导图社区 语言学 第二章 语音
- 244
- 19
- 6
- 举报
语言学 第二章 语音
胡壮麟 语言学教程 第二章 语音知识梳理,包括语音学分析、音系学分析和转写三部分内容。
编辑于2022-11-20 21:48:25 山西- 英专
- 语言学
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
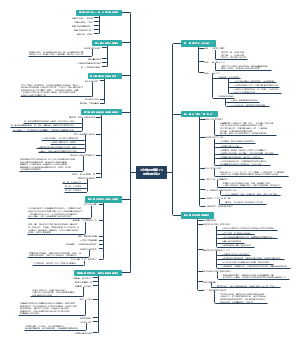
语音 Speech Sounds
语音学分析
发音 Speech Production
音姿 Gestures
Definition
音是通过舌和唇的运动产生的 Most speech sounds are made by movements of the tongue and the lips.
发音器官 Speech /Vocal organs
肺部 lungs
发音以气流作为能量来源,多数情况下气流来自于肺部
气管 trachea (/ windpipe)
顶端为
喉 larynx
声带 vocal folds
横卧结构(前段相连,后端分离)
三种状态
分离 apart
产生
不带声音/清辅音 voiceless consonants
[p,s,t]
贴近 close together
产生
带声音/浊辅音 voiced consonants
[b,z,d]
紧闭 totally closed
产生
声门塞音
[ʔ]
前段为
喉结 Adam’s apple
三大声腔 three cavities of the vocal tract
咽 pharynx
常称为
咽腔 pharynx
口 mouth
常称为
口腔 oral cavity
上部/内部器官 the contents of mouth
上齿 upper teeth
齿龈 alveolar
硬腭 hard palate
小舌 uvula
软腭 sore palate
上唇 upper lips
下部 the bottom part of the mouth
下齿 Lower teeth
舌 tongue
发音涉及舌位
舌冠音(舌尖、舌叶) coronal
舌背音(舌前、舌后) dorsal
舌根音(舌根) radical
下颌(下颚) mandible
下唇 lower lip
鼻 nose
常称为
鼻腔 nasal cavity
语音转写 Phonetic Transcriptions
国际语音协会 IPA(International Phonetic Alphabet)
国际音标表 the IPA chart
提出者
叶斯帕森 Otto Jespersen
语音音段 sounds segments
元音 vowels
发音时声带不受任何压缩或阻碍,不会有气流的混乱或停滞,从而产生的音
只涉及舌位 position of the tongue
基本元音 CV(Cardinal Vowels )
definition
人为确定的,固定不变的元音音质,为实际语言中的元音描写提供参照框架 a set of qualities arbitrary defined , fixed and unchanging, intended to provide a frame of reference for the description of the actual vowels of existing languages
需要区分
舌的前、中、后部 the front, center and the back of the tongue
舌位的四个高度 four levels of tongue height
舌在不产生可闻摩擦时所达到的最高位置
“高”或“闭”
将中部空间分成听觉上相等的两块区域
“中高 或“中闭”及“中低”或“中开”
舌所达到的最低位置
“低”或“开”
中元音[ə]——舌位非高非低,非前非后
定义出8个主要基本元音
发音过程中,音质 whether the quality remains consistent throughout the articulation
保持不变
纯元音/单元音 pure / monophthongs
有听觉上的变化
滑元音 vowel glides
舌运动一次 single movement of the tongue
二合元音/双元音 diphthongs
E.g. way(路)[weɪ] tide(浪潮)[taɪd] how(怎样)[həʊ]
舌运动两次 a double movement of the tongue
三合元音 Triphthongs
实际上为二合元音之后加一个[ə]
E.g. wire(连线)[waɪə] tower(塔)[təʊə]
描述方式
四个基本要求(划分标准) four basic requirements
舌抬起的高度(高、中、低) the height of tongue raising (high - mid - low)
舌最高部分的位置(前、央、后) the position of the highest part of the vowel (front - central - back)
元音的紧度和长度(紧-松/长-短) the length or tenseness of the vowel (tense vs.lax / long vs. short)
唇的圆展(圆唇-展唇) lip-rounding (rounded vs. unrounded)
E.g. [i:] high front tense unrounded vowel 高前展唇紧元音
辅音 Consonants
分为
肺气流音 Pulmonic consonants
多数辅音
非肺气流音 non-pulmonic
挤喉音
内爆音
吸气音
发音方式 manner of articulation
definition
完成发音过程的方法
发音器暂时或长时间关闭口腔通道
发音器使空间明显变窄
发音器相互贴近,改变声道的形状
includes
塞音/爆破音/破裂音 Stop / Plosive
[p, b, t, d, k, g]
鼻音 Nasal
[m, n, ŋ]
擦音 Fricative
[f, v, θ, ð, s, z, ʃ, ʒ, h]
通音 Approximant
[w, ɹ, j]
边音 Lateral
[l]
颤音 Trill
[r]
触音和闪音 Tap and Flap
塞擦音 Affricate
[tʃ] [dʒ]
