导图社区 2022年-ACCA-SBL知识结构图
- 78
- 0
- 1
- 举报
2022年-ACCA-SBL知识结构图
2022年ACCA SBL考试知识结构图 【知识结构 案例分析 答题套路 记忆要点】
编辑于2022-02-20 11:18:30- 底层逻辑【看清这个世界的底牌】 刘润 著 《读书笔记》
底层逻辑,源于不同中的相同,变化背后的不变,让我们在千变万化的复杂世界中如鱼得水 读了这本书,启发颇多,尤其是人生三层智慧,层层递进,对电视剧、电影主人公的发展有了不一样的感知,原来就是那么回事儿;对工作的益处就不用提了。 将此书用思维导图呈现出来,时刻提醒自己,现已完成第一章《是非对错的底层逻辑》,后续持续更新中,有兴趣一起交流的朋友可加 微信号 15620587698
- SBL
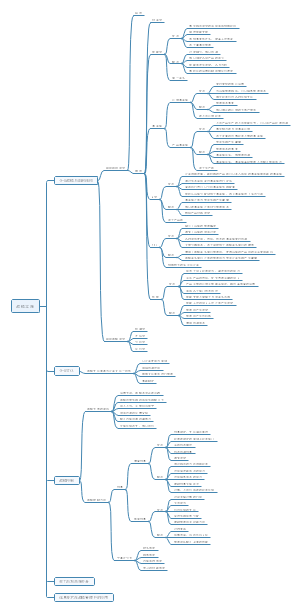
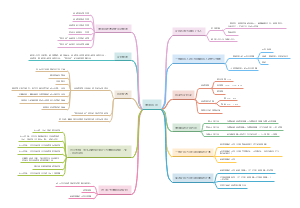
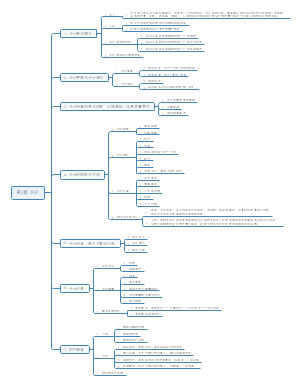
本图整理的内容有: Chapter 01 Strategy, leadership and culture Chapter 02 Stakeholders and social responsibility Chapter 03 Impact of corporate governance on strategy ...
- 2022年-ACCA-SBL知识结构图
2022年ACCA SBL考试知识结构图 【知识结构 案例分析 答题套路 记忆要点】
2022年-ACCA-SBL知识结构图
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- 底层逻辑【看清这个世界的底牌】 刘润 著 《读书笔记》
底层逻辑,源于不同中的相同,变化背后的不变,让我们在千变万化的复杂世界中如鱼得水 读了这本书,启发颇多,尤其是人生三层智慧,层层递进,对电视剧、电影主人公的发展有了不一样的感知,原来就是那么回事儿;对工作的益处就不用提了。 将此书用思维导图呈现出来,时刻提醒自己,现已完成第一章《是非对错的底层逻辑》,后续持续更新中,有兴趣一起交流的朋友可加 微信号 15620587698
- SBL
本图整理的内容有: Chapter 01 Strategy, leadership and culture Chapter 02 Stakeholders and social responsibility Chapter 03 Impact of corporate governance on strategy ...
