导图社区 7 Derivatives
- 69
- 0
- 1
- 举报
7 Derivatives
CFA一级课程Derivatives,根据考纲编写,公式、内容全面,具体,是你备考2022年CFA一级有力工具
编辑于2022-06-15 11:56:32- 2024cpa会计科目第17章收入、费用和利润
2024cpa会计科目第17章,本章属于非常重要的章节,其内容知识点多、综合性强,可以各种题型进行考核。既可以单独进行考核客观题和主观题,也可以与前期差错更正、资产负债表日后事项等内容相结合在主观题中进行考核。2018年、2020年、2021年、2022年均在主观题中进行考核,近几年平均分值 11分左右。
- 2024cpa会计科目第十二章或有事项
2024cpa会计科目第十二章,本章内容可以各种题型进行考核。客观题主要考核或有资产和或有负债的相关概念、亏损合同的处理原则、预计负债最佳估计数的确定、与产品质量保证相关的预计负债的确认、与重组有关的直接支出的判断等;同时,本章内容(如:未决诉讼)可与资产负债表日后事项、差错更正等内容相结合、产品质量保证与收入相结合在主观题中进行考核。近几年考试平均分值为2分左右。
- 2024cpa会计科目第十一章借款费用
2024cpa会计科目第十一章,本章属于比较重要的章节,考试时多以单选题和多选题等客观题形式进行考核,也可以与应付债券(包括可转换公司债券)、外币业务等相关知识结合在主观题中进行考核。重点掌握借款费用的范围、资本化的条件及借款费用资本化金额的计量,近几年考试分值为3分左右。
7 Derivatives
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- 2024cpa会计科目第17章收入、费用和利润
2024cpa会计科目第17章,本章属于非常重要的章节,其内容知识点多、综合性强,可以各种题型进行考核。既可以单独进行考核客观题和主观题,也可以与前期差错更正、资产负债表日后事项等内容相结合在主观题中进行考核。2018年、2020年、2021年、2022年均在主观题中进行考核,近几年平均分值 11分左右。
- 2024cpa会计科目第十二章或有事项
2024cpa会计科目第十二章,本章内容可以各种题型进行考核。客观题主要考核或有资产和或有负债的相关概念、亏损合同的处理原则、预计负债最佳估计数的确定、与产品质量保证相关的预计负债的确认、与重组有关的直接支出的判断等;同时,本章内容(如:未决诉讼)可与资产负债表日后事项、差错更正等内容相结合、产品质量保证与收入相结合在主观题中进行考核。近几年考试平均分值为2分左右。
- 2024cpa会计科目第十一章借款费用
2024cpa会计科目第十一章,本章属于比较重要的章节,考试时多以单选题和多选题等客观题形式进行考核,也可以与应付债券(包括可转换公司债券)、外币业务等相关知识结合在主观题中进行考核。重点掌握借款费用的范围、资本化的条件及借款费用资本化金额的计量,近几年考试分值为3分左右。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
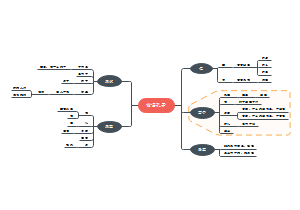
Derivatives
Derivative Markets andInstruments
Definition and introduction
Definition: A derivative is a financial instrument whose value is transformed from the performance of an underlying asset
特点: Traded in future,while spot market is traded now
Derivative act as insurance: the underlying is the source of risk; derivative allow transfer of risk
Four types of derivatives
类型
Forward
定义: one party agrees to buy and the counterparty to sell a physical or financial asset at a specific price on a specific date in the future
Terms
The physical or financial asset is the underlying
A specific price is forward price
A specific date is maturity date
The long and short position
Long position: the party will buy the underlying at time T for a price of K
Short position: the party will deliver the underlying at time T for a price of K
特点
OTC traded
Customized contracts
Low liquidity
Settlement at maturity
No margin deposit required
Deliver asset or settle by cash
Default risk is present
Largely unregulated
Trade with counterparty
Payoff
K =Delivery price ST =Price of the underlying at maturity
Purpose of forward contracts
Hedge: forward contracts lock buying or selling price of an underlying asset in the future
Speculation: assume the risk laid off by hedgers and make bets on the direction of the underlying asset
Settlement
Deliverable forwards: settled by physical delivery, the long pays K and receives an asset worth ST
Non-deliverable forwards (cash-settled forwards): settled by cash, the short simply pay cash to the long in the amount of (ST-K) at expiration
Forward rate agreement (FRA)
定义: a derivative contract that has a future interest rate, rather than an asset, as its underlying, and the purpose to enter a FRAis to lock the borrowing rate in the future
Long/short
Long position: Borrower- earn a profit when market price> forward price
Short position: Lender- earn a profit when market price< forward price
表示
e.g.,2*3FRA
Pricing
e.g.,60-LIBOR=3%, 90-LIBOR-3.9%
(1+3%*60/360)(1+FRA*30/360)=(1+3.9%*90/360)
Synthetic FRA
Futures
定义: a standardized forward contract that one party agrees to buy and the counterparty to sell a physical or financial asset (the underlying) at a specific price (futures price) on a specific date in the future
特点
Mark to market & Daily settlement
The most important distinctive characteristic of future contracts is the daily settlement of gains and losses
Mark to market/daily settlement: at the end of trading days, clearinghouse will determine the settlement price, and all contracts are to be marked to the settlement price
Price limits: Exchange prohibits members from executing trades at prices outside (settlement price of previous day±price limits)
Margin
Initial margin (初始保证金): when two parties enter into a futures contract, both parties are required to deposit a minimum sum of money, which is referred to as the initial margin
Maintenance margin (维持保证金):during the holding period, each party must maintain the required amount of money, which is referred to as the maintenance margin. Maintenance margin is always lower than initial margin
Margin call (追加保证金通知): when the amount of money in the margin account is below the maintenance margin requirement, then the party will get a margin call to bring the balance up to the initial margin
实例
Margin: assume initial margin is 15%, maintenance margin is 8%
Settlement methods
At maturity
Asset delivered: settled by physical delivery, the long pays K and receives an asset worth ST, the contract is worth ("#-K) to the long at expiration
Cash settled: settled by cash, the short simply pay cash to the long in the amount of (ST-K).
Prior to maturity
Offsetting: making an exact opposite transaction to current position, the clearinghouse will net positions out
Neither party makes a payment at the initiation,V0=0
比较
Swaps
定义: two parties agree to exchange a series of payments on periodic settlement dates
At each settlement date, the two payments are "netted", only one party with the greater liability makes a payment
Similarity to forwards
At initiation, require no payment by either party
Custom instruments
Are not traded in any organized secondary market
Are largely unregulated
Default risk is present
Most participants are large institutions
Individuals are rarely swaps market participants
实例: Simplest type of swap - plain vanilla interest rate swap
Also called fixed-for-floating interest rate swap, which is based on a notional principal (not exchanged)
Fixed payments payer: the party makes fixed-rate interest payments, in return receiving floating-rate payments
Floating payments payer: the party makes floating-rate interest payments, in return receiving fixed-rate payments
Options
定义: the buyer pays a sum of money (option price; option premium) to the seller, and receive the right to either buy or sell an underlying asset at a fixed price (exercise price or strike price) either on or before a specific expiration date
Classification of options
根据未来标的物资产价格涨跌的判断
基本关系
图示
Long call
当ST<X ,看涨期权的多头方不会行权;当ST>X ,看涨期权的多头方会选 择行权,且随着ST价格越高,其收益和净利润越高
Short call
一份看涨期权的多头方和空头方的收益和净利润的图形是对称的,也就是说看涨期权的多头方的收益相对于就是看涨期权的空头方的亏损。 当ST<X ,看涨期权的多头方不会行权;当ST>X,看涨期权的多头方会选择行权,且随着ST价格越高,看涨期权的多头方收益和净利润越高,相对应的看涨期权的空头方亏损越大
Long put
当ST<X ,看跌期权的多头方会选择行权,且随着ST价格越低,看跌期权的 多头方收益越高;当ST>X,看跌期权的多头方不会行权
Short put
看跌期权的多头方和空头方的收益和净利润图形也是关于横坐标对称的,也就是说多头方的收益相对应就是空头方的亏损,当 ST < X ,看跌期权的多头方会选择行权,看跌期权的空头方只有义务以行权价格买入标的物资产;当ST≥X ,看跌期权的多头方不会行权,看跌期权空头方收获期权费用
根据期权是否可以提前交割
European Options: can be exercised only on the expiration date
American options: can be exercised on or before the expiration date
根据多头方的到期日是否获利分为一一实值期权、平价期权和虚值期权
Value of options
Intrinsic Value(or exercise value)
call option: cT= max[0, ST — X]
Intrinsic value of put option: pT= max[0,X — ST]
Time Value
定义: The difference between the price(or value) of an option and its intrinsic value
计算: option value=intrinsic value+time value
分类
Prior to expiration: option value>intrinsic value
At expiration: option value=intrinsic value
Credit derivatives
Definition: a contract that the credit protection seller (lender or bondholder) provides protection to the credit protection buyer against a downgrade or a default by the borrower
Types
Total return swap
Underlying: typically a bond or loan
Consists of all interest and principal paid by the borrower plus any changes in the bond's market value. In return, the credit protection seller typically pays the credit protection buyer either a fixed or a floating rate of interest
If the bond incurs a loss, as it surely will if it defaults, the credit protection seller effectively pays the credit protection buyer
Credit-linked note (CLN)
The credit protection buyer holds a bond or loan that is subject to default risk (the underlying reference security) and issues its own security (the credit-linked note)
The buyer of the credit-linked note effectively insures the credit risk of the underlying reference securi
Credit default swap(CDS)--most common type
CDS is essentially an insurance contract against default. A bondholder pays a series of cash flows to a credit protection seller and receives a payment if the bond issuer defaults
Credit spread option
credit spread option is typically a call option that is based on a bond's yield spread relative to a benchmark. If the bond,s credit quality decreases, its yield spread will increase and the credit protection buyer will get a payoff on the option
分类方式
按照买卖双方的权利义务划分
Forward commitments: force the two parties to perform some actioni n the future
Forwards
Futures
Swaps
Contingent claims: provide the right to buy or sell the underlying that depends on a particular event
Option
Credit derivative
ABS
按照交易场所划分
Over-the-Counter: no central location, largely unregulated markets
Forwards
Swaps
Options
Exchange-Traded: with central location, backedby clearinghouse, regulated markets
Furures
Options
OTC v.s. Exchange-traded
The benefits and criticism of derivatives markets
Benefits
Risk allocation, transfer and management
Provide price information
Operational advantages: low transaction costs/greater liquidity/low capital requirements/go short
Improve market efficiency
Criticisms
Speculative devices: too risky
Destabilization and systemic risk
Basics of Derivative Pricing and Valuation
The risk aversion of the investor
Risk averse: risk-averse investors require a positive premium on risky asset
Risk neutral: risk-neutral investors require no risk premium on risky asset