发音部位 place of articulation
辅音几乎可以产生于唇和声带之间的任何部位
includes
双唇音 Bilabial
[p, b, m]
唇齿音 Labiodental
[f, v]
齿音 Dental
[θ, ð]
齿龈音 Alveolar
[t, d, n, s, z, l, ɹ]
齿龈后音/腭龈音 Postalveolar / Palato-alveolar
[ʃ, ʒ]
卷舌音 Retroflex
硬腭音 Palatal
[j]
软腭音 Velar
软腭塞音
[k, g]
软腭鼻音
[ŋ]
小舌音 Uvular
咽音 Pharyngeal
声门音 Glottal
声门擦音/喉擦音
[h]
声门塞音
[ʔ]
描述方式
带声性
不带声音(清音) voiceless
[p], [f], [t], [k], [s], [ʃ], [θ], [tʃ]
带声音(浊音) voiced
[b], [v], [d], [g], [z], [ʒ], [ð], [dʒ]
不需要区分带声性
[m], [j], [h], [w], [n], [l]
E.g. [p] voiceless bilabial stops不带声双唇塞音
变音符号 diacritic
与元音或辅音结合使用的一些附加符号或记号
超音段符号 suprasegmentals
表示重音和音节
根本区别——气流是否受阻
英语语音
被接受的发音 RP(Received Pronunciation)
BBC英语/牛津英语/国王英语/女王英语
通用美音 GA(General American )
音系学分析
最小对比对测试
用来发现哪些语音替换会导致意义上的变化
区分出40多个重要的语音单位
音位 Phonemes
definition
明显的语音对立单位 a unit of explicit sound contrast
一组语音特征的抽象集合体 An abstract collection of phonetic features
用来区别意义 to distinguish meaning
区分意义的最小单位
最小对比对 minimal set
自动地赋予具有区别对立功能的语音以音位的地位
不局限于两词之间——两词及以上
E.g. kill , till , bill , pill ——/k/ /t/ /b/ /p/
最小对立体 minimal pair
当两词出现在同一位置上的一个音外,其余的音都一样,那么这两个词就构成了一个最小对立体
E.g. bed & bad map & mop | beat & bit bet & bat
不同语言在选择对立音方面不同
英语
送气音
变音符号
ʰ
E.g. [pʰ] —— peak [pʰi:k] ——清辅音/p/
不送气音
E.g. [p] —— speak [spi:k] ——浊辅音/b/
区别
带声性
两个音属于同一个音位
汉语普通话
送气音
变音符号
'
E.g. /p'/ —— 拼 /pīn/
不送气音
E.g. /p/ —— 宾 /p'īn/
区别
音位性
普通话中没有带声音/b/
音位变体 allophones
音子
音位的变化形式
[p] & [pʰ]
音位变体现象 allophony
同音位变体 allophonic
互补分布 Complementary Distribution
同一音位的两个或两个以上的音位变体不区别意义,并且出现在不同的语音环境中 two or more than two allophones of the same phoneme not distinguish meaning and occur in different phonetic environments
并非所有处于互补状态的音都是同一音位的变体
E.g. 英语中[h]只出现在元音前,[ŋ]只出现在元音后
不能出现在同一环境——属于互补分布
不属于同一音位——分别属于/h/,/ŋ/这两个音位
发音相似性
一个音位的变体在语音上必须相似
E.g.
[p]& [pʰ]都是不带声双唇塞音,都是两个不同的音素,是同一音位/p/的一组音位变体
[l] & [ɫ] 都是边擦音,都是两个不同的音素,是同一音位/l/的一组音位变体
规则表述
[p] & [pʰ]
speak 记为 [spi:k] & peak 记为 [pʰi:k]
[l] & [ɫ]
lead 记为 [li:d] & deal 记为 [di: ɫ]
音系过程 Phonological Process
在此过程中,目标音段或涉事音段在特定的环境或语境中发生了结构上的变化 a target or affected segment undergoes a structural change in certain environments and contexts
规则表述
当带声擦音出现在不带声音前时,变成相对应的不带声擦音
同化现象 assimilation
definition
一个音获得邻音的某些或全部特征
feature
可以跨越音节和词的界限发生
相互同化 mutual assimilation
definition
两辅音合二为一,成为第三个音
[d] + [j] → [dʒ]
would you
[t] + [j] → [tʃ]
meet you
[s] + [j] → [ʃ]
miss you
[z] + [j] → [ʒ]
here’s yours
可能性
顺同化 progressive assimilation
前期协同发音 Anticipatory coarticulation
前面的音影响后面的音
逆同化 regressive assimilation
后期协同发音 perseverative coarticulation
后面的音影响前面的音
英语中最普遍的同化现象
发声位置
一词的音节中间
鼻音化 nasalization
表述形式
[-nasal]
[+nasal] / __ [+nasal]
E.g. can / tan
齿音化 dentalization
表述形式
[-dental]
[+dental] / __ [+dental]
E.g. tenth / ninth
软腭化 velarization
表述形式
[-velar]
[+velar] / __ [+velar]
E.g. since [sɪns] / sink[sɪŋk]
两词之间
a pan[ŋ] cake / sun[ŋ] glasses / you can[ŋ] keep them
增音 Epenthesis
E.g.
