导图社区 大物实验
- 138
- 2
- 0
- 举报
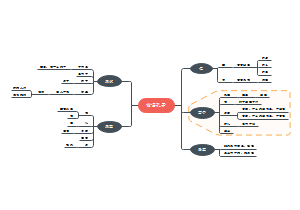
大物实验
《大学物理实验(高等院校物理教材)》是2010年由清华大学出版社出版的图书,作者是郭悦韶等。图书简介 本实验教材根据教育部颁发的《高等工业学校物理实验课程教学基本要求》,结合高校专业设置特点和实验设备的具体情况,
编辑于2022-06-21 21:48:53- 大学物理实验
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
大物实验
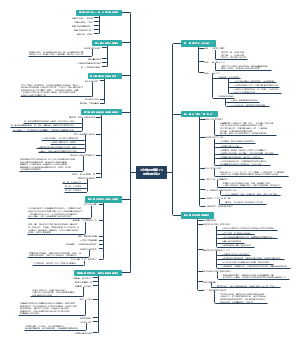
Measurement and Error
Basic concept of measurement and error
Measuring
Meaning of measuring
Measure
elements of measurement
Method,Accuracy,Object,Unit
Classification
According to the method
Direct measurement
basic
Indirect measurement
a large number of data
can be converted into direct measurement
According to the measurement conditions
Same precision measurement
Error
True value
Absolute error and relative error
Absolute error 绝对误差
True value
Known correction value
Relative error 相对误差
Sources of error
Instrument error
Method error
Enviromental error
Persons error
Classification of errors
Systematic error 系统误差
Features:certainty
Homodyne(零差) of micrometer screw/pointer voltmeter
Random error 偶然误差
Several related concepts of error
Precision---Random error
Accuracy---Systematic error
Estimate random error of direct measurement
Normal distribution for random error
single peak
boundedness
symmetry
Use arithmetic mean value as measurement result
同一对象
不同对象
Estimation error by standard deviation
Confidence probability and confidence limits
Excluding bad value
Pauta criterion
Mean value N and error S should be calculated after excluding the bad value, Until there is no bad value.
Note:N<10 is not reliable when using Pauta criterion.
Measurement Uncertainty
Conception
Role
Quality assessment for measurements ( International standard )
Implication
Because of error,the uncertainty degree of measurement result
Classification
A type uncertainty
Using statistical
B type uncertainty
Not using statistical
Calculations
Direct measurement
Table
Estimation error
Satisfy conditions?
NO: Enlarge the estimate error
Yes:Continuous reading instruments?
No: No estimation error
Yes: Estimate error
Instrument error
Labeling on the instrument
Vernier Caliper
Label accuracy class on the instrument
Pointer Meter
meaning of accuracy level
Resistance box
Numerator of percentage of maximum percentage error to measured value
Pointer meter
Numerator of Percentage of maximum error to full-scale values
Implied or instructions labeling
Ruler
Instrument error estimation
Continuous reading instruments
Discontinuous reading instruments
Single measurement
Often use single measurement
Conditions
No significant fluctuation measurements
Combined uncertainty
Indirect measurement
Total Differential of Multi-Function
Transfer expressions for uncertainty
Simplify calculation of Uncertainty principle to abandon the small error
Any one less than another one for 1/3 → Square less than 1/10 →ignore
Overall uncertainty
Expression of measurement result
Significant numbers
Conception
In the measurement results , consists of several reliable numbers and onesuspicious number, to be a Significant figures
Notes and expalnation
Significant figures of “0”
0’ in the middle or at the end is significant
Can't add and delete“0”at the end of result!
In front of the decimal point“0” and behind the point“0”invalid
When unit conversion,the same number of significant figures
Values in scientific notation
Data into appropriate units more concise, more readable
Relationship between instrument and significant figures
Significant figures are determined by the accuracy of theinstrument range and the measured quantity
Determine significant figures of the direct measurement-how to read
General rules
A Instrument error known-result has the same bit as that ofinstrument error or one more bit
Determine significant figures of the indirect measurement-algorithms
Addition and Subtraction
Leave the same number of decimal places in theanswer as there are in the quantity with leastnumber of decimal places答案小数点后小数位数与所给数据小数点后小数位数最小的数相同
Multiplication and division
Leave as many significant figures in the answer as thereare in the quantity with the least number of significantfigures在答案中留下有效数字的个数与所给数据有效数字个数最少的个数相同
Power and roots
Significant figures are the same as its substrate or square root有效数字与所给底物或平方根的有效位数相同
logarithm
Lg x mantissa and x have the samenumber of significant figures.Lgx的小数部分和x的小数部分有效位数相同
functions
Significant figures are determined by transfer relationship of uncertainty
Natural numbers and constants
Significant figures are infinite
Constants A e significant figures take the least or one moresignificant figures involved in computing quantity
Data Processing
Table
clear, order, concise
Indirect measurement values in the table must be listed after the tablewith complete calculation process; if it is the same calculation, one completecalculation must be listed.
Drawing method
intuitively, regularly, subjective and arbitrary large (roughly
function
Average performance
Seeking empirical formula
Interpolation and Extrapolation内插和外推
Calibration curve校准曲线
Fold line connected with the line section between points
Curve linearization
Mapping rules
Axis no need the same ratio
Axis no need through zero
Scale simple, No need follow significant figure rule
Greater the slope, smaller the horizontal data spacing
Find linear equations
Not use experiment data, use data on the both sides of fitting line
Read conditions by grid's 1/10, meets the rule of significant figures
Completely process in calculating the slope and intercept
Successive minus method
relatively simple and objective, but the argument should be equal intervals, less rigorous
Divided into two groups, Subtract corresponding items
Applications
Odd data exit, delete first\last\middle data
Successive minus of numerator and denominator at the same time
Least sauqres method
objective rigorous,but more complex
Regression Analysis
Processing data by the statistical, so as to determine its function by calculation
Step
Infer functional form(regression functions)
Determine the parameters with experimental data to find best a, b, c
Least squares method
Test the function resonale or not using experimental data
Calculate the correlation coefficient equal to 1 or not
Find linear equation using least squares
这个公式好像是错的
Correlation coefficient
Notes and examples
6 steps, include formula, process, results, and significant figures
Not meet significant figures rule, Keeping more bits
Correlation coefficient |r| close to 1, intercept a last position same as y
Slope b significant figures the same as that of slope b' calculated by first and last data
Computer-aided process data
overcome the arbitrariness ofmapping method, but also make the complicated least square methodvery simple