- 2022年-ACCA-SBL知识结构图
2022年ACCA SBL考试知识结构图 【知识结构 案例分析 答题套路 记忆要点】
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
SBL
Chapter 01 Strategy, leadership and culture
1. Leadership
1.4 Change and leadership (K)
2. Strategy
2.6 Strategic management (M)
3. Culture
3.2 Culture web (M)
知识点
案例
Chapter 02 Stakeholders and social responsibility
1 Principles and agents in governance
1.1 Agency theory (K)
1.2 Stakeholders (K)
1.3 Power and interest (M)
2 Social responsibility
2.1 Carroll's four levels of CSR
2.2 Corporate citizenship (K)
2.3 Ethical stances
2.4 CSR viewpoints (M)企业社会责任七层次理论模型
3 Sustainability
3.1 Environment and social issues
3.2 Integrated reporting <IR> (K)
3.3 Social and environment audit
Chapter 03 Impact of corporate governance on strategy
1 What is corporate governance?
1.1 Definition of corporate governance
1.2 Regulatory guidance(监管原则)
2 How is corporate governance achieved across the world?
2.1 Principles vs rules(K)
2.2 Different jurisdictions(不同司法体系下,公司治理的守则)
2.2.1 Corporate governance in the UK
2.3 Board responsibilities(董事会的责任)
3 What impact does ownership have on CG?(所有权对公司治理的影响)
3.1 The role of the investor
3.2 Disclosures and reporting
3.3 Public sector and third sector governance (K)-记忆
Chapter 04 The external environment
1 The external environment
2 The macro environment (M)【宏观环境】-PESTEL模型
3 National environment【所在国和投资国环境】-钻石模型
3.1 Porter‘s Diamond (M)
3.2 Components of the Diamond (M)
4 Industry or sector environment(行业环境)-波特五力模型
4.1 Porter's five forces
4.2 Industry life cycle
5 Customers and markets【客户和市场环境】
6 Scenario planning (情景规划)
Chapter 05 Strategic capability
1 Strategic capability【战略能力】
2 Sustainable competitive advantage
3 Organisational knowledge
4 Porter’s value chain model (M)
5 Value network
6 SWOT analysis
Chapter 06 Competitive advantage and strategic choice
1 Porter’s generic strategies(M)
1.1 Cost leadership【成本领先=规模经济+提升效率+使用最新技术】
1.2 Differentiation【差异化】
1.3 Focus on (niche) strategy (K)
2 Sustainable competitive advantage
2.1 Marketing mix (7Ps)
2.2 Sustainable strategies
3 Managing organisational portfolios
3.1 The BCG (Boston Consulting Group) matrix
3.2 Public sector portfolio matrix【政府投资组合矩阵】
4 Product-market strategy: direction of growth
4.1 Growth vector matrix (Ansoff matrix) (M)
5 Diversity of products and markets
5.1 The need for diversification【环境变化+分散风险+股东要求回报】
5.2 Types of diversification【多元化类型=相关多元化+复合多元化】
5.3 International diversification【国际多元化】
6 Methods of development【多元化开发方式】
6.1 Internal development【内部发展】
6.2 Business combinations【企业合并】(K)
6.3 Partnering【强强联合】
7 Suitability, acceptability and feasibility【适合+利益相关者接受+能力】 (M)
7.1 Suitability (M)【战略逻辑在哪些方面是否适应】
7.2 Acceptability (M)【利益相关者能否接受】
7.3 Feasibility (M)
Chapter 07 Assessing and managing risk
1 Organisational strategy and risk management
1.1 Understanding stakeholder responses to risk
1.2 Embedding risk in an organisation’s culture and values (K)
2 Risk management process
2.1 Who is responsible for risk?
2.2 Risk appetite (K)【态度和能力】
2.3 Identify risks
2.4 Assess risks【风险评估=技术+地图+主观判断】
2.5 Respond to risks【TARA+ALARP+Diversification】
2.6 Monitoring
Chapter 08 Internal control systems Governance, control and risk · Risk management · Internal control · Corporate governance
1 Internal control【定义+目标+要素+分类+程序+报告】
1.1 Definitions of internal control
1.2 Objectives of internal control: RORCS (K)【风险控制+运营有效+财报可靠+合规+资产安全】
1.3 Elements of internal control
1.4 Categories of control
1.5 Control procedures 【控制程序】
1.6 Control over financial reporting
2 Monitoring
2.1 Information
2.2 Reviewing internal controls
2.3 Audit committees
2.4 Internal audit【内审的作用+内审的质量(4)+持续评价内审成立的必要性】
Chapter 09 Applying ethical principles
1 Doing the wrong thing
1.1 Fraud【方式+{舞弊三角:压力(动机)+机会+合理化}】
1.2 Responding to fraud risks【prevention+detection】
1.3 Bribery and corruption
1.4 Measures to combat bribery and corruption
2 Doing the right thing【企业的道德(5个问题)+道德守则+对专业人士的要求+会计的职业道德(5个原则)+对会计师的威胁和防范】
2.1 Tucker’s 5 questions (M)道德决策模型
2.2 Corporate codes of ethics
2.3 Professions and the public interest
2.4 The code of ethics for accountants
2.5 Threats and safeguards for accountants
Chapter 10 Financial analysis
1 Financial objectives and business strategy【财务目标和企业战略的关系】
2 The finance function
3 Financial analysis and decision-making techniques
3.1 Financing requirements
3.2 Sources of finance
3.3 Investment appraisal
3.4 Dealing with risk and uncertainty 【如何解决在投资评价过程中的风险和不确定性】
3.5 Financial reporting and tax implications
3.6 Organisation performance and position
4 Cost and management accounting
5 Standard costing and variance analysis
6 Evaluating strategic options using marginal costing techniques
Chapter 11 Applications of IT
1 Applications of IT (K)
2 Mobile technologies and cloud computing
