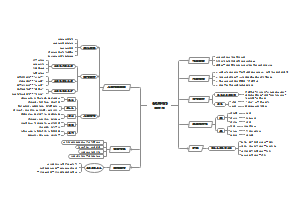
导图社区 句子种类
- 45
- 0
- 0
- 举报
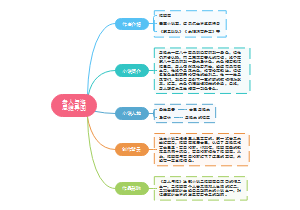
句子种类
这是一篇关于句子种类的思维导图,主要内容包括:感叹句,疑问句,祈使句,陈述句。无论是初学者还是进阶学习者,都能从中受益,提升自己的英语语法水平。
编辑于2025-01-01 15:59:29- 祈使句
- 疑问句
- 句子种类
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
句子种类
陈述句
用来叙述一件事情或者表明说话人的看法
语序:主语+谓语+其他成分
分类
肯定形式
We all felt excited when China succeeded in launching its first manned spaceship.
否定形式
句子的谓语为be,have,can,could(be动词,助动词,情态动词在后面加not)
One cannot go back to his youth.
句子的谓语是实义动词时候,在谓语动词前要加dont,doesnt,didn't
They didn't know my address and telephone number.
Lung cancer, like some other cancers, often doesn't produce symptoms until it is too late.
其他否定词(hardly, no, never, seldom, nobody等) 也可构成否定式。
Laws too gentle后置定语 are seldom否定词 obeyed; too severe, (省略了be动词)seldom executed.
祈使句
表示请求或者命令的句子是祈使句,谓语动词无时态与数的形式变化。就是v原形表达
祈使句的两种类型
第一、三人称
带有第一三人称主语的祈使句通常以let为引导词,需要体现出来
Let me tell you
Let life be beautiful like summer flowers and death like autumn leaves.
let us try again
let's 包括说话的对方也去
比如对老师说我们一起考雅思
let us 不包括听话人
比如对老师说我们考四级,老师不考
第二人称
第二人称主语通常不表示出来,加进去也可以,但是不变化单复数
be careful next time
• Close the window!
You强调你 be不变 quiet for a moment.
有肯定形式和否定形式,但是用dont否定时,只能用其缩略形式
以no开始的禁止性祈使句
no entry
no parking
No peeking.
疑问句
陈述语序: “主语+谓语+其他成分”
疑问语序:谓语+主语+其他成分
只有实义动词
do助动词(do/does/did)+主语+实义动词
只有实义动词的意思是:没有时态的情态助动词(will do),也没有助动词(have done)中的have助动词,没有情态助动词may do 也没有be动词做主系表,实义动词是原形
其他情况
谓语的一部分(be动词/情态动词/助动词)+主语+其他谓语部分。
be/情态动词/助动词放前面,其他部分不变
分类
一般疑问句
用yes和no回答的疑问句叫做一般疑问句
—Are your parents doctors? —Yes, they both are.
一般疑问句也可以用其他表示肯定或者否定的词回答
certainly, surely, of course, I think so, all right, certainly not, not at all, never, sorry, not yet, I'm afraid not
回答带有否定词的一般疑问句时候
yes+肯定句
no+否定句
-Haven't you been to England? -No, I haven’t.(没有用no回答) - Yes, I have.(去过用yes回答)
直接根据问题回答,去就是yes没去就是no
特殊疑问句
特殊疑问句的引导词有
就句子中某一部分进行提问的疑问句叫做特殊疑问句
what, who, whom, whose, where, when, why, how
what做主语宾语、who做主语、whom做宾语、whose做定语,where做地点状语,when做时间状语,how做方式状语,why做原因状语
语序
特殊疑问词做主语:特殊疑问词+陈述句语序
Whoever has taken away my English books? whoever做主语,后面语序是陈述句
Who主语 judges best副词(副词最高级省略the) of a man, his enemies or himself?
特殊疑问词做其他成分:特殊疑问词+部分倒装语序
部分倒装:只有实义动词
What do you want? 原形应该是you want to what。所以提炼出do
What do you want? you want what做宾语
部分倒装:还有其他情况
Where can I lay all these packs of books? where做地点状语,不做主语,所以部分倒装
How should we做主语 deal with做谓语 the increasing pollution?how做方式状语
Where can I lay all these packs of books?where做状语
就划线地方进行提问
You invited Jack.
Whom did you invite ?
Jack will be invited.
Who will be invited?
That happened last week .
When did that happen?
You are home at 7
When are you home?
You are from China.
where r u from?
You come from China.
where do u come from?
You came from Beijing.
Where did you come from?
选择疑问句
选择疑问句是说话者对问题提出两个或两个以上的答案,供对方选择其一,由or连接
两个并列成分:宾语,状语,表语,谓语或者两个句子
Are you German or French?
Shall I do it or两个句子并列 will you do it yourself?
Which do you prefer, cold drinks or hot?
Would you like tea or coffee?
which would you like to drink ,tea or coffee?
