导图社区 ear infection
- 8
- 0
- 0
- 举报
ear infection
这是一张关于ear infection(耳部感染)英文的思维导图,从定义、分类、诱因、症状、并发症、基本表现、病理描述、预防和治疗等多个方面进行了详细阐述。
编辑于2025-10-09 11:31:01- 医学
- 英文版
- 耳部感染
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
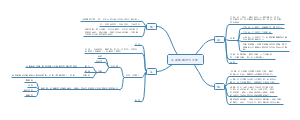
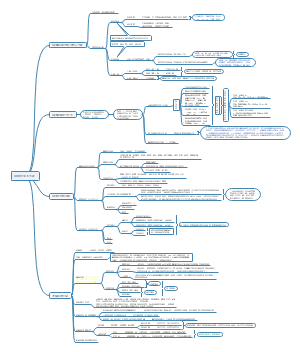
ear infection
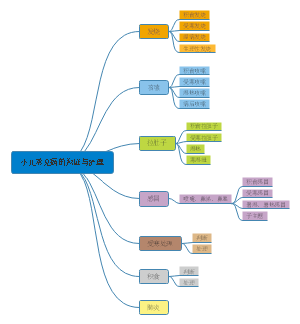
定义
Otitis media is a common condition, particularly in children, characterized by the buildup of fluid and inflammation in the air-filled space behind the eardrum (the middle ear). This usually occurs when the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the throat, becomes blocked or dysfunctional, leading to bacterial or viral growth. Symptoms may include ear pain, fever, and hearing loss.
分类
· Otitis Media (OM) - 中耳炎(总称) · Acute Otitis Media (AOM) - 急性中耳炎 · Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) - 分泌性中耳炎(伴积液) · Chronic Otitis Media - 慢性中耳炎 · Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) - 慢性化脓性中耳炎 · Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) - 咽鼓管功能障碍
症状
· Earache / Otalgia - 耳痛 · Ear Fullness / Pressure - 耳闷胀感 · Hearing Loss / Hearing Impairment - 听力下降/听力损失 · Conductive Hearing Loss - 传导性听力损失(由外耳或中耳问题引起) · Tinnitus - 耳鸣· Otorrhea - 耳漏(耳流液/流脓) · Purulent Discharge - 脓性分泌物 · Fever - 发烧 · Irritability (especially in children) - 烦躁(尤其在儿童中) · Pulling at the Ear - 拉扯耳朵
早期症状· Earache (耳痛)· Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear (耳内胀满感或压迫感)· Mild hearing loss or muffled hearing (轻度听力丧失或听力沉闷) 中期症状· Severe, sharp pain (严重、剧烈的疼痛)· Fever (发烧)· Persistent fluid buildup behind the eardrum (鼓膜后持续积液)· More noticeable hearing impairment (更明显的听力受损) 晚期/严重症状· Ruptured eardrum with pus or blood drainage from the ear (鼓膜穿孔,耳内有脓液或血液流出)· Significant hearing loss (显著的听力丧失)· High fever (高烧)· Dizziness or vertigo (头晕或眩晕)· Symptoms spreading beyond the ear (e.g., headache, neck stiffness) (症状扩散到耳外,如头痛、颈部僵硬) 婴幼儿出现症状:Infants or young children exhibit symptoms such as irritability, persistent crying, fever, refusal to feed, or ear tugging.表现为烦躁不安、持续哭闹、发烧、拒绝吃奶、抓挠耳朵等。
病理描述
· Fluid Accumulation / Effusion - 液体积聚 / 渗出液 · Bulging Tympanic Membrane - 鼓膜膨出 · Reddened / Inflamed Tympanic Membrane - 鼓膜充血/发红 · Retracted Tympanic Membrane - 鼓膜内陷 · Perforated Tympanic Membrane / Tympanic Membrane Perforation - 鼓膜穿孔
基本表现
· Otoscope - 耳镜(最重要的工具) · Pneumatic Otoscope - 气动耳镜(带充气功能,用于评估鼓膜活动度) · Tuning Fork - 音叉(用于初步区分传导性耳聋和神经性耳聋) · Weber Test - 韦伯试验(将音叉置于头顶) · Rinne Test - 林纳试验(比较气导和骨导听力)
并发症
Hearing-Related Complications
Eardrum Perforation
Mastoiditis
Intracranial Complications
诱因
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections (URIs): Viral or bacterial URIs (e.g., colds, flu, sinusitis) are the most common triggers. Pathogens spread from the nasal cavity and throat to the middle ear through the eustachian tube, causing infection and inflammation. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Structural or functional issues of the eustachian tube (a passage connecting the middle ear to the throat) block airflow and fluid drainage. This is more common in children, as their eustachian tubes are shorter, wider, and more horizontal. Allergic Reactions: Allergies (e.g., allergic rhinitis, hay fever) cause swelling of the nasal and eustachian tube mucous membranes, leading to blockage and increased risk of middle ear fluid buildup or infection. Adenoid Hypertrophy: Enlarged adenoids (lymphoid tissue at the back of the nasal cavity) in children can block the eustachian tube opening, trap bacteria, and repeatedly trigger otitis media. Environmental Factors: Exposure to secondhand smoke irritates the middle ear mucosa and weakens local immunity. Additionally, water entering the ear during swimming or diving (especially with a damaged eardrum) may introduce pathogens.
治疗
急性中耳炎的治疗 Treatment for Acute Otitis Media (AOM)1. 观察等待 对症治疗 Observation Symptomatic Management对于症状轻微、年龄较大的儿童(通常>2岁)或不确定是否为细菌感染时,医生可能会建议先不使用抗生素,而是进行观察和止痛治疗。 For older children(usually >2 years) with mild symptoms or when bacterial infection is uncertain, doctors may recommend observation without immediate antibiotics, focusing on pain relief.· 止痛药 Pain Relief: · 布洛芬: 如美林 Motrin (Ibuprofen) · 对乙酰氨基酚: 如泰诺 Tylenol (Acetaminophen) · 注意: 儿童和青少年应避免使用阿司匹林,以防发生瑞氏综合征。 · Note: Aspirin should be avoided in children and teenagers due to the risk of Reye's syndrome.· 局部滴耳剂 Topical Ear Drops: · 如含有麻醉成分的滴耳剂,可帮助缓解疼痛(仅当鼓膜未穿孔时使用)。 · Such as ear drops containing anesthetic to help relieve pain (only used when the eardrum is not perforated).2. 抗生素治疗 Antibiotic Therapy如果症状严重、持续超过48-72小时、或患者年龄小于2岁,通常需要抗生素治疗。 Antibiotics are usually required if symptoms are severe,persist for more than 48-72 hours, or if the patient is under 2 years of age.· 首选药物 First-line Antibiotics: · 阿莫西林 Amoxicillin · 阿莫西林-克拉维酸钾 Amoxicillin-Clavulanate· 青霉素过敏者的替代药物 Alternatives for Penicillin Allergy: · 头孢菌素类 Cephalosporins · 大环内酯类 Macrolides 二、渗出性中耳炎的治疗 Treatment for Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) 1. 观察观察 Observation许多渗出性中耳炎病例会在3个月内自行痊愈。医生通常会建议定期复查,监测积液和听力情况。 Many cases of OME resolve on their own within 3 months.Doctors often recommend periodic follow-up to monitor the fluid and hearing. 2. 手术治疗 Surgical Treatment如果积液持续超过3个月,并导致明显听力下降、语言发育迟缓或反复发作的急性中耳炎,则需考虑手术。 If fluid persists for more than 3 months and causes significant hearing loss,speech delay, or recurrent AOM, surgery may be considered.· 鼓膜切开术 Myringotomy: · 在鼓膜上做一个小切口,吸出中耳内的积液。 · A small incision is made in the eardrum to suction out the fluid from the middle ear.· 鼓膜通气管置入术 Tympanostomy Tube Insertion: · 这是最常用的手术方法。在鼓膜切开后,植入一个微小的通气管。 · This is the most common surgical procedure. A tiny tube is inserted into the eardrum after the myringotomy. · 作用 Benefits: · 使中耳通气,保持压力平衡。 · Ventilates the middle ear and equalizes pressure. · 引流积液。 · Drains fluid. · 提高听力。 · Improves hearing. · 降低急性中耳炎的发作频率。 · Reduces the frequency of acute otitis media episodes. · 通气管通常会留置6-12个月,之后大多会自行脱落。 · The tubes usually fall out on their own after 6-12 months. 3. 治疗相关病因 Treating Underlying Causes· 腺样体切除术 Adenoidectomy: · 如果肥大的腺样体堵塞了咽鼓管开口,可能会建议切除腺样体,尤其对于反复发作的中耳炎。 · If enlarged adenoids are blocking the Eustachian tube, their removal may be recommended, especially for recurrent otitis media.
