导图社区 Cambridge IGCS Chemistry Coursebook 2015 Chapter 2 知识点整理
- 15
- 0
- 0
- 举报
Cambridge IGCS Chemistry Coursebook 2015 Chapter 2 知识点整理
物质的本质是指物质所固有的根本属性,包括其组成、结构、性质以及变化规律。在物理学、化学、生物学等多个学科领域,科学家们都对物质的本质进行了深入的研究和探讨。
编辑于2024-07-20 13:43:24- IGCSE化学
- Cambridge IGCS Chemistry Coursebook 2023 Chapter 21 知识点整理
This is a mind map about Experimental design and separa,Main content: Chromatography,Separation and purification,Experimental design。
- Cambridge IGCS Chemistry Coursebook 2023 Chapter 20 知识点整理
This is a mind map about Petrochemicals and polymers,Main content: Plastics,Polymers,Petroleum and its products。
- Cambridge IGCS Chemistry Coursebook 2023 Chapter 19 知识点整理
This is a mind map about Reactions of organic compounds,Main content: Carboxylic acids and esters,Chemistry of ethanol,Characteristic reactions of different homologous series。
Cambridge IGCS Chemistry Coursebook 2015 Chapter 2 知识点整理
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- Cambridge IGCS Chemistry Coursebook 2023 Chapter 21 知识点整理
This is a mind map about Experimental design and separa,Main content: Chromatography,Separation and purification,Experimental design。
- Cambridge IGCS Chemistry Coursebook 2023 Chapter 20 知识点整理
This is a mind map about Petrochemicals and polymers,Main content: Plastics,Polymers,Petroleum and its products。
- Cambridge IGCS Chemistry Coursebook 2023 Chapter 19 知识点整理
This is a mind map about Reactions of organic compounds,Main content: Carboxylic acids and esters,Chemistry of ethanol,Characteristic reactions of different homologous series。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
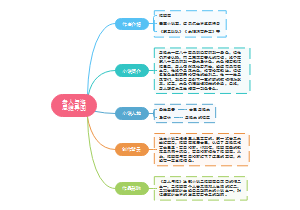
The nature of matter
Atoms and molecules
elements and compounds
elements
compounds
chemical reactions and physical changes
decomposition, synthsis
chemical reaction
new chemical substances are formed
usually the process is not easily reversed
energy is often given out
physical change
atomic theory
a chemical language
symbol
the kinetic model of matter
lattices
Solid: • packed close together • in a regular arrangement or lattice • not able to move freely, but simply vibrate in their fixed positions.
Liquid • closely packed together • in an irregular arrangement • able to move around past each other.
Gas • arranged totally irregularly • spread very far apart compared to solids and iquids • able to move randomly.
diffusion in fluids
the dissolving of gases
Brownian motion.
atoms and molecules
elements
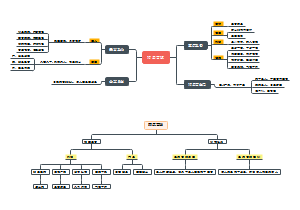
The structure of the atom
atomic stucture
subatomic particles
protons
neutrons
electrons
measuring the size of atoms
mass spectrometer
relative atomic mass
carbon-12
subatomic particles
Protons and neutrons have almost the same mass. Electrons have virtually no mass at all ( 1/1840 of the mass of a proton).
proton (atomic) number and nucleon number
proton number : Z
nucleon number : A
=number of protons + number of neutrons
isotopes
The number of neutrons in the atoms is the difference between isotopes. They have the same number of protons and electrons.
radioisotopes
relative atomic masses
1 atomic mass unit (a.m.u.) = 1/12 × mass of one atom of carbon-12.
the uses of radioactivity
radioactive dating
half-life
industrial uses of radioisotopes
Major : nuclear power stations
Other : monitoring the level of filling in containers, checking the thickness of sheets of plastic, paper or metal foil (for example, aluminium baking foil) during continuous production, and detecting leaks in gas or oil pipes
medical and food-safety uses of radioisotopes
chemotherapy
radiotherapy
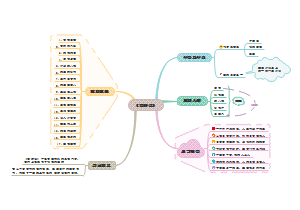
Electron arrangements in atoms
energy levels
Bohr's theory
◆ Electrons are in orbit around the central nucleus of the atom.
◆ The electron orbits are called shells (or energy levels) and have different energies.
◆ Shells which are further from the nucleus have higher energies.
◆ The shells are filled starting with the one with lowest energy (closest to the nucleus).
◆ The first shell can hold only 2 electrons.
◆ The second and subsequent shells can hold 8 electrons to give a stable (noble gas) arrangement of electrons.
The states of matter
solid, liquid, gas
changes in physical state
melting and freezing
melting point freezing point
sublimation
evaporation, boiling and condensation
pure substance
the effect of impurities
heating and cooling curves
types of mixture
solution
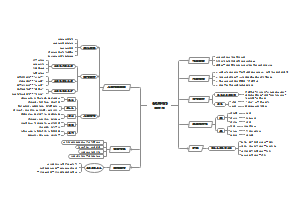
Separating and purifying substance
separating insoluble solids from liquids
decanting
filtration
separating immiscible liquids
separating mixtures of solids
separations based on differences in density
separations based on magnetic properties
separations based on differences in solubility
separations based on sublimation
separating solutions
distillation
fractionating column
chromatogrtaohy
the purity and identity of substances
a closer look at solutions
the solubility of solids in liquids
solution
solute
solvent
solubility
saturated solution
the solubility of gases in liquids