2.1 Mobile technology
2.2 Benefits and risks of mobile technology(K)
2.3 Cloud computing
2.4 Benefits and risks of cloud computing (K)
2.5 Cloud computing v owned technology
3 Information technology and data analysis
4 Big data
5 Data for decision making
5.1 New product development decisions
5.2 Marketing decision
5.3 Pricing decision
5.4 Sources of data-Market research
6 Information system controls from a strategic perspective
6.1 Need for IS controls from a strategic perspective (K)【IS是资源+成功关键+影响多级管理+影响客户服务+高成本+结果性改变 】
7 IT and systems security controls
8 Cybersecurity【网络安全】
8.1 Promoting cyber security in organisations (K)【企业内控、风险管理、网络安全=套路】
9 Improving IT/IS controls
Chapter 12 E-business
1 Delivering e-business
2 Strategy models for e-business
3 Applications of technology to support e-business
4 Characteristics of e-marketing: the 6 Is model (M)网络营销的6个模式
5 Comparison of traditional and online branding【线上和传统品牌管理】
6 Acquiring and managing suppliers and customers using technology【用信息技术管理客户和供应商】
7 New developments and innovation【新的开发和创新】
Chapter 13 Enabling success and managing changes【实现成功和企业变革】
1 Organisational structure and internal relationship
1.1 Organisational structure
1.2 Internal relationship【与决策相关的职责和权限=集权程度】
2 Collaborative working
2.1 Boundary-less organisations
2.2 Outsourcing
3 Performance excellence
3.1 The Baldrige Excellence Framework(M)
4 Empowering organisations
4.1 Empowerment
5 Talent management【人力管理】
5.1 The benefits of talent management (K
5.2 Talent management activities (K)
6 Strategic change
6.1 Type of change(M)
7 Contextual features of change【变革的特征】
8 The four-view (POPIT) model
8.1 Usefulness of POPIT
9 Lewin's three-stage model
9.1 Unfreeze
9.2 Change (or 'move’)
9.3 Refreeze
Chapter 14 Process redesign
1.1 Drivers of process redesign
2 Harmon's process-strategy matrix (M)
2.1 Low complexity/low strategic importance processes
2.2 Low complexity/high strategic importance processes
2.3 High complexity/low strategic importance processes
2.4 High complexity/high strategic importance processes
3 Process redesign options
3.1 Re-engineering (business process re-engineering
3.2 Simplification
3.3 Value-added analysis
3.4 Gaps and disconnects
4 Feasibility
4.1 Areas of feasibility (K)
5 Harmon‘s process redesign methodology
5.1 Planning
5.2 Analysing the existing process
5.3 Designing the new process
5.4 Development
5.5 Transition
Chapter 15 Project management
1 Project management
1.1 What is a project
1.2 What is project management
1.3 Project and strategy
2 Project initiation
2.1 Pre-initiating tasks
2.2 The project manager (K)
2.3 Project sponsor
2.4 Initiating tasks
3 Project costs and benefits
3.1 Identifying the benefits
3.2 Measuring benefits (K)
3.3 Identifying the costs (K)
4 Project planning
4.1 Work breakdown structure (WBS) 任务分解结构
4.2 The project budget
4.3 Gantt charts 甘特图
4.4 Network analysis 关键路径分析
5 Project execution and control
5.1 Controlling projects
5.2 Project slippage
5.3 Project change procedure
5.4 Responding to project risk
6 Project completion
6.1 The completion report
6.3 The post-implementation review
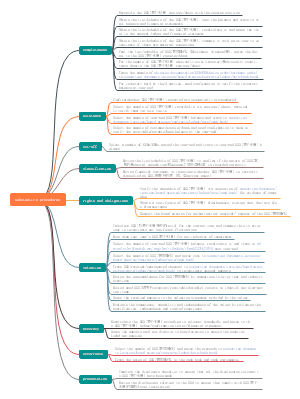
culture-web案例
案例一
要求
Analyse the culture of Frigate Ltd using the cultural web.(15 marks)
答案
suggested solution 开场白+提示 [The cultural web illustrates the combination of assumptions that make up the paradigm,] together with the physical manifestation of culture. It is applied to Frigate below. Paradigm +1 傻白甜知识点+心机表案例信息 [The paradigm refers the basic assumptions and beliefs that an organisation‘s decision makers hold.] It summarises and reinforces the rest of the cultural web. The paradigm at Frigate shows a company run for the personal gratification of Ron and his family. Ron believes that his lifestyle and benefits are the reward for taking risks in a hostile environment. 个人私欲,价值观扭曲 Symbols +2 [Organisations are represented by symbols such as logos, offices, dress, language and titles.] [One of symbols at Frigate is Ron's nickname 'The Commander’ and motor cruiser is the main symbol of his success.] Other symbols include: ·Ron's use of naval terminology ·The naval inspired name of the company Power structures +1 [Power structures look at who holds the real power within an organisation.] At Frigate the power comes from one person, Ron, whose leadership style is based on his strong opinions and beliefs. Organisational structures +1 [The structure of the organisation often reflects the power structure. There is little formal structure at Frigate,] and the attempt to install a formal organisational structure failed. Control systems +2 [Organisations are controlled through a number of systems including financial systems, quality systems and rewards.] The areas that are controlled closest