导图社区 BISM 7406 Information Retrieval and Mana2
- 22
- 0
- 0
- 举报
BISM 7406 Information Retrieval and Mana2
midterm 考试内容整理,前四章节主要知识点框架,必备复习资料分享,方便大家备考时翻阅查看,提高复习效率,希望对大家备考有所帮助。
编辑于2021-08-30 18:35:48- 考试内容
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
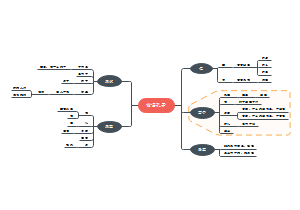
Information Retrieval and Management
Overview and Architecture
Traditional file-based systems
The definition of File-Based Approach
Limitations of File-Based Approach
Separation and isolation of data
Duplication of data (data
redundancy)
Data dependence
Incompatible file formats
Fixed queries/proliferation of application programs
Database Approach
The definition of Database Approach
Purpose of a Database System
Advantages of the Database Approach
Control of data redundancy
Data consistency
More information from the same amount of data
Sharing of data
Improved data integrity
Improved security
Enforcement of standards
Economy of scale
Balance conflicting requirements
mproved data accessibility and responsiveness
Increased productivity
Improved maintenance through data
independence
Increased concurrency
Improved backup and recovery services
Disadvantages of the Database Approach
Complexity
Size
Cost of DBMS
Additional hardware costs
Costs of conversion
Performance
Impact of failures
Database Management Systems (DBMS)
The definition of Database Management Systems (DBMS)
Components of the DBMS environment
Hardware
Software
Data
Procedures
People
DBMS functions
Data Storage, Retrieval, andUpdate
Data definition language (DDL)
Data manipulation language (DML)
A user-accessible catalogue
Data Dictionary or System Catalogue
Transaction support
Create
Read
Update
Delete
Concurrency control services.
Backup and recovery services
Authorization Services
Support for Data Communication
Integrity Services
Services to Promote Data Independence
Utility Services.
Database Environment
The definition of Database Environment
Three-level Database Architecture
External Level(logical)
Conceptual Level(logical)
Internal Level(physical)
Three Types of Database Schema
External schema
Conceptual schema
Internal schema
Data Models
The definition of Data Models
Various Model Types
Object-Based Data Models
Entity-Relationship
Semantic
Functional
Object-Oriented
Record-Based Data Models
Relational Data Model
Network Data Model
Hierarchical Data Model
Physical Data Models
Entity Relationship Modelling
Database System Development Lifecycle
Information System (IS)
The definition of the Information System
Components of an Information System
Database
Database Software
Application Software
Computer Hardware including storage media
People using
Developing the system
The relationship between the IS and Database System
Database is a fundamental component of IS
Database System Development Lifecycle Stages
database planning
system definition
requirements collection and analysis
database design
DBMS selection (optional)
application design
prototyping (optional)
implementation
data conversion and loading
testing
operational maintenance
Mission Objective
identify the particular tasks that the database must support
Mission Statement
defines the major aims of the database system
database design
The definition of Datebase Design
Date Modelling
Importance of Data Models
Communication tool
Give an overall view of the database
Organise data for various users
Abstraction for the creation of a good database
Purposes of data modeling
assist in the understanding of the meaning (semantics) of the data and to facilitate communication about the information requirements
Various data modelling techniques/model types
Entity-Relationship model
Hierarchical model
Relational model
Object-oriented model
Criteria for data models

Three phases of database design
Conceptual database design
Logical database design
Physical database design
fact-finding
The definition of the Fact-Finding
Fact-finding Techniques
Examining documentation

Interviewing

Observing the organization in operation

Research

Questionnaires

Brainstorming
DB System Development Lifecycle & DB Analysis
Relational Modelling
Definition
Objectives of the Relational Model
o To allow a high degree of data independence. o To provide substantial grounds for dealing with the problems of data semantics, consistency, and redundancy. o To enable the use of set-oriented data manipulation languages.
Terminology
Degree
Domain
Tuple
Primary Key
Alternate Key
Foreign Key
Attribute
Cardinality
Composite Key
Relation
Characteristics of a Relational Table

Relational Database Keys

Mathematical Relations
Definition
In order to better understand relations, some mathematical concepts are briefly explored here.
Relational Algebra
-Relational algebra is a theoretical language -It is the theoretical basis of query languages such as SQL -It contains operators that work on one or more relations. -These operators give us the means to construct new relations from given ones.
Cartesian Product
Integrity Constraints
Aims
Protect the database from becoming: • Incomplete • Inaccurate •Inconsistent
Integrity Constraints Content
Required data
Nulls
How to Ensure Referential Integrity
Attribute domain constraints
Not null
Data type restrictions
Limit or range checks
Completeness checks
Format or template checks
Check digit
Set membership
Master file reference
Record checks
Multiplicity
Entity integrity

Referential integrity

General constraints
➢ Updates to entities may be controlled by general constraints. ➢ General constraints reflect “real world” transactions represented by updates. E.g. DreamHome has a rule that prevents a staff member from managing >100 properties
Views

Entity Relational Modelling
Entity-Relationship Modelling
The definition of Entity-Relationship Modelling
Main components of ERD
Entities
Strong Entity
Weak Entity
Relationships
Binary relationship
Ternary relationship
Quaternary relationship
Recursive relationship
Strong Relationships
Weak Relationships
Attributes
Attribute domain
Simple attribute
Composite attribute
Single-valued attribute
Multi-valued attribute
Derived Attributes
Constraints
Definition
Multiplicity consists of two types of restrictions on relationships
Multiplicity
Cardinality Constraints
Participation Constraints
ERD Notation/ Multiplicity Constraints – different notations
 
Other business rules
 
Cardinality
Cardinality 1, A author can have many books 1 to many ( 1, M) But A book has one author 1 to 1 (1,1) 2, A book has one publisher (1,1) But a publisher can publish many books 1 to many (1, M) 3, A warehouse can have many books ( 1 to M ) A book can only store in a warehouse ( 1 to 1)
Participation
Participation: All books must have an author. (mandatory) An Author must have a book (mandatory) All books have a publisher (mandatory) A publisher can publish many books. (mandatory) A warehouse can have many books . ( mandatory) Books can store in a warehouse ( mandatory)
Key
Superkey
Candidate Key
Secondary key
Alternate key
Primary key
Foreign key
Composite key
Enhanced Entity-Relationship Modelling
The reasons of Enhanced Entity-Relationship Modelling
Specialisation
Definition
Superclasses
Subclasses
Process
Generalization
Definition
Process
Attribute inheritance
ACID
Atomicity
Consistency
Isolation
Durability
Date Independence
data independence
logical data independence
physical data independence
important reasons for introducing the concepts of superclasses and subclasses into an ER model
First, it avoids describing similar concepts more than once, thereby saving time for the designer and making the ER diagram more readable. Second, it adds more semantic information to the design in a form that is familiar to many people. For example, the assertions that “Manager IS-A member of staff” and “flat IS-A type of property,” communicates significant semantic content in a concise form
Constraints on Specialization/Generalization
Two constraints may apply to specialization/generalization: ➢ participation constraints ➢ disjoint constraints. 1. Participation constraint ➢ Shows whether every member in superclass must also participate as a member of a subclass. ➢ May be mandatory or optional. 2. Disjoint constraint ➢ Indicates whether member of a superclass can be a member of one, or more than one, subclass. ➢ May be disjoint (can be member of only one subclass) or nondisjoint (entity may be member of more than one subclass).