反诘疑问句
以否定的形式出现的疑问句,反问,责怪或者证实一件事实
一般情况下要用助动词的缩略形式
Why don't you let him speak the secret out?
• Can’t you tell me what has happened?
反意疑问句
反意疑问句是附加在陈述句后的简单句,征询对它前面陈述句所说的事实的肯定或者否定的意见
否定,+肯定?
• Sophia is not good at playing the piano, is she
是就是yes,不是就是no
肯定,+否定?
• You like sports, don't you?
肯定的回答前要用yes,否定的回答前要用no,是针对事实本身回答,不针对任何一个肯定或者否定的回答
You didn't attend the discussion, did you?你没有参加讨论会吧,是吗?
no,i didn't 没有,w没有参加
yes,i did. 是的,我参加了
例句:Sophia is not good at playing the piano, is she?
含有特殊主语的反意疑问句
表“人”的不定代词作主语
主语是不定代词:no one, nobody, everyone, someone, everybody, somebody, none等
• No one phoned me while I was out, did they/he? • Everyone is having a good time, aren't they?
主语当强调全部的时候可以用they,当强调个体时也可以用he
• Someone is expecting you, isn't he?
表“物”的不定代词作主语
陈述句的主语是everything, anything, something, nothing时,附加的问句主语用it
Everything goes well with you, doesn't it?
one指“人”时作主语
不定代词one作主语:附加问句的主语在正式的场合用 one , 在非正式场合用 you。
• One can't be too careful, can one (you)?再怎么小心都不过分 • One should do one's duty, shouldn't one (you)?
指示代词作主语
指示代词作主语,当陈述句的主语是指示代词时,其后的附加问句的主语要用相应的人称代词。
即this或that后用it
these或those后用they
• That was a hundred years ago, wasn't it?时态不变 • Those books are yours, aren't they?
there be 结构
there be引导陈述句时候,其后的附加问句仍然用引导词there
There will be an art exhibition tomorrow, won't there?
含有否定【副词】或者否定【代词】
陈述部分的主句带有no,never,nothing,nowhere,rarely,hardly,seldom,few,little等否定或者半否定词时候,附加问句一般用肯定式。
• You have never read Gorky's works, have you?
• You dislike playing the piano, don't you? (dislike是实义动词)这个是动词的否定,不会有到影响
A hibernating animal 【needs不是助动词,因为不可能只有一个助动词不加实义动词】 hardly any food all through the winter, _____c___ ? A. need it B. needn’t it C. does it D. doesn’t it
祈使句的反意疑问句
当陈述部分是祈使句的时候,反意疑问句的助动词不用do
陈述部分是肯定的祈使句。祈使句后面的附加问句一般用will you或won't you。(这两个不管否定肯定都可以互换)
• Leave all the things as they are, won't you?祈使句肯定否定都可以
• Give me a hand, will you?
Do help yourself to some fruit, _____d____ you? A. can’t B. don’t C. wouldn’t D. won’t
若陈述句部分是否定的祈使句,问句除了用will you外,也可以用can you。此时附加部分必须是肯定式。
Don't make much noise, will/can you?
When you have finished with that book, don’t forget to put it back on my desk, will you?
When you have finished with that book状语从句, don’t forget to put it back on my desk, ____c____ ? A. do you B. don’t you C. will/can you D. won’t you
肯:will/won‘t 否:will/can
let us和let‘s(let me)区别
以let‘s开头的祈使句(包括听话的人),后面的问句部分要用shall we;
• Let‘s try another way, shall we?
而以let us或以let me开头的祈使句,其后的问句部分应用will you。翻译成“你回容许吗?”
• Let us have a go, will you?
感叹句
定义:感叹句是用来表示喜怒哀乐情感的句子
两种形式
how作状语,修饰形容词,副词或者句子
how引导的感叹句结构
how+形容词/副词+(主语+谓语)
how+(主语+谓语)=句子
• How short life is主谓结构!
• How much I have still to do, to think and to say!
• How I wish to join the football club!
• 可数名词复数和不可数名词前不可用“how+形容词”
What great changes we have had these years! (√)
How great changes(必须带不定冠词单数名词) we have had these years! (×)
• What good news it is! (√)
• How good news(名词单数也不可以) it is! (×)
What a wonderful plan这个是固定的 you’ve made! (√)
• How wonderful a plan只能是带不定冠词的单数名词 you’ve made! (对)
可以用
“what+形容词+可数名词复数或不可数名词”。
how+形容词可以置于带不定冠词的单数名词之前,是顺序变了 how cute a boy! = what a cute boy!
• How wonderful a plan you’ve made! (√)
what作定语,修饰名词(名词前可以有形容词或者冠词)
what引导感叹句的结构
what+【(a/an)+形容词+可数名词的单数 】名词词组+(主语+谓语)!
what+形容词+可数名词复数+其他!
what+形容词+不可数名词+其他!
• What interesting books you’ve bought us!
• What a great pity名词词组 you missed the lecture again! pity抽象名词