导图社区 IG物理
- 217
- 3
- 1
- 举报
IG物理
关于IG物理的思维导图,汇总了turning effects、force and motion、electrical quantities、magnetism知识。
编辑于2023-07-18 12:22:27 江苏省- IG物理
关于IG物理的思维导图,汇总了turning effects、force and motion、electrical quantities、magnetism知识。
- IGCSE化学 Chemistry chapter3, 4, 5
IGCSE化学 Chemistry chapter3, 4, 5的思维导图,具体是quantitative chemistry、electrochemistry、bonding and structure.
- firms
剑桥IGCSE教材经济:chapter3.5(Firms):How to classify firms?How to measure the size of the company……
IG物理
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- IG物理
关于IG物理的思维导图,汇总了turning effects、force and motion、electrical quantities、magnetism知识。
- IGCSE化学 Chemistry chapter3, 4, 5
IGCSE化学 Chemistry chapter3, 4, 5的思维导图,具体是quantitative chemistry、electrochemistry、bonding and structure.
- firms
剑桥IGCSE教材经济:chapter3.5(Firms):How to classify firms?How to measure the size of the company……
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
物理暑假作业
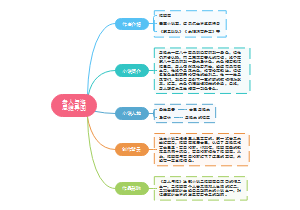
turning effects
the moment of a forcce
a moment(力矩) is a turning effect caused by a force
the bigger the force, the larger the moment
the moment of a force is bigger if it acts further from the pivot
the moment of a force is greatest if it acts at 90° to the object it acts on
turning effect: when a force causes an object to rotate or would make the object rotate if there were no resistive forces
pivot(轴心): the fixed point about whitch a lever turns, also known as the fulcrum
equilibrium: when no net force and no net moment act on a body
the forces on it must be balanced
the turning effects of the forces on it must also be balanced
calculating moments
moment(Nm)=force(N)*perpendicular distance from pivot(m) moment=F*⊥d
stability and centre of gravity
stable: an object that is unlikely to topple over, often because it has a low center of gravity and a wide base
unstable: an object that is likely to topple over, often because it has a high centre of gravity and a narrow base
centre of gravity: all the mass of an object could be located here and object would behave the same
find the centre of gravity
for regular figures, the center of gravity is the geometric center of them
for irregular figures, Suspension method is most commonly used
step1: find a string, find a point on the object, hang with the rope, wait for the object to rest, connect a vertical line through the suspension point
step2: Find a little bit of suspension outside of that vertical line.
step3: The intersection of two vertical lines is the center of gravity of the irregular object.
force and motion
mass, weight and gravity
weight=mass*acceleration of free fall W=mg
gravitational field strength=weight/mass g=W/m
gravity: the force that exists bwtween any two objects with mass
acceleration of free fall: the acceleration of an object falling freely under gravity
acceleration due to gravity: the acceleration of an object falling freely under gravity
gravitational field strength: the gravitational force exerted per unit mass placed at that point
falling and turning
terminal velocity: the greatest speed reached by an object when moving through a fluid
a bigger force is needed if
the object's mass is bigger(and speed and radius stay the same)
the object's speed is bigger(and speed and radius stay the same)
the radius of the circle is smaller(and speed and mass stay the same)
force, mass and acceleration
force(N)=mass(Kg)*acceleration(m/s^2) F=ma
momentum(动量)
momentum is the basic quantity of motion
momentum(kg m/s)=mass(kg)*velocity(m/s) P=mv
the effect of a force F depends on
how big the force is
the time interval Δt it acts for
impulse(冲量): the change in an object's momentum , Δp, or the force acting on an object multiplied by the time for whitch the force acts
impulse=force*time for whitch the force acts I=FΔt=Δ(mv)
resultant force(合力): the single force that has same effect on a body as two or more forces
resultant force=change in momentum/unit of time F=Δp/Δt
more about scalrs and vectors
scalrs and vectors
scalrs have magnitude(size) only and no direction, but vectors have both direction and magnitude
rules for vector addtion
draw arrows end-to-end, so that the end of one is the start of the next
choose a scale that gives a large triangle
join the start of the first arrow to the end of the last arrow to find the resultant force
electrical quantities
current in electric circuits
current: the rate at whitch electric charge passes a point in a circuit
cell: a device that provides an electromotive force(emf电压/电势差)in a circuit by means of a chemical reaction
battery: two or more electrical cells connected together in series
direct current(dc)直流电: electric current that flows in the same direction all the time
alternating current(ac)交流电: electric current that changes direction
conductors(导体) and insulators(绝缘体)
conductor: a material that allows an electric current to flow through it
insulator: a materiall that not allows an electric current to flow through it
charge: carried around a circuit by the ccurrent, negative charge is carried by electrons
most metals, including copper, silver, goldand steel are goods conductors
polymers聚合物(eg: perspex塑料 and polythene聚乙烯)are goods insulators
measureing electric current
galvanometer(电流表): a meter for measuring tiny electric current
ammeter(电流表): a meter for measuring electric current
amphere(安培): the SI unit of electric current(A)
current and charge
current(A)=charge(C)/time(S) I=Q/t
voltage in electric circuits
voltage电压: the energy tranferred or work done per unit charge, it can be imagined as the push of a battery or power supply in a circuit
potential different电势差(pd): the work done by the a unit of charge passing through an electrical component, another name for the voltage between two points
electromotive force电动势(emf): the electrical work done by a source in moving a unit of charge around a circuit, the voltage across the terminals of a source
combining emfs: E=E1+E2+......
work done by the charge/charge W/Q
volts(V): the SI unit of voltage(pd or emf), 1V=1C/S
voltmeter: a meter for measuring the pd between two point
electrical resistance
resistance电阻: a measure of how difficult it is for an electric current to flow through a device or a component in a circuit, it is the pd across a component divided by the cuurent through it
resistance(Ω)=potential differnence(V)/current(A) R=V/I
Ohm(Ω): the SI unit of electrical resistance, 1Ω=1V/A
resistance and thickness
the longer a wire, the greater its resistance
the greater the diameter of a wire, the less its resistance
electrical energy, wore and power
electrical power
electrical power: power=current*pd(p=VI)
calculating energy
energy transferred=current*pd*time E=VIt
magnetism
permanent magnets
bar magnets: a rectangular-shaped permanent magnet with a north pole and south pole
when two magnets are brought close together: like poles repel, unlike poles attarct
magnetised磁化: when a magnetic material has been made magnetic
demagnetised消磁: when a magnetic material has not been made magnetic
induced magnetism诱导磁性: when a magnetic material is only magnetised when placed in a magnetic field
permanent magnet永磁体: magnetised magnetic material that produces its own magnetic field that does not get weaker with time
hard material硬磁材料: a material that, once magnetised, is difficult to demagnetise
soft material软磁材料: a material that, once magnetised, is easy to demagnetise
magnetic field
two things about the field
direction: the direction of a magnetic field line at any point is the direction of force on the north pole of a magnet at that point. We use a convention that says that field lines come out from north poles and go in to south poles
strength: lines that are close togther indicate a strong field