导图社区 IGCSE physics Unit6
- 88
- 0
- 0
- 举报
IGCSE physics Unit6
IGCSE physics Unit6内容,包括magnets、magnetising、current and magnetism、 induction、transformers、the motor effect。
编辑于2023-01-27 20:49:10 湖北省- 课本
- 相似推荐
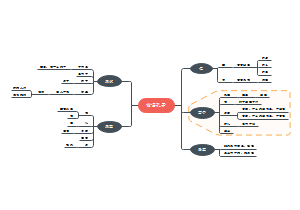
- 大纲
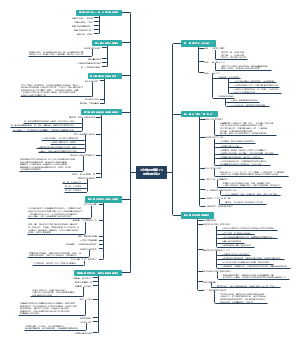
Magnetism and electromagnetism
magnets
poles
north
south
magnetic fields
closer- stronger,further- weaker
lines are not real,never cross
natural point-the point that two magnetic fields cancel out.
uniform field-the area the field lines are equally spaced,all point in the same direction
there is a magnetic south pole near the geographic North Pole
like poles repel,unlike poles attract
magnetising
magnetically hard material becomes a permanent magnet when it's magnetized
magnetically soft material will make an induced or temporary magnet
domain-insides of magnetic materials are split up small region
Magnetically soft materials are induced magnets. Permanent magnets are magnetically hard materials
An induced magnet is only magnetic. as long as it is placed in a magnetic field.
current and magnetism
When the current is small, the field is weak. But when a large current is used the iron filings show a circular magnetic field pattern.
The magnetic field gets weaker further away from the wire.
The direction of the magnetic field can be found using a compass. If the current direction is reversed, the direction of the magnetic field is reversed.
the right-hand grip rule
producing large magnetic fields
using a larger current
using more turns of wire
putting some iron into the middle of the solenoid
superconducting magnets
electromagnetic induction
• Reversing the direction of motion reverses the direction of the voltage. If moving the wire up makes the meter move to the right, moving the wire down will make the meter move to the left.
•Reversing the direction of the magnetic field reverses the direction of the voltage.
• Moving the wire more quickly induces a greater voltage. When the wire is stationary no voltage is induced.
• Using stronger or bigger magnets induces a greater voltage for the same speed of movement.
transformers
A transformer is made by putting two coils of wire onto a soft iron core
step-down transformers
set-up transformers
Vs/Vp=Ns/Np
Vp=primary voltage
Vs=secondary voltage
Np=number of turns on the primary coil
Ns=number of turns on the secondary coil
Vp✖️Ip=Vs✖️Is
the motor effect
• the strength of the magnetic field between the poles • the current • the length of the foil between the poles.
the left-hand rule
Spread out the first two fingers and the thumb of your left hand so that they are at right angles to each other. Let your first finger point along the direction of the magnet's field, and your second finger point in the direction of the current. Your thumb then points in the direction in which the wire moves.
a large number of turns is used on the coil
strong magnets are used
weak springs are used.
The size of the force depends on
•the strength of the magnetic field
• the speed of the particles
• the charge on the particle.
if the electrons are travelling to the right, the direction of the current is to the left.
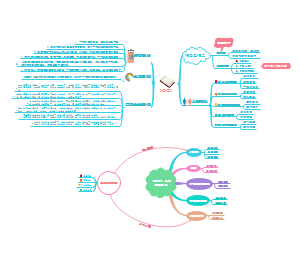
generators
a.c.
By turning the axle you can make a coil of wire move through a magnetic field. This causes a voltage to be induced between the ends of the coil.
1.rotating the coil faster using stronger magnets 2.using more turns of wire 3.wrapping the wire round a soft iron core.
The important steps in the generation of electricity in a coal-fired power station are these:
1.Coal is burnt to boil water. 2.High-pressure steam from the boiler is used to turn a turbine. 3.The drive shaft from the turbine is connected to the generator magnets, which rotate near to the stationary coils. The output from the coils has a voltage of about 25 000 V. 4.The turbine's drive shaft also powers the exciter. The exciter is a direct current (d.c.) generator that produces current for the rotating magnets, which are in fact electromagnets.
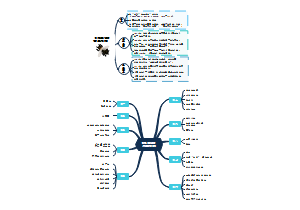
electric motors
A coil carrying a current rotates between the poles of a magnet. The coil is kept rotating continuously by the use of a split-ring commutator, which rotates with the coil between the carbon brush contacts.
(a) A current flows into the coil through the commutator so that there is an upwards push on side A, a downwards push on B.
(b)When the coil reaches the vertical position there is no current through the coil. It continues to rotate past the vertical due to its own momentum.
(c) The coil rotates in a clockwise direction.
(d) Now side A is on the right-hand side. The direction of the current has been reversed.
(e) Side A is pushed down and side B is pushed upwards. The coil continues to rotate in a clockwise direction