预防
· The cornerstone of preventing ear infections is maintaining good eustachian tube function. (预防耳朵感染的基石是保持咽鼓管功能良好。) · It is recommended to stay up-to-date with vaccinations, particularly the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and the annual influenza vaccine. (建议及时接种疫苗,特别是肺炎球菌结合疫苗和年度流感疫苗。) · Vaccinations help prevent respiratory infections that can lead to an ear infection. (疫苗接种有助于预防可能引发耳朵感染的呼吸道感染。)关于卫生习惯: · Frequent handwashing is essential to reduce the spread of germs that cause colds and other illnesses. (经常洗手对于减少引起感冒和其他疾病的病菌传播至关重要。) · Teach children not to share eating utensils or cups to minimize exposure to viruses and bacteria. (教育孩子不要共用餐具或杯子,以尽量减少接触病毒和细菌。) · Breastfeeding for at least the first six months provides antibodies that help protect infants from infections, including ear infections. (至少进行前六个月的母乳喂养可以提供抗体,帮助保护婴儿免受感染,包括耳朵感染。) · When bottle-feeding, hold the infant in an upright position rather than letting them lie down. This prevents milk from flowing into the eustachian tube. (用奶瓶喂养时,让婴儿保持直立姿势,而不是让他们躺着。这可以防止乳汁流入咽鼓管。) · Avoid exposure to tobacco smoke, as it irritates the eustachian tube and impairs its function. (避免接触烟草烟雾,因为它会刺激咽鼓管并损害其功能。) · Reducing exposure to air pollutants and allergens can also be beneficial. (减少接触空气污染物和过敏原也可能有益。) · For children in group daycare settings, good hygiene practices are even more critical due to increased exposure to germs. (对于在集体托儿所的孩子,由于接触病菌的机会增加,良好的卫生习惯更为关键。) · Managing allergies effectively can help prevent eustachian tube dysfunction, which is a common cause of ear infections. (有效控制过敏有助于预防咽鼓管功能障碍,这是耳朵感染的一个常见原因)
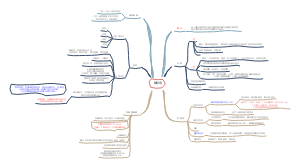
ear infection
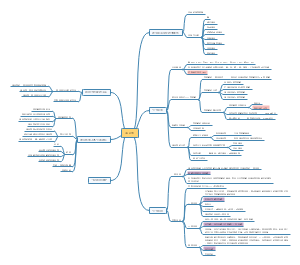
定义
Otitis media is a common condition, particularly in children, characterized by the buildup of fluid and inflammation in the air-filled space behind the eardrum (the middle ear). This usually occurs when the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the throat, becomes blocked or dysfunctional, leading to bacterial or viral growth. Symptoms may include ear pain, fever, and hearing loss.
