导图社区 Invitations to Linguistics-Chapter
- 42
- 2
- 2
- 举报
Invitations to Linguistics-Chapter
语言学教程 胡壮麟第五版 主要介绍了 Invitations to Linguistics-Chapter的相关内容。
编辑于2023-01-01 12:50:07 河南- 语言学
- Words and Morphology Chapter 3
这是一篇关于Words and Morphology Chapter 3的思维导图,A word including only one morpheme is a simple word,while complex word contains more than one morphem。
- Speech Sounds--Chapter 2
胡壮麟语言学导论第五版第二章:Tap and Flap促音和闪音:当舌对齿龈进行一次触及,发生一次颤动,就是促音;闪音是首先以卷舌音的音姿将舌尖向上并向后卷,然后返回到下齿后面位置。
- Invitations to Linguistics-Chapter
语言学教程 胡壮麟第五版 主要介绍了 Invitations to Linguistics-Chapter的相关内容。
Invitations to Linguistics-Chapter
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- Words and Morphology Chapter 3
这是一篇关于Words and Morphology Chapter 3的思维导图,A word including only one morpheme is a simple word,while complex word contains more than one morphem。
- Speech Sounds--Chapter 2
胡壮麟语言学导论第五版第二章:Tap and Flap促音和闪音:当舌对齿龈进行一次触及,发生一次颤动,就是促音;闪音是首先以卷舌音的音姿将舌尖向上并向后卷,然后返回到下齿后面位置。
- Invitations to Linguistics-Chapter
语言学教程 胡壮麟第五版 主要介绍了 Invitations to Linguistics-Chapter的相关内容。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
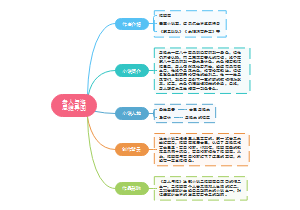
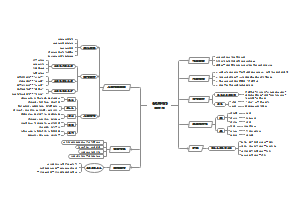
Invitations to Linguistics-Chapter 1
1.1 Why Study Language?
a vital human resource
Play a central role in our lifes
as a tool
1.2What is Language?
Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communications.
1.3 Design Features of Language
Arbitrariness任意性
the form of linguistic signs and their meaning.
the sound of a morpheme and its meaning
the syntactic level -----syntax<words
arbitrariness and convention----convention is worth more noticing.
Duality二层性
the primary level,as words, have distinct and identifiable meaning
上层结构:词素-构词材料 ;词-造句材料;句子-交际基本单位
the secondary level,as sounds,is meaningless
底层结构:音位和由音位组成的音节
The units of the primary level are composed of elements of the secondary level .
lies in the great productive power
Creativity
One part from duality
The recursive nature 递归性of language provides a theoretical basis.递归性:反复使用相同的规则来生成无穷的短语或句子的一种语法手段
Displacement
stimulus-free
make it possible for us to talk and think in abstract terms.
1.4 Origin of Language
The "bow-wow" theory-imitate the sound of animals-lacks supportive evidence
The "pooh-pooh"theory--utter instinctive sound of pain ,anger and joy-a limited number- not good evidence.
The”ye-he-yo“theory--primitive people worked together,producing some rhythmic grunts --at most speculation 推测
fruitless search for the origin of language对语言的探寻无果
evolveswith specific historical ,social and cutural contexts.
1.5 Functions of Language
Informative Function
the prerequisite of social development
crusial function
another meaning:ideational function
Interpersonal Function
interaction in the discourse situation
the addresser's attitude
expressing identity
Performative Function行事功能
change the social status of persons
the control of reality as on some magical or religious occasions
Emotive Fuction
crucial in changing the emotional status of an audience for or against someone or something
discussed under the term expressive function
Phatic Communion寒暄交谈
maintain a comfortable relationship between people without involving any factual content
different cultures have different topics of phatic communion
help define and maintain interpersonal relations
Recreational Function
the hearty joy of using it
For example:dui ge(对歌),the repetive rhythms help to control the game;poetry writing
Metalingual Fuction
meshes with the thematic function of language in functional grammar 通过变换单词或短语在一句话中的位置改变着重想要表达的内容
infinitely self-reflexive无限的自我反身性,着重表达人类可以谈论谈话,思考思考
1.6 What Is Languistics?
As a science,linguistics now has a set of established theories,methods and sub-branches.
1.7 Main Branches of Linguistics
Phonetics
the study of sounds which are used in linguisticscommunication.
发音语音学:发音器官
声学语音学:声波
听觉语音学:听者如何分析和处理收到的声波
语言学是对人们能够发出的声音进行研究。
Phonology
the study of how sounds are put togetherand used in communication.
音系学以音位为起点来处理语言的语音系统。
音系学是对人们发出的声音中的能够组成语言和产生意义的语音进行研究。
Morphology形态学
the study of the way in which morphemes are arranged to form words.
关心词的内在构造,研究意义最小的单位
语素是语音和意义的结合体
不同语言对语素的依赖程度不同。
Syntax
the study of how morphemes and words are combined to form sentences.
句子的形式和结构受制于句法规则。
句意不仅和词序有关,还和结构的组合方式有关。eg:The chicken is too hot to eat.
Semantics
the study of meaning in language.
语义成分,词的所指,词之间的意义联系,句子之间的意义联系
Pragmatics
the study of meaning in context of use.
语用学关心的是语言如何用来交际的
1.8 Macrolinguistics
Psycholinguistics,Sociolinguistics,Antropological Linguistics,Computational Linguistics.
1.9 Important Distinctions in Linguistics
Descriptions vs.Prescriptive
Synchronic vs. Diachronic
Langue & Parole
Competence& Performance