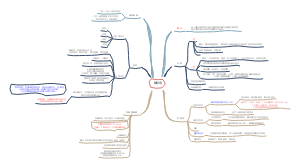
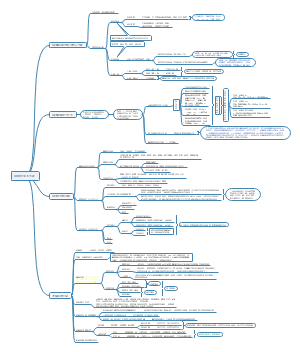
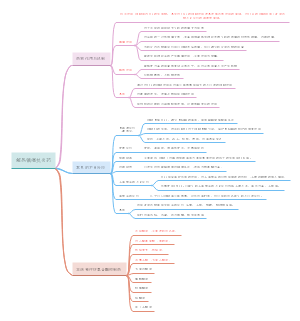
Gas exchange and smoking
Gas exchange
1.clean and warm the air that enters during breathing;2.maximise the surface area for diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and atmosphere;3.minimise the distance for this diffusion;4.maintain adequate gradients for this diffusion
In humans, the gas exchange surface is the alveoli (singular: alveolus)( 70 m^2) in the lungs-- at any one moment to give us a high rate of gas exchange
Lungs

Trachea, bronchi and bronchioles

Warming and cleaning the air
air is warmed to body temperature and moistened by evaporation-- protecting the delicate surfaces inside the lungs from desiccation
against the suspended matter( dust, sand, pollen, fungal spores, bacteria and viruses)-- All are potential threats to the proper functioning of the lungs
Particles larger than about 5–10 μm are caught on the hairs inside the nose and the mucus lining the nasal passages and other airways
the mucus is produced by the goblet cells of the ciliated epithelium; Mucus is composed of glycoproteins with many carbohydrate chains that make them sticky and able to trap inhaled particles.
Some chemical pollutants(sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide)can dissolve in mucus to form an acidic solution that irritates the lining of the airways

Phagocytic white blood cells (macrophages )patrol the surfaces of the airways scavenging small particles such as bacteria and fine dust particles
Alveoli
alveoli:At the end of the pathway between the atmosphere and the bloodstream
Alveolar walls contain elastic fibres --stretch during inspiration and recoil during expiration-- the surface area available for diffusion increases
extremely thin walls; a single layer of squamous epithelial cells -- Oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules diffuse quickly
a steep concentration gradient:by breathing and by the movement of the blood
Short-term effects on the cardiovascular system
Nicotine
a highly addictive drug in tobacco
It stimulates the nervous system to reduce the diameter of the arterioles and to release the hormone adrenaline; It stimulates nerve endings in the brain to release the transmitter substance dopamine
heart rate and blood pressure increase; a decrease in blood supply to the extremities of the body;increases the risk of blood clotting; hard to give up smoking.
Carbon monoxide
combines with haemoglobin to form the stable compound carboxyhaemoglobin-- haemoglobin does not become fully oxygenated;damage the lining of the arteries
Coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke may be the result--death and disability
reversible in people who have not smoked for very long
Smoking is just one factor that increases the chances of developing one of the cardiovascular diseases(CHD and stroke)
Lung diseases
Chronic (long-term) obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD)
asthma, chronic bronchitis and emphysema
Atmospheric pollution from vehicle and industrial emissions and tobacco smoke
Chronic bronchitis:Infections such as pneumonia easily develop in the accumulated mucus. When there is an infection in the lungs, the linings become inflamed and this further narrows the airways.
a severe cough, producing large quantities of phlegm, which is a mixture of mucus, bacteria and some white blood cells.
Emphysema


The loss of elastin makes it difficult to move air out of the lungs.
the blood vessels in the lungs become more resistant to the flow of blood; the blood pressure in the pulmonary artery increases;need a continuous supply of oxygen through a face mask
Chronic bronchitis and emphysema often occur together;The WHO predicts that COPD will become the third leading cause of death worldwide by 2030.
Lung cancer
carcinogens produce mutations leading to the development of a mass of cells, known as a tumour; it spreads through the bronchial epithelium and enters the lymphatic tissues in the lung; Cells spread to other organs ,so that secondary tumours become established-- a malignant tumour
Lung cancer takes 20–30 years to develop; coughing up blood; chest pain; difficult to breathe;rare for a cancer to be diagnosed before 1 cm in diameter
bronchoscopy;chest X-ray ; CT scan
treatment involves surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy
Tobacco smoke
there are over 4000 different chemicals in cigarette smoke;Tobacco smoke is composed of ‘mainstream’ smoke (from the filter or mouth end) and ‘sidestream’ smoke (from the burning tip)
passive smoking: Breathing in someone else's cigarette smoke
The main components of cigarette smoke pose a threat to human health:1.tar, which contains carcinogens (cancer-causing compounds) (damage the gas exchange system);2.carbon monoxide;3.nicotine (2 and 2 damage the cardiovascular )
Smoking
The World Health Organization (WHO) considers smoking to be a disease
1.describe the structure of the human gas exchange system 2. describe and explain the distribution of tissues and cells within the gas exchange system 3.describe the functions of these tissues and cells 4.explain how gases are exchanged in the lungs 5.explain how tobacco smoke affects the gas exchange system 6.describe the effects of nicotine and carbon monoxide on the cardiovascular system