分类
· Otitis Media (OM) - 中耳炎(总称) · Acute Otitis Media (AOM) - 急性中耳炎 · Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) - 分泌性中耳炎(伴积液) · Chronic Otitis Media - 慢性中耳炎 · Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) - 慢性化脓性中耳炎 · Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) - 咽鼓管功能障碍
症状
· Earache / Otalgia - 耳痛 · Ear Fullness / Pressure - 耳闷胀感 · Hearing Loss / Hearing Impairment - 听力下降/听力损失 · Conductive Hearing Loss - 传导性听力损失(由外耳或中耳问题引起) · Tinnitus - 耳鸣· Otorrhea - 耳漏(耳流液/流脓) · Purulent Discharge - 脓性分泌物 · Fever - 发烧 · Irritability (especially in children) - 烦躁(尤其在儿童中) · Pulling at the Ear - 拉扯耳朵
早期症状· Earache (耳痛)· Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear (耳内胀满感或压迫感)· Mild hearing loss or muffled hearing (轻度听力丧失或听力沉闷) 中期症状· Severe, sharp pain (严重、剧烈的疼痛)· Fever (发烧)· Persistent fluid buildup behind the eardrum (鼓膜后持续积液)· More noticeable hearing impairment (更明显的听力受损) 晚期/严重症状· Ruptured eardrum with pus or blood drainage from the ear (鼓膜穿孔,耳内有脓液或血液流出)· Significant hearing loss (显著的听力丧失)· High fever (高烧)· Dizziness or vertigo (头晕或眩晕)· Symptoms spreading beyond the ear (e.g., headache, neck stiffness) (症状扩散到耳外,如头痛、颈部僵硬) 婴幼儿出现症状:Infants or young children exhibit symptoms such as irritability, persistent crying, fever, refusal to feed, or ear tugging.表现为烦躁不安、持续哭闹、发烧、拒绝吃奶、抓挠耳朵等。
病理描述
· Fluid Accumulation / Effusion - 液体积聚 / 渗出液 · Bulging Tympanic Membrane - 鼓膜膨出 · Reddened / Inflamed Tympanic Membrane - 鼓膜充血/发红 · Retracted Tympanic Membrane - 鼓膜内陷 · Perforated Tympanic Membrane / Tympanic Membrane Perforation - 鼓膜穿孔
基本表现
· Otoscope - 耳镜(最重要的工具) · Pneumatic Otoscope - 气动耳镜(带充气功能,用于评估鼓膜活动度) · Tuning Fork - 音叉(用于初步区分传导性耳聋和神经性耳聋) · Weber Test - 韦伯试验(将音叉置于头顶) · Rinne Test - 林纳试验(比较气导和骨导听力)
并发症
Hearing-Related Complications
Eardrum Perforation
Mastoiditis
Intracranial Complications
诱因
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections (URIs): Viral or bacterial URIs (e.g., colds, flu, sinusitis) are the most common triggers. Pathogens spread from the nasal cavity and throat to the middle ear through the eustachian tube, causing infection and inflammation. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Structural or functional issues of the eustachian tube (a passage connecting the middle ear to the throat) block airflow and fluid drainage. This is more common in children, as their eustachian tubes are shorter, wider, and more horizontal. Allergic Reactions: Allergies (e.g., allergic rhinitis, hay fever) cause swelling of the nasal and eustachian tube mucous membranes, leading to blockage and increased risk of middle ear fluid buildup or infection. Adenoid Hypertrophy: Enlarged adenoids (lymphoid tissue at the back of the nasal cavity) in children can block the eustachian tube opening, trap bacteria, and repeatedly trigger otitis media. Environmental Factors: Exposure to secondhand smoke irritates the middle ear mucosa and weakens local immunity. Additionally, water entering the ear during swimming or diving (especially with a damaged eardrum) may introduce pathogens.
治疗
急性中耳炎的治疗 Treatment for Acute Otitis Media (AOM)1. 观察等待 对症治疗 Observation Symptomatic Management对于症状轻微、年龄较大的儿童(通常>2岁)或不确定是否为细菌感染时,医生可能会建议先不使用抗生素,而是进行观察和止痛治疗。 For older children(usually >2 years) with mild symptoms or when bacterial infection is uncertain, doctors may recommend observation without immediate antibiotics, focusing on pain relief.· 止痛药 Pain Relief: · 布洛芬: 如美林 Motrin (Ibuprofen) · 对乙酰氨基酚: 如泰诺 Tylenol (Acetaminophen) · 注意: 儿童和青少年应避免使用阿司匹林,以防发生瑞氏综合征。 · Note: Aspirin should be avoided in children and teenagers due to the risk of Reye's syndrome.· 局部滴耳剂 Topical Ear Drops: · 如含有麻醉成分的滴耳剂,可帮助缓解疼痛(仅当鼓膜未穿孔时使用)。 · Such as ear drops containing anesthetic to help relieve pain (only used when the eardrum is not perforated).2. 抗生素治疗 Antibiotic Therapy如果症状严重、持续超过48-72小时、或患者年龄小于2岁,通常需要抗生素治疗。 Antibiotics are usually required if symptoms are severe,persist for more than 48-72 hours, or if the patient is under 2 years of age.· 首选药物 First-line Antibiotics: · 阿莫西林 Amoxicillin · 阿莫西林-克拉维酸钾 Amoxicillin-Clavulanate· 青霉素过敏者的替代药物 Alternatives for Penicillin Allergy: · 头孢菌素类 Cephalosporins · 大环内酯类 Macrolides 二、渗出性中耳炎的治疗 Treatment for Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) 1. 观察观察 Observation许多渗出性中耳炎病例会在3个月内自行痊愈。医生通常会建议定期复查,监测积液和听力情况。 Many cases of OME resolve on their own within 3 months.Doctors often recommend periodic follow-up to monitor the fluid and hearing. 2. 手术治疗 Surgical Treatment如果积液持续超过3个月,并导致明显听力下降、语言发育迟缓或反复发作的急性中耳炎,则需考虑手术。 If fluid persists for more than 3 months and causes significant hearing loss,speech delay, or recurrent AOM, surgery may be considered.· 鼓膜切开术 Myringotomy: · 在鼓膜上做一个小切口,吸出中耳内的积液。 · A small incision is made in the eardrum to suction out the fluid from the middle ear.· 鼓膜通气管置入术 Tympanostomy Tube Insertion: · 这是最常用的手术方法。在鼓膜切开后,植入一个微小的通气管。 · This is the most common surgical procedure. A tiny tube is inserted into the eardrum after the myringotomy. · 作用 Benefits: · 使中耳通气,保持压力平衡。 · Ventilates the middle ear and equalizes pressure. · 引流积液。 · Drains fluid. · 提高听力。 · Improves hearing. · 降低急性中耳炎的发作频率。 · Reduces the frequency of acute otitis media episodes. · 通气管通常会留置6-12个月,之后大多会自行脱落。 · The tubes usually fall out on their own after 6-12 months. 3. 治疗相关病因 Treating Underlying Causes· 腺样体切除术 Adenoidectomy: · 如果肥大的腺样体堵塞了咽鼓管开口,可能会建议切除腺样体,尤其对于反复发作的中耳炎。 · If enlarged adenoids are blocking the Eustachian tube, their removal may be recommended, especially for recurrent otitis media.
预防
· The cornerstone of preventing ear infections is maintaining good eustachian tube function. (预防耳朵感染的基石是保持咽鼓管功能良好。) · It is recommended to stay up-to-date with vaccinations, particularly the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and the annual influenza vaccine. (建议及时接种疫苗,特别是肺炎球菌结合疫苗和年度流感疫苗。) · Vaccinations help prevent respiratory infections that can lead to an ear infection. (疫苗接种有助于预防可能引发耳朵感染的呼吸道感染。)关于卫生习惯: · Frequent handwashing is essential to reduce the spread of germs that cause colds and other illnesses. (经常洗手对于减少引起感冒和其他疾病的病菌传播至关重要。) · Teach children not to share eating utensils or cups to minimize exposure to viruses and bacteria. (教育孩子不要共用餐具或杯子,以尽量减少接触病毒和细菌。) · Breastfeeding for at least the first six months provides antibodies that help protect infants from infections, including ear infections. (至少进行前六个月的母乳喂养可以提供抗体,帮助保护婴儿免受感染,包括耳朵感染。) · When bottle-feeding, hold the infant in an upright position rather than letting them lie down. This prevents milk from flowing into the eustachian tube. (用奶瓶喂养时,让婴儿保持直立姿势,而不是让他们躺着。这可以防止乳汁流入咽鼓管。) · Avoid exposure to tobacco smoke, as it irritates the eustachian tube and impairs its function. (避免接触烟草烟雾,因为它会刺激咽鼓管并损害其功能。) · Reducing exposure to air pollutants and allergens can also be beneficial. (减少接触空气污染物和过敏原也可能有益。) · For children in group daycare settings, good hygiene practices are even more critical due to increased exposure to germs. (对于在集体托儿所的孩子,由于接触病菌的机会增加,良好的卫生习惯更为关键。) · Managing allergies effectively can help prevent eustachian tube dysfunction, which is a common cause of ear infections. (有效控制过敏有助于预防咽鼓管功能障碍,这是耳朵感染的一个常见原因)