导图社区 Cambridge IGCS Chemistry Coursebook 2023 Chapter 13 知识点整理
Cambridge IGCS Chemistry Coursebook 2023 Chapter 13 知识点整理
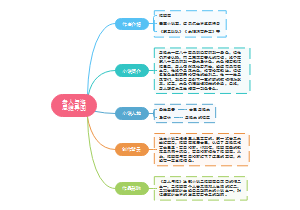
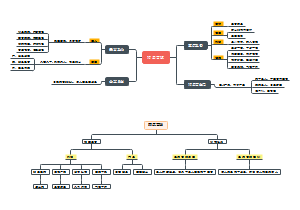
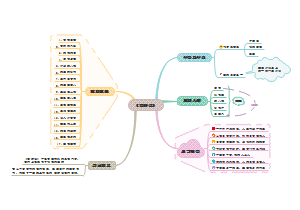
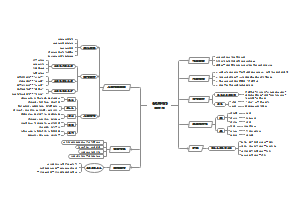
这是一篇关于The periodic Table的思维导图,主要内容包括:Trends across a period,Trends in groups,Classifying the elements。
编辑于2024-11-23 20:49:35- IGCSE化学
- 相似推荐
- 大纲