indicate the priorities of the organisation. The focus in Frigate is on cost control and the emphasis is on punishment rather than reward. [There are few formal process controls at Frigate, and the attempt to install such controls was heavily resisted.] Routines and rituals +2 [The daily behaviour and actions of staff signal what the organisation considers to be ‘acceptable’.] At Frigate, there is one rule for Ron and another for everyone else. [Flexible hours, extended holidays etc for Ron but minimum holiday, no flexibility, wage deductions for arriving late etc for employees.] Stories +1 [The stories concern past events and people talked about inside and outside the company.] Stories at Frigate relate to Ron as 'The Commander’. He is the hero of the organisation who constantly has to deal with lazy employees, poor quality suppliers, customers who delay paying, the tax authority, and society in general.
案例二
要求
(a)Analyse the culture of iCompute, and assess the implications of your analysis for the company’s future performance.(15 marks)
答案
1/ Stories a/ Stories are told by employees in an organisation. These often concern events from the history of the organisation. b/ In the context of iCompute, there is evidence of stories that celebrate the earlier years of the organisation when founder Ron Yeates had an important role. ‘Ron used to debate responsibility for requirements changes with the customer.’ In contrast modern management is perceived as weak, giving in too easily in negotiations with customers. c/ Not only is this perceived weakness affecting morale, but it also appears to be affecting profit margins. 2/ Symbols a/ Symbols include visible representations such logos, offices, cars, titles and the type of language and terminology commonly used. b/ The language and symbols of technology appear to dominate at iCompute. Software developers constantly scan the horizon for new technological opportunities. They embrace these technologies and solutions and, as a result, continually distract the organisation. c/ As soon as a technical solution is agreed, or almost agreed, a new alternative is suggested. One of the managers claimed that the company was ‘in a state of constant technical paralysis’. 3/ Power structure a/ Power structure concern who has the greatest amount of influence on decisions, operations, and the strategic position. b/ The perceived inability of managers is derided by software developers who are an important and powerful group within the organisation. It suggest that they are technically out of touch and ownership and understanding of up-to-date mobile phones is perceived to be important. c/ It means that technological objectives can outweigh business and financial objectives, to the detriment of the company as a whole. 4/ Control systems a/ The control systems include measurement and reward systems. b/ In iCompute, ‘there is a limit to what you can earn as a software developer’. To earn more, you have to become managers. Meanwhile, the absence of measurement systems has recently been led to an in-house project to improve time recording. c/ The developers see the in-house project as an unwelcome initiative. Besides, many managers are unsuited to the positions, unable to deal appropriately with former peers and also seem anxious to show that their technical expertise is not diminishing, emphasising the technology as a symbol. 5/ Routines a/ Routines concern the ‘way we do things around here’. b/ At iCompute this involves long working hours and after-work social activities such as football, socialising and playing computer games. c/ This would almost certainly contribute to the company’s inability to recruit and retain women employees. Furthermore, long working hours and after-work activities will also alienate employees who have to get home to undertake family commitments or simply do not wish to be ‘one of the lads’. Almost one third of all employees leave within their first year. The consequence of this culture is an expensive recruitment and training process. The paradigm and conclusion Initially, iCompute was an entrepreneurial organisation with a significant work ethic based on long hours, technical innovation and competitive management. However, the stories told and the recruitment and retention of similarly minded people, has led to a male-oriented, technologically focused workforce managed by unprepared and unsuitable managers. Managers’ reaction to conflict is to avoid it (agreeing with customers over requirements), outsource it (software support)or put in formal computer systems to control it (the time recording system). So, this culture needs to change if the company is to employ a more balanced workforce that is focused on business.