以元音开头的词,前面都用不定冠词an
两个元音间缺少一个辅音 → 冠词a后加一个鼻音[n]
增音规则 Insertion rules
Ø表示空位
清音化 devoicing
带声音变成不带声音的过程
出现在清辅音前——变成相对应的清辅音
Includes
受 [k] / [p] / [t] 影响
/z/ → [s]
受 [k] / [g] / [b] / [m] 影响
/n/ → [ŋ]
受 [k] / [p] / [t] / [g] 影响
/v/ → [f]
E.g.
five past
缓慢或正常言语中的发音
[faɪvpa:st]
连贯语言中的发音
[faɪfpa:st]
规则序次 Rule Ordering
步骤
基础形式
底层形式/底层表达式 Underlying Form / UR(Underlying Representation)
增音
清音化
遵循原则
剩余位置条件
较为特殊的规则应用在先 the more specific rules applies first
复数的三种变体
基础形式
[z]
前面是/z, ʒ, dʒ/以外的带声辅音及元音
清音化
[s]
前面是/s, ʃ, tʃ/以外的不带声辅音
增音
[əz]
前面是/s, z, ʃ, ʒ, tʃ, dʒ/
咝音 Sibilants
超音段特征 Suprasegmental Features
definition
语音问题中超出单节音段以上的方面 those aspects of speech that involve more than single sound segments
includes
音节 Syllable
词
单音节词 monosyllabic word
E.g. cat dog
多音节词 polysyllabic word
音节划分规则
最大节首原则 MOP(Maximal Onset Principle)
当辅音的位置面临选择时,将其归入节首而不是节尾
E.g. telling → /l/ 的发音为 [l],而不是 [ɫ]
E.g. festival transplant
includes
韵基 R(Rime)
元音(有时为辅音)
节核/韵峰 N(Nucleus)
所有音节必须有
节核后的辅音
节尾 Co(Coda)
有节尾
开音节 open syllable
无节尾
闭音节 close syllable
节首 O(Onset)
不是所有音节都有
音响阶 Sonority
解释了
为什么在英语的辅音丛中,许多辅音的组合不能出现在节首和节尾位置
重音 Stress
definition
音节发音时所用的力度 the degree of force used in producing a syllable
特写形式
[‘]
只适用于至少有两个音节的词
单音节词相对于句子中的其他词是加重的
位置
许多语言的重音位置非常固定
英语中的重音原则上可以放在任何一个音节
usually called
重读 accent
位置影响因素
语法功能
名词n. & 动词v.
后缀
历史发展
区域/方言差异
合成词、词组
E.g.
长词
两个重音节
主重音 primary stress
相对更重
[‘]
次重音 Secondary stress
相对较弱
[,]
句子
一般情况
实词重读 Lexical/notional words are normally stressed
虚词不重读 structural/functional words are unstressed
重音用来表强调、惊讶等
语调和声调 Intonation and Tone
声调
声调变化可以改变一组词的意义
连续变调 Tone Sandhills
语调
涉及重复出现的升降模式,每个模式都应用于一套相对一致的意义
运用单位
词/词群
转写
语音转写/严式转写 Phonetic Transcriptions / Narrow Transcriptions
记录“音素”
写法
[pʰ](方括号之间)
E.g. peak—— [pʰi:k]
用复杂的符号精确地标记语音所有可能的细小变化 symbolize all the possible speech sounds, including even the minutest of pronunciation
音位转写/宽式转写 Phonemic Transcriptions / Broad Transcriptions
记录“音位”
写法
/p/(放双斜线//内)
E.g. peak ——/pi:k/
用一套简单的符号记音,试图把一个词语同其他的词区分开(关注点在于特定语音的对照) use a set of simple symbols in our transcription, trying to indicate only those sounds capable of distinguishing one word from another in a given language.
用途
教材、词典
强制性曲线原则 OCP(Obligatory Contour Principle )
不允许具有共性的元素连续出现 identical adjacent elements are not allowed