Risk seeking: risk-seeker prefer risk over certainty, even if the investment implying negative risk premium, the risk-seeker is willing to engage
Pricing of the underlying
No benefits or cost during holding and the asset is risk-free asset
The asset at time 0, spot price is
No benefits or cost during holding and the asset is risky asset
Assume investors are risk-averse, so they require positive premium for risky asset
The asset at time 0, spot price is
Incur benefits or cost during holding and the asset is risky asset
Assume investors are risk-averse, so they require positive premium for risky asset
Assume during holding period, generate benefits and incur costs
The asset at time 0, spot price is
Benefits and costs
Storage costs: incurred in owning commodities, such as gold, oil, or wheat would incur some costs in storing them Convenience yieId: refers to nonmonetary benefits from holding an asset. Convenience exist when the asset is difficult to sell short or unusually tight
The holding period from time 0 to time; The investor forecasts the expected price of the asset at time T is E(ST)
The basis of Derivative pricing and valuation: No-Arbitrage Principle
No-arbitrage principle
Arbitrage
In a well-functioning markets with low transaction costs and a free flow of information, arbitrage opportunities arise when the same assets are mispriced
Law of one price: The same assets (the identical assets or two assets or portfolios with identical future cash flows) should be sold at identical price
Limits to arbitrage
Transaction costs
Require capital
Some assets can be difficult to short
Arbitrage opportunity
Replication
定义: replicate the payoffs on one asset or portfolio with those of a different asset or portfolio
方法: An asset and a derivative on the asset can be combined to produce a risk-free asset
计算
Asset + Derivative = Risk -free asset
Equation transformation
Asset - Risk-free asset = -Derivative
Derivative - Risk-free asset = -Asset
Pricing and valuation for four types of derivatives
Forwards
At time 0
No benefits and costs during holding period
Price
Value
Incur benefits and costs during holding period
Price
Value
At time t (t<T)
No benefits and costs during holding period
Value to long position
Value to short position
Incur benefits and costs during holding period
Value to long position
Value to short position
At time T
Value to long position
Value to short position
Futures
The value of futures at time 0, V0=0
Futures marked to market on a daily basis: futures price is reset to the settlement price and value goes to zero
Differences in futures price and forward price
ρ is the correlation coefficient between the spot price of the underlying and risk-free rate
Swaps
Swaps are similar to a series of forwards
Time periods of forwards are different, the forwards prices are not equal:
For swaps, all the fixed payments are equal,
Replicate swaps with a series of forwards, the forwards prices should be all the same. Use off-market forward--a forward transaction that starts with a nonzero value. A series of off-market forwards can be equivalent to the swaps
General idea of pricing and valuation
Pricing of swaps is to find the fixed rate (the contract rate)
Valuation
An increase in floating rate —benefit fixed-rate payer—increase contract value to fixed-rate payer
A decrease in floating rate —benefit floating-rate payer —increase contract value to floating-rate payer
Options
公式
Put-call parity
基本关系
Synthetic equivalents
Put-call-forward parity
The put-call forward parity relationship is derived by substituting the synthetic asset for the underlying asset in the put-call parity relationship
Binomial valuation of options
Binomial model: is based on the idea that, over the next period, some value will change to one of two possible values (binomial)
Risk-neutral probability an up move is Πu; a down move is Πd
Pricing and valuation of options
Hedge ratio
Minimum value of options
表示方法
c0—European call option premium; C0—American call option premium
p0—European call option premium; P0—American call option premium
关系
Values of European and American options differ
The only difference between European and American options is that the holder of an American option has the right to exercise prior to expiration. If the American option exercise at the expiration, then both options are equivalent
Circumstances that makes values of European and American options are different
American call options
If the underlying asset has no cash flow during the life of the option, there is no advantage to early exercise
If the underlying asset pays cash flow during the life of the option, early exercise can be valuable
American put options
Cash distributions rather than cash flows make American put options more valuable
If the American put options are deep in the money, early exercise can be valuable
Factors that determine option prices