导图社区 Speech Acts Theory
- 175
- 0
- 0
- 举报
Speech Acts Theory
Austin's Speech Acts Theory:According to traditional language usage;Accordingtorhetoricalclassification。
编辑于2022-05-19 20:02:04- Speech Acts Theory
Austin's Speech Acts Theory:According to traditional language usage;Accordingtorhetoricalclassification。
- Pragmatics
语用学思维导图,包括:一、Definition;二、 a brief historical overview;三、 different categories of meaning;四、Pragmatics features of language use;五、Sone terms related with Pragmatics;六、 The Scope of Pragmatics。
Speech Acts Theory
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- Speech Acts Theory
Austin's Speech Acts Theory:According to traditional language usage;Accordingtorhetoricalclassification。
- Pragmatics
语用学思维导图,包括:一、Definition;二、 a brief historical overview;三、 different categories of meaning;四、Pragmatics features of language use;五、Sone terms related with Pragmatics;六、 The Scope of Pragmatics。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
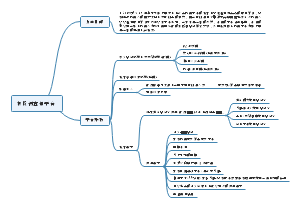
Speech Acts Theory
Introduction
说 做
言行一致
Austin's Speech Acts Theory
John Langshaw (J. L.) Austin (26, March 1911-8, February 1960)
According to traditional language usage
(1)Declarativesentence(陈述句)
(2)Interrogativesentence(疑问句)
(3)Imperativesentence(祈使句)
(4)Exclamatorysentence(感叹句)
Accordingtorhetoricalclassification
(1) Simple, compound and complex sentences
(2) Short and long sentences
(3)Periodic[,prarr'odrk](掉尾句/圆周句) and loose sentences
(4)Elliptical(省略句)andrepetitivesentences
(5) Inverted and balanced sentences
(6) Active and passive voice sentences
(7)Cumulativerkju:mjalatrv了(渐进句)andanti- climax(突降句)sentences
(8) Declarative( PriutA]), interrogative ( hE|] 4J ), imperative(祈使句)andexclamative(感叹句)sentences
(9)Rhetoric(修辞问句)question
4)According to functional classification
(1)phatic(寒暄)/'faetrk/function (2)recreational(娱乐)function (3)informative(信息 function (4) interrogative (疑问) function (5) expressive (表达 function (6) evocative (表情) function (7)directive(指令) function (8) performative (行事) function (9)metalingual(元语言)function
Metalingualfunction(元语言功能)
Language can be used to talk about itself.
Speech act classification of utterance
Traditional direct speech acts: Linguistic form basis
1)Declarativesentence—statementorassertion断言 function
2) Interrogative sentence-interrogative function
3) Imperative sentence-directive function
4) Exclamatory sentence-expressive or emotive function
Indirect speech acts: linguistic form basis doesnotalwