导图社区 ACCA SBR 思维导图
- 122
- 4
- 2
- 举报
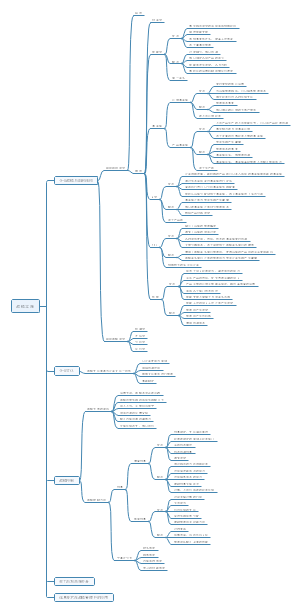
ACCA SBR 思维导图
你是否想要通过ACCA SBR考试,拿到专业会计师的证书?你是否想要掌握SBR课程的核心知识和技能?如果你的答案是肯定的,那么我有一个好消息要告诉你。我做了一份关于ACCA SBR课程的思维导图,它包含了SBR课程的主要内容。我想把这份思维导图分享给大家,希望能帮助更多人通过ACCA SBR考试,实现自己的职业目标。如果你对这个项目感兴趣,请关注我的社交媒体账号,我会定期更新更多内容。让我们一起学习一起进步吧!
编辑于2023-03-31 23:20:40 江苏省- ACCA
- 《吃掉那只青蛙》精简版
《吃掉那只青蛙》通过易懂的比喻和大量实际案例,为读者描绘了一张清晰的时间管理与自我调控路线图。这是一本非常实用的成功学著作,让人受益匪浅。坚持每天完成一小步,持续进步,我们就能取得最后的胜利,享受成功的喜悦。这是一本激励人心的正能量读物。
- 《波士顿咨询工作法》精简版
《波士顿咨询工作法》是日本管理学专家内田和成所著,向读者介绍了波士顿咨询公司独特而高效的工作方法。这本书深入浅出地剖析了波士顿咨询公司如何通过“分解法”、“事实调查法”和“目的导向法”等方法,在复杂的商业顾问领域保持卓越的市场地位。内田和成先生融汇中西方管理思想,探讨怎样运用这些先进方法提高工作效率、分析复杂问题、制定有效决策。这本书为商界人士提供了宝贵的解决问题思路,也为所有的职场工作者提升自身管理能力提供了科学指导。
- 《蓝海战略》精简思维导图
这份详细的“蓝海战略”思维导图为你提供了深入理解和应用蓝海战略的全方位视角。首先,它定义了蓝海战略,并明确区分了蓝海战略和红海战略的本质区别。接着,该导图指导你如何步步深入地制定并执行蓝海战略,包括如何构建战略画布,寻找蓝海,并且执行这一策略。为了更具操作性,它还列举了“四个关键动作框架”,旨在启发你如何在实践中具体应用蓝海战略,包括创新、消除、减少和提升四个方向。最后,导图通过列举几个著名的成功案例,如“太阳马戏团”、“瑞士瑞银”和“苹果公司”,使得理论知识更有生动感,更便于理解和学习。这份思维导图希望能够帮助刚步入职场的你,深入理解并巧妙运用蓝海战略,开启你的职业生涯新篇章。
ACCA SBR 思维导图
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- 《吃掉那只青蛙》精简版
《吃掉那只青蛙》通过易懂的比喻和大量实际案例,为读者描绘了一张清晰的时间管理与自我调控路线图。这是一本非常实用的成功学著作,让人受益匪浅。坚持每天完成一小步,持续进步,我们就能取得最后的胜利,享受成功的喜悦。这是一本激励人心的正能量读物。
- 《波士顿咨询工作法》精简版
《波士顿咨询工作法》是日本管理学专家内田和成所著,向读者介绍了波士顿咨询公司独特而高效的工作方法。这本书深入浅出地剖析了波士顿咨询公司如何通过“分解法”、“事实调查法”和“目的导向法”等方法,在复杂的商业顾问领域保持卓越的市场地位。内田和成先生融汇中西方管理思想,探讨怎样运用这些先进方法提高工作效率、分析复杂问题、制定有效决策。这本书为商界人士提供了宝贵的解决问题思路,也为所有的职场工作者提升自身管理能力提供了科学指导。
- 《蓝海战略》精简思维导图
这份详细的“蓝海战略”思维导图为你提供了深入理解和应用蓝海战略的全方位视角。首先,它定义了蓝海战略,并明确区分了蓝海战略和红海战略的本质区别。接着,该导图指导你如何步步深入地制定并执行蓝海战略,包括如何构建战略画布,寻找蓝海,并且执行这一策略。为了更具操作性,它还列举了“四个关键动作框架”,旨在启发你如何在实践中具体应用蓝海战略,包括创新、消除、减少和提升四个方向。最后,导图通过列举几个著名的成功案例,如“太阳马戏团”、“瑞士瑞银”和“苹果公司”,使得理论知识更有生动感,更便于理解和学习。这份思维导图希望能够帮助刚步入职场的你,深入理解并巧妙运用蓝海战略,开启你的职业生涯新篇章。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
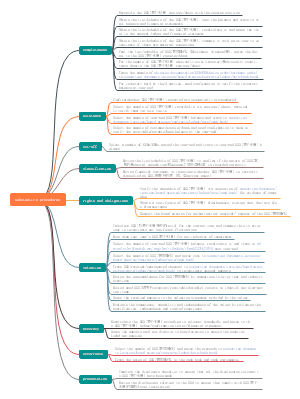
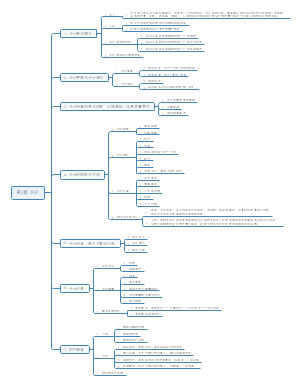
SBR
Code of Ethics and conducts
Ethical principles
Integrity (straightforward and honest)
Objective (no self interest or bias)
Professional competence and due care
Confidentiality
Professional behaviour (compliance with laws and regulations)
Threats to fundamental principles
Self interest
Self review
Advocacy
Familiarity
Intimidation
Appropriate action
1. Disclose this to appropriate internal governance authority
2. Seek professional advice from ACCA and legal advice if necessary
3. Resign
Stakeholders
Shareholders
Financing source
Customers
Social responsible policy
Creditors
Sourcing of key components
Employees
Working hard
Good ideas
Regulators
Litigation costs
Steps in ethical questions
1. Why and to who is it important?
2. What are the impact of each items?
3. What is wrong with the decision? What are the consequences?
Directors are appointed to run the business on behalf of the company's shareholders who are the primary stakeholder. Deliberate manipulation of financial statements will reduce stakeholders' confidence in the reliability of the financial statements and the accountancy profession as a whole. directors are deliberating flouting International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS® Standards) to improve their bonus and maintain debt covenant obligations
4. It is in contrary with which ethical principles?
Financial statements should be
Fair
Transparent
Comply with accounting standards
Information should be
Relevant
Provide faithful representation
Qualitative characteristics of useful fin. information
Comparability
Verifiability
Timeliness
Understandability
Related parties
Related entity (controlled by related parties)
Definition
Has control or joint control
Significant influence
Member of the key management personel (also family)
must disclose the nature of the related party relationship as well as information about all transactions and outstanding balances
Revised 2018 Conceptual Framework
Elements of FS should be recognised when it provides
Relevant informaiton
Faithful representation
Recognition should be cost constrain (cost effective)
Economic resource
A right that has the potential to produce economic benefits
Assets
A present economic resource controlled by the entity as a result of past events.
Liability
A present obligation of the entity to transfer an economic resource as a result of past events.
Obligation
A duty of responsibility that an entity has no practical ability to avoid.
Valuation
Inventory
Lower of historical cost and NRV
Values
Value in use
PV of future cash flows
Fair value
Market based measurement, assumption that market participants would use the price.
Net realiasable value
Estimated selling price in the ordinary course of business less cost of completion and costs of sale.
Employee benefits (pension) IAS 19
Defined benefit scheme
Calculation
1. Calculate change in PV of defined benefit obligation
+ Opening defined benefit obligation
+ interest on obligation
(PV of future benefit obligation + past service cost) * r
+ current service cost
advisory cost during the year
+ past service cost
cost of pensions earned in the period
- benefit paid
in current year to former empoloyees
+ Curtailment
Reduntance employee
- Settlement
Disposal or restructuring
- gain on remeasurement through OCI
balancing figure
= Closing defined benefit obligation
2. Calculate changes in FV of plan asset
+ Opening FV of plan assets
+ Interest on plan assets
FV of plan asset begin * r
+ Contributions
received current year
- Benefit paid
in current year
- Settlement
Disposal or restructuring
+ loss on remeasurement through OCI
balancing figure
= Closing FV of plan assets
3. P&L
Defined benefit expense
+ Current service cost
advisory cost during the year
+ Past service cost
cost of pension earned in the period
+ Net interest on net defined benefit asset
(PV of future benefit obligation + Past service cost - FV of plan asset) * r
= Defined benefit expense recognised in P&L
OCI
+ Remeasurement gain on defined benefit obligation
- Remeasurement loss on plan assets
if loss was negative at plan asset, then plus
= Remeasurement of defined benefit plans
4. BS
+ PV of pension obligation
20X1 20X0
- FV of plan assets
20X1 20X0
= Net pension liability
20X1 20X0
Curtailment => Past service cost
Reduction in net pension liability when the number of employees becomes redundance
Recognise at earlier of:
Plan curtailment occurs
Entity recognises the related restructuring costs
Basic settlement => Past service cost
obligation which Hudson has to pay as compensation for terminating the employee’s services regardless of when the employee leaves the entity
Recognise earlier of when the plan of termination is announced and when the entity recognises the associated restructuring costs associated with the closure
Remeasurement component => OCI
Actuarial gain and losses
Changes in asest ceiling
Defined contribution scheme
Only recognise amount due to pension scheme at year end as current liability
Contribution paid by company
PL
Contribution paid by employee
Adjusted in employee's net salary
IAS 19 Amendment 2018
When a plan amendment, curtailment or settlement take place, the actuarial assumptions should also be remeasured
Business combination IFRS 3
Goodwill
Explaination
Recognised when one company obtains the control over the other
Presentation
As a non-current asset at acquisition date
Valuation
+ Fair value of consideration
Deferred consideration
present value at acquisition date, changes to PL
Contingent consideration
Fair value at acquisition date, changes to PL
+ NCI
- Fair value of net assets
Fair value of net asset should be adjusted for the adjustment info available within 12 months after acquisition
= Goodwill
Valuation subsequently
Impairment test every year
Negative goodwill
Review the identified net asset amount
PL
Business
Integrated set of activities and assets which can be conducted and managed to provide a return to investors.
Require
Input
Process
If no input and process, then as asset acquisition
no business acquisition occurs where substantially all of the fair value of the gross assets acquired is concentrated in a single asset or group of similar assets
Asset acquisition
Only if it is not a business acquisition
Control
Power over the investee
No need to be exercised
Or arrangement to appoint/remove and set remuneration of management
Exposure or rights to variable returns
Ability to use its power
Business combination
In which an acquirer obtains control of one or more businesses.
Consolidated financial statements IFRS 10
Groups
Subsidiary (with control)
Full consolidation
Goodwill
NCI
Associate IAS28 (significant influence, >20%)
Equity method
+ Cost of investment
+ Share of post-acquisition retained earnings & OCI
PL
- Impairment losses to date
= Investment in associate
Financial instrument (not for trading, <20%)
Initial measurement
Fair value + transaction cost
Subsequent measurement
Amortised cost if
Is held within a business model and collect contractual cash flows, and
cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest
Financial instrument (all other cases)
Initial measurement
Fair value
Subsequent measurement
Fair value through PL
Partial acquisition (from associate to subsidiary)
As if two steps
1. As the shareholding is sold
+ Fair value of shareholding
- Carring amount
= Remeasurement gain
2. Subsidiary has been purchased
+ Consideration new
+ FV of current shareholding
+ NCI
- FV of all net assets
= Goodwill
Partial disposal (control is lost)
Working
1. Goodwill
2. Group retained reserve
saparate retained reserves b/f
3. Group profit on disposal
+ FV of consideration received
+ FV of remaining investment
- Net asset when control is lost
- Goodwill
+ NCI when control is lost
= Group profit on disposal
4. NCI
5. Investment in associates
+ FV at date control lost
+ Share of post acquisition retained reserves
= Investment in associate year end
Additional acquisition from 60% to 80%
Already a subsidiary, so just transaction between shareholders
No new goodwill
Only adjustment to NCI
i.e. 20% / 40% x NCI share at further acquisition
Consolidation financial statement question
Associate
With control: full consoliation
No control: as investment in associate
Working
1. Fair value adjustment table
2. Unrealised profit on inventories
Inventory in stock * profit margin / (1+profit margin)
Deferred tax because group pays tax before the profit is realised
3. Goodwill
+ Consideration transferred
+ NCI
- Share capital
- Retained earnings at acquisition
- Fair value adjustment
Net assets acquired
- Impairements to date
= Year-end value
4. Retained earnings
5. Non-controlling interest NCI
+ NCI at acquisition
+ NCI share of post acquisition
- NCI share of impairment loss
= NCI end date
6. Investment in associates (no control)
+ Cost of associate
+ Share of post-acquisition retained reserves
- Impairment of investment
= Investment in associate
Consolidation of cash flow statements IAS 7
Steps
1. Assets
2. Equity
3. Liabilities
4. Working capital
5. Purshase of subsidiary
6. Cash flow statement
Net cash flow from operating activities
+ Cash from operating activities
Profit before tax
Adjustments
+ Non-cash transaction regarding PPE
+ Depreciation
+ Impairment
+ Interest
+ service cost of pension
- Contributions of pension
Changes in working capital
- Tax
- Interest
= Net cash flow from operating activities
Effect of subsidiary
Assets and liabilities
100% consolidate
Fair value adjustment
Deferred tax effect
Dividend
No effect since it is from one to anohter
NCI share of divident
Cash outflow in financing cash
Methods
Direct method
Shows major classes of gross cash receipts and payments
Advantage
Easier for user to understand
Discloses information not available elsewhere in the financial statements
Disadvantage
More time consuming and expensive
Indirect method
Advantage
Easier to use
Nearly all companies use it
Disadvantage
Difficult to understand
Open to manipulation
Asset held for sale and discontinued operations IFRS 5
Held for sale
Definition
The carrying amount will be recovered through a sale transaction rather than through continueing use.
Valuation
Lower of carrying amount and fair value less cost to sell
Carring amount= net assets + goodwill - NCI
If the asset was impaired previously, than any increase of the measure can reverse the impairment loss
Subsequent change in FV => PL
Steps
1. Calculate CA
To PL
2. Revaluate
Higher of CA and FV
To OCI
3. Impairment
Lower of CA and recoverable amount
Recoverable amount: higher of value in use and FV less cost to sell
To PL
4. Classify as Held to sale
Lower of CA and FV less cost
5. Sell profit
Criteria:
Available for immediate sale in its present condition
Sale must be highly probable
Reasonable price
Significant changes are unlikely
Management is committed to the plan
Actively locating a buyer
Expected to be in one year from the date
Within 12 months time
Approach
Assets written down to fair value less cost to sell
PL
No further depreciation or amortisation
Subsequent change to further impairment loss
Present
Single amount
Separately from other assets and liability
As Current asset and liability (no offset)
Restructuring provision
Only directly attributable costs of the restructuring
Criteria
Restructuring has been communicated to media
Detailed formal plan is in place
Discontinued operations
Classification
Separate major line of business or geographical area of operaitons
Part of a single co-ordinated plan to dispose
Subsidiary was acquired exclusively with a view to resale
When losing control, must disclose the following in the cash flow statement
Total consideration received
Cash consideration
Amount of cash held by subsidiary
Amount of assets and liabilities summarised by each category
Financial instrument IFRS 9
Financial assets
Derecognised when
Contractual right has expired
All risk and rewards are transferred
Debt and equity instrument (not held for trading)
Initial measurement
Fair value + transaction cost
Subsequent measurement
Amortised cost if
Is held within a business model and collect contractual cash flows, and
cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest
All other cases
Initial measurement
Fair value
Subsequent measurement
Fair value through PL
Convertible bond IAS 32
Presentation
NCL component
= principal payable / (1 + r for non convertible liability)^n + PV of coupon interests using r
Equity
= principal - NCL component
Factoring
Derecognise AR when
has no further right to receive cash
All risk and rewards are transferred
No control over AR
Accounting
Initial part of AR derecognise
Difference in PL
Guarantee as financial liability
Bond with credit risk
Low credit risk
Stage one financial asset
Credit allowance for 12 month expected loss
High credit risk
Stage two financial asset
Credit allowance for lifetime losses
Fair value measurement IFRS 13
Value in use
Present value of cash flows generated discounted at suitable rate of interest
Impairment loss
Reduce the carrying amount of the asset
Expensed in PL
Cannot be netted off the revaluation surplus if no specific surplus was formed
IAS 40 Investment property
Valuation
Fair value model
Cost model
Hierarchy
Quoted price in active markets
Directly or indirectly observable price
Unobservable input
Determine FV
Definition of FV
An exit price in the principal market
Principal market
The accessable market with highest volume and level of activity in general.
If no principal market, then Most advantageous market
The market where the profit is maximise
FV should not consider transaction cost, but only consider transportation cost.
Lease IFRS 16
Definition
Contract conveys the right to control
Identifiable assets
For a period of time (more than 12 months)
Exchange for consideration (high value)
Lessor
Financial lease
Derecognise asset
Recognise lease receivable equal to net investment
Lessee
Lease liability
Equal to sum of payments
NCL
Total lease liability in n+1
CL
Total lease liability - NCL part
Total lease liability
Liability begin + interest - instalment
Finance costs
PL
ROU * r
Add to carrying amount of lease liability
Payments
Deduct from carrying amount of lease liabiilty
ROU
Equal to cumulative PV of annual payable + initial costs
Depreciation
PL
ROU / n
Deferred tax
Temporary difference between carrying amount of ROU and Lease liability
Sales and lease back
1. Identify sales contract as IFRS 15 Revenue from contract with customers
Yes, sales
Asset derecognise
No sales
Asset remain in SOFP
2. Calculate carrying amount
3. Calculate remaining ratio = PV of lease / FV of asset
4. ROU = CA * remaining ratio
Provision, Contigent liabilities and assets IAS 37
Should be recognised if
Obligation from a past event
No realistic alternative but to settle
Outflow of economic resource is probable
Obligation can be measured reliably
Provision should be reviewed at the end of each accounting period
Reimbursement ie. insurance
Recognised only when it is virtually certain
Amount recognised
Best estimate of expenditure required to settle the obligation
Restructuring provision
Should be recognised when
Detailed formal plan for the restructuring
Valid expectation has been created in those affected
Onerous contract
A contract in which the unavoidable costs of meeting the obligations under the contract exceed the economic benefits expected to be received under it
present value of the unavoidable costs, net of the expected benefits under the contract
Foreign currency
Types
Presentation currency
currency in which the financial statements are presented
Functional currency
primary economic environment in which the entity operates
primary factors: the currency which mainly influences the sales price for their goods
Secondary factors including the currency in which financing activities are obtained
Steps
1. SOFP of associate
2. PL of associate
3. Goodwill
4. Group retained earnings
5. NCI
6. Translation reserve
7. Exchange difference
Rates
Share capital and pre-acquisition retained earnings subsidiary
fx at acquisition date
Post acquisition retained earnings
average fx rate at each year
Dividend
Actual rate
Goodwill
Closing rate each year
Monetary and non-monetary item
Closing rate
Foreign subsidiary
FX difference to OCI & Translation reserve
if dispose then to PL
Other topics
Accounting policies and changes IAS 8
Prior period error
Retrospectively
Restating the comparative figures
Restating opening balances
Event after reporting date IAS 10
Material non-adjusting event after reporting date but before FS is authorised
Should be disclosed
Income tax IAS 19
Deferred tax asset
Based on carry forward of unused tax losses
Only recognise when there is strong evidence that future taxable profit will be available.
Possible to offset if
There is legally enforceable right to offset the current tax asset and liability as amount relate to the same taxation authority on the same entity.
When calculating temporary difference for PPE
PPE use historical rate
Tax base use closing rate
Revenue IFRS15
Single performance satisfied over time
If a contract contains significant financing component
Adjust the promised amount for the effect of time value.
Entity should only account for revenue from a contract with a customer when it meets the following criteria. If not meet, then recognise as receivable and loss allowance.
The contract has been approved;
Rights regarding goods and services can be identified;
Payment terms can be identified;
It is probable the seller will collect the consideration it is entitled to.
Revenue should be recognised
when or as a performance obligation is satisfied by transferring the promised good or service to the customer
Gift card
Unexercised right as breakage.
For every 1 $ redeemed, 1.43 (1/0.7) recognise as revenue. The reset recognise as contract liability
If consideration is not in form of cash
Then measure FV of the consideration
If FV cannot be estimated, then use stand-alone selling price
Intangible asset IAS 38
Definition
Identifiable asset
Non-monetary
Has no physical substance
Valuation
Without finite useful life
Impairment at the end of each period
PL
With finite useful life
Amortise from the start date
PL
R&D costs
Only recognise when tech and commercially feasible
Impairment each year
start when regulatory approval is obtained
Intangible asset held for sale
Should be accounted under IAS 2 Inventory
Joint arrangement IFRS 11
with separate vehicle
Joint venture
Equity accounting
without separate vehicle
Joint operation
Joint operator must recognise proportionally
Government grants IAS 20
Grant relates to assets
Deferred income or deduction from PPE
Grant relates to income
PL
Financial instrument Disclosure IFRS 7
Entity must enable users of FS to evaluate
1. Significance of financial instrument
2. Nature and extent of risks arising form financial instrument
Different types of risks
Credit risk
Qualitative
Quantitative
Market risk
Currency risk
Interest rate risk
Price risk
Management commentary Practice statement 1
Objective
1. Provide management's view of entity's performance, position and progress
2. To supplement and complement information presented in FS
Should contain
1. Nature of the business
2. Objectives and strategies
3. Major resources, risks and relationships
4. Results of operation and prospects
5. Critical performance measures and indicators
Making materiality judgements Practice statement 2
Key points
FS should provide financial info that is useful to primary users
Disclose does not need to be made if the information is not material
Assessed both from quantitative and qualitative perspective
4 steps process
1. identify
2. Assess
3. Organise
4. Review
Integrated reporting
Conveys business model and sources of value creation
Primary purpose
Explain how the organisation generates value over time
Examine external environment
Describes prospects and challenges for the future
Capital
Financial
Social
Human
Natural
Manufactural
Human
Benefits
Enhanced sys of accountability
Stronger decision making
Better reputation
More harmonisation
Better communication and relationship
Impairment of assets IAS 36
No asset should be carried at more than its recoverable amount
indicate impairment
Recoverable amount
Higher of fair value less costs of disposal and its value in use
Value in use
PV of future cash flows
Operating segment IFRS 8
Definition
A component of an entity which engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur cost
Does not prescribe a basis for allocating costs, but requires a reasonable basis.
Suggest reasonable basis!
Requires reconciliation between segment reported amounts and those in the consolidated FS
Disclose
Nature of difference
Basis of accounting transactions
Should be reported separately if > 1 criteria are not met:
Nature of the product
Production process
Method used to distribute product
Customer
Regulatory environment
Quantitative thresholds
Revenue, Profit, or Asset of the segment is 10% or more of the group combined
Alternative performance measure
APMs are not defined in IFRS, hence less comparable
Some not uniform APMs such as free cash flow, should be clear descript and calculation is disclosed
Reconciliation is needed
APMs should use measures equal or more prominent than IFRS standards
Should provide income tax effects
Inventory IAS 2
NRV
estimated selling price in the ordinary course of business less the costs of completion and costs of sale
Share-based payment IFRS 2
Cash settled Share-based payment
Liability
Using option pricing model
FV of the liabiilty at the date, * n/vesting period
Difference => PL
Recognise at grant date
Each year recognise over the vesting period proportionally
Equity settled share based payment
As equity
FV on the grant or issue date
Share based payemnt with choice of settlement
Split in equity and liability components
+ FV of the good or service
- FV of debt component
= FV of equity component