导图社区 英语课程教学
- 149
- 6
- 2
- 举报
英语课程教学
这是一篇关于英语课程教学的思维导图
编辑于2022-03-21 14:38:13- 相似推荐
- 大纲
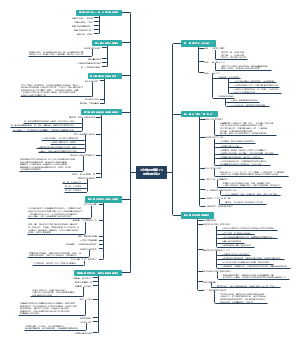
English Language Teaching
U1.Language and Language Learning
1.1 How do we learn language?
1.2 Views on language
1.3 Views on language learning and learning in general
1.4 What makes a good language teacher?
1.5 How can one become a good language teacher?
1.6 An overview of the book
U2.Communicative Principles and Task-based Language Teaching
2.1 Language use in real life vs. traditional pedagogy
2.2 What is communicative competence?
2.3 Implications for teaching and learning
2.4 Principles of Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)
2.5 CLT and the teaching of language skills
2.6 Main features of communicative activities
2.7 Task-based Language Teaching (TBLT)
2.8 PPP and Task-based Language Teaching
2.9 How to design tasks?
2.10 Appropriateness of CLT and TBLT in the Chinese context
2.11 Conclusion
U3.The National English Curriculum
3.1 A brief history of foreign language teaching in China
3.2 Designing principles for the National English Curriculum
3.3 Goals and objectives of English language teaching
3.4 Design of the National English Curriculum
3.5 Performance standards for different levels of competence
3.6 Challenges facing English language teachers
3.7 Conclusion
U4.Lesson Planning
4.1 Why is lesson planning important?
4.2 Principles for good lesson planning
4.3 Macro planning vs. micro planning
4.4 Components of a lesson plan
4.5 Sample lesson plans
4.6 Conclusion
U5.Classroom Management
5.1 The role of the teacher
5.2 Classroom instructions
5.3 Student grouping
5.4 Discipline in the language classroom
5.5 Questioning in the classroom
5.6 Dealing with errors
5.7 Conclusion
U6.Teaching Pronunciation
6.1 The role of pronunciation
6.2 The goal of teaching pronunciation
6.3 Aspects of pronunciation
6.4 Practising sounds
6.5 Practising stress and intonation
6.6 Conclusion
U7.Teaching Grammar
7.1 The role of grammar in language learning
7.2 Grammar presentation
7.3 Grammar practice
7.4 Conclusion
U8.Teaching Vocabulary
8.1 Understanding vocabulary and vocabulary learning
8.2 What does knowing a word involve?
8.3 Ways of presenting vocabulary
8.4 Ways of consolidating vocabulary
8.5 Developing vocabulary learning strategies
8.6 Conclusion
U9. Teaching Listening
9.1 Why does listening seem so difficult?
9.2 What do we listen to in everyday life?
9.3 Characteristics of the listening process
9.4 Principles and models for teaching listening
9.5 Pre-listening activities
9.6 While-listening activities
9.7 Post-listening activities
9.8 Conclusion
U18.Evaluating and Adapting Textbooks
18.1 What are textbooks for?
18.2 Why and what?
18.3 Evaluating textbooks
18.4 Selecting textbooks
18.5 Adapting textbooks
18.6 Conclusion
U17.Using and Creating Resources
17.1 What resources are available for teaching?
17.2 Exploring hidden resources
17.3 Conclusion
U16.Learner Differences and Learner Training
16.1 Understanding learner differences
16.2 Learner training in language teaching
16.3 Conclusion
U15.Assessment in Language Teaching
15.1 Understanding assessment
15.2 Assessment purposes
15.3 Methods for assessment
15.4 Criteria for assessment
15.5 Assessment principles
15.6 Tests in assessment
15.7 Conclusion
U14.Moral Learning
14.1 Moral learning and English
14.2 Activities for moral learning
14.3 The roles of the teacher
The roles of the teacher
14.4 The roles of the school
14.5 Conclusion
U13.Integrated Skills
13.1 Why should we integrate the four skills?
13.2 How can we integrate the four skills?
13.3 What are the implications for teaching?
13.4 What are the limitations of integrating the four skills?
13.5 Conclusion
U12.Teaching Writing
12.1 What, why and how do we write?
12.2 A communicative approach to writing
12.3 Problems in writing tasks
12.4 A process approach to writing
12.5 Motivating students to write
12.6 Designing writing tasks
12.7 Using the Internet to promote process writing
U11.Teaching Reading
11.1 Reflecting on your own reading experiences
11.2 How do we read?
11.3 What do we read?
11.4 Strategies involved in reading comprehension
11.5 The role of vocabulary in reading
11.6 Principles and models for teaching reading
11.7 Pre-reading activities
11.8 While-reading activities
11.9 Post-reading activities
11.10 Conclusion
U10.Teaching Speaking
10.1 Differences between spoken and written language
10.2 Principles for teaching speaking
10.3 Designing speaking tasks
10.4 Types of speaking tasks
10.5 Organising speaking tasks
10.6 Conclusion