要求
(b)iCompute is currently re-considering three high level processes: (i)Advice on legal issues (currently outsourced) (ii)Software support (currently outsourced) (iii)Time recording (in-house, bespoke software development) Evaluate, using an appropriate framework or model, the suitability of iCompute’s current approach to EACH of these high level processes. (10 marks)
答案
1/ Advice on legal issues a/ This could be classified as a process of high complexity and low strategic importance on the process/strategy matrix. b/ Consequently, it seems that continuing the outsourcing arrangement should be the preferred option. Bespoke systems development is risky. c/ There is evidence in the scenario of litigation between iCompute and two of its customers. Although iCompute is considering moving this process in-house, it seems unlikely that it will be able to afford, attract or motivate an internal legal team. 2/ Software support a/ Service is one of the primary activities of Porter’s value chain and directly influences the customer’s perception. Not only is support relatively complex (as acknowledged by the manager who made the outsourcing decision)but it is also of strategic importance. b/ This suggests that iCompute should bring support back in-house, perhaps by the use of an automated systems. c/ This used to be organised in-house, but was outsourced a year ago. Subsequent customer feedback has been poor, but even without this feedback, it could be argued that outsourcing was a poor decision. 3/ Time recording a/ It could be argued that the application is a relatively simple low-value process which only shows hours employees have worked on certain tasks. b/ According to Harmon, it should be automated or outsourced. c/ Within iCompute, some contracts are on a time and materials basis, but most contracts are on a fixed price basis. Meanwhile, as accurate time recording is a key requirement in many professions, it seems highly likely that a range of off-the-shelf packages would be available to fulfill their needs. Consequently, an ERP or outsourcing would release resources which could be employed on external fee-earning contracts.
必备套路
开场白
[The cultural web illustrates the combination of assumptions that make up the paradigm,] together with the physical manifestation of culture. It is applied to Frigate below.
正文
1. symbols
Symbols +2 含义:[Organisations are represented by symbols such as logos, offices, dress, language and titles.] 案例:[One of symbols at Frigate is Ron's nickname 'The Commander’ and motor cruiser is the main symbol of his success.]
2. control system
Control systems +2 含义:[Organisations are controlled through a number of systems including financial systems, quality systems and rewards.] 案例: [There are few formal process controls at Frigate, and the attempt to install such controls was heavily resisted.]
3. power structure
Power structures +1 含义:[Power structures look at who holds the real power within an organisation.] 案例:At Frigate the power comes from one person, Ron, whose leadership style is based on his strong opinions and beliefs.
4. organisation structure
Organisational structures +1 含义:[The structure of the organisation often reflects the power structure. 案例:There is little formal structure at Frigate,] and the attempt to install a formal organisational structure failed.
5. routine
Routines and rituals +2 含义:[The daily behaviour and actions of staff signal what the organisation considers to be ‘acceptable’.] 案例:At Frigate, there is one rule for Ron and another for everyone else.[Flexible hours, extended holidays etc for Ron but minimum holiday, no flexibility, wage deductions for arriving late etc for employees.]
6. story
Stories +1 含义:[The stories concern past events and people talked about inside and outside the company.] 案例:Stories at Frigate relate to Ron as 'The Commander’. He is the hero of the organisation who constantly has to deal with lazy employees, poor quality suppliers, customers who delay paying, the tax authority, and society in general.
结尾
paradigm and conclusion
Paradigm and conclusion +1 含义:[The paradigm refers the basic assumptions and beliefs that an organisation‘s decision makers hold.] 案例:The paradigm at Frigate shows a company run for the personal gratification of Ron and his family. Ron believes that his lifestyle and benefits are the reward for taking risks in a hostile environment.