导图社区 语言学导论第四章From Word to Text
- 490
- 11
- 3
- 举报
语言学导论第四章From Word to Text
From Word to Text:The properties of subject in English: Word order词序;Pro forms代词形式;Agreement with verb与动词一致;Content questions特殊疑问句; Tag questions反义疑问句.
编辑于2022-04-26 20:49:20- 中西翻简史 第十四章 中西翻译思想及理论
这是一篇关于中西翻简史 第十四章 中西翻译思想及理论的思维导图,主要内容有从西塞罗到泰特勒、从支谦到钱钟书、当代西方翻译思想的最新进展。
- 毛概第六章“三个代表”重要思想
毛泽东思想和中国特色社会主义理论体系概论第六章三个代表重要思想。该思想的形成:1.是在对冷战结束后国际局势科学判断的基础上形成的;2.是在科学判断党的历史方位和总结历史经验的基础上提出来的。
- 语言学导论第四章From Word to Text
From Word to Text:The properties of subject in English: Word order词序;Pro forms代词形式;Agreement with verb与动词一致;Content questions特殊疑问句; Tag questions反义疑问句.
语言学导论第四章From Word to Text
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- 中西翻简史 第十四章 中西翻译思想及理论
这是一篇关于中西翻简史 第十四章 中西翻译思想及理论的思维导图,主要内容有从西塞罗到泰特勒、从支谦到钱钟书、当代西方翻译思想的最新进展。
- 毛概第六章“三个代表”重要思想
毛泽东思想和中国特色社会主义理论体系概论第六章三个代表重要思想。该思想的形成:1.是在对冷战结束后国际局势科学判断的基础上形成的;2.是在科学判断党的历史方位和总结历史经验的基础上提出来的。
- 语言学导论第四章From Word to Text
From Word to Text:The properties of subject in English: Word order词序;Pro forms代词形式;Agreement with verb与动词一致;Content questions特殊疑问句; Tag questions反义疑问句.
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
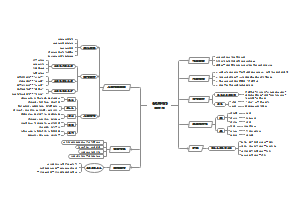
From Word to Text
1.Syntactic Relation
1.1 Positional relation位置关系, or word order, refers to the sequential arrangement of words in a language.
1.2 Relation of substitutability替代关系refers to classes or sets of words substitutable for each other grammatically in sentences with the same structure.
1.3 Relation of Co-Occurrence 同现关系 It means that words of different sets of classes may permit, or require, the occurrence of a word of another set of class to form a sentence or a particular part of a sentence.
2.Grammatical Constituents and Its Construction
2.1 Grammatical Construction
Grammatical construction or construct can mean any syntactic construct which is assigned one or more conventional functions in a language, together with whatever is linguistically conventionalized about its contribution to the meaning or use the construct contains.
On the level of syntax, we distinguish for any construction in a language its external and internal properties外部特征和内部特征. • External:clausal type、phrasal type • Internal:make up
2.2 Immediate Constituents
Constituent is a term used in structural sentence analysis for every linguistic unit, which is a part of a larger linguistic unit. Constituent can be a word or a group of words.
Immediate constituent analysis, IC analysis for short, refers to the analysis of a sentence in terms of its immediate constituents –word groups (phrases), which are in turn analyzed into the immediate constituents of their own, and the process goes on until the ultimate constituents are reached (word). The IC analysis of a sentence may be carried out with brackets or shown with a tree diagram.((The) (schoolmaster)) ((drove) ((the) (car)))
2.3 Endocentric and Exocentric Constructions
Endocentric Construction向心结构is one whose distribution is functionally equivalent to that of one or more of its constituents, i.e. a word or a group of words, which serves as a definable centre or head. Typical endocentric constructions are noun phrases(two old bridges), verb phrases(will leave) and adjective phrases(very late).
Exocentric Constructions离心结构refers to a group of syntactically related words where none of the words is functionally equivalent to the group as a whole, that is, there is no definable “centre” or “head” inside the group. It usually includes basic sentence(Alice smiles), prepositional phrase, predicate(verb+object) and connective(be+complement) construction.
2.4 Coordination and Subordination
Coordination并列关系 is formed by grouping together two or more categories of the same type with the help of a conjunction such as and, but, and or. And these two or more words or phrases or clauses have equivalent syntactic status, each of the constituents can stand for the original construction functionally
Subordination从属关系 refers to the process or result of linking linguistic units so that they have different syntactic status, one being dependent upon the other, and usually a constituent of the other.Thus the subordinate constituents are words which modify the Head, so they can be called modifiers.
3.Synactic Function
3.1 Subject
The properties of subject in English: Word order词序;Pro forms代词形式 ;Agreement with verb与动词一致;Content questions特殊疑问句; Tag questions反义疑问句.
3.2 Predicate
Predicate refers to a major constituent of sentence structure in a binary analysis in which all obligatory constituents other than the subject were considered together.The verb is called predicator.
3.3 Object
In English, object is recognized by tracing its relation to word order (after the verb and preposition)and by inflections (of pronouns).Modern linguists (e.g. Chomsky, Halliday) suggest that object refers to such an item that it can become subject in a passive transformation.
3.4 The Relation Between Classes and Functions
Classes and functions determine each other, but not in any one to one relation. A class item can perform several functions. For instance, a noun or a nominal phrase can function as the subject, object, modifier, adverbial and complement of a sentence.He changed trains at BJ. (complement) Similarly, a function can be fulfilled by several classes.For instance, the subject of a sentence can be realized by a noun, pronoun, numeral, infinitive, etc.
4.Category
4.1 Number
Number is a grammatical category for the analysis of word classes displaying such contrasts as singular, dual, plural, etc. In English, number is mainly observed in nouns, and there are only two forms: singular and plural. Number is also reflected in the inflections of pronouns and verbs, such as He laughs: They laugh.
4.2 Gender
English gender contrast can only be observed in pronouns and a small number of nouns, and they are mainly of the natural gender type.
4.3 Case
The case category is used in the analysis of word classes to identify the syntactic relationship between words in a sentence. In English, case is a special form of the noun which frequently corresponds to a combination of preposition and noun, and it is realized in 3 channels: Inflection; following a preposition;word order.
4.4 Agreement
Agreement (or Concord) may be defined as the requirement that the forms of two or more words in a syntactic relationship should agree with each other in terms of some categories.
5.Phrase,Clause and Sentence
.5.1 Phrase
Phrase is a single element of structure containing more than one word, and lacking the subject predicate structure typical of clauses.
5.2 Clause
A constituent with its own subject and predicate, if it is included in a larger sentence, is a clause. It can be classified into finite and non-finite clauses.
5.3 Sentence
Sentence is the minimum part of language that expresses a complete thought.
6.Recursiveness
6.1 Conjoining
It refers to the process where one clause is coordinated or conjoined with another. The sentences made up in this way can be understood as instances of coordination. The conjunctions used in this case are and, but, or.
It refers to the means by which one clause is included in the sentence (main clause) in syntactic subordination.The three basic types of subordinate clause are complement, adjunct (or adverbial) and relative clauses.
6.2 Embedding
7.Beyond the Sentence
7.1 Sentential Connection
Hypotactic主从关系: (subordinate clauses主从句)
Paratactic并联关系: (coordinate clauses并列句)
7.2 Cohesion
It is a concept to do with discourse or text rather than with syntax, it refers to relations of meaning that exist within the text, and defines it as a text.
7.3 Coherence
The connectedness of a text depends not only on the cohesion of a text, but also on language users establishing coherence by actively relating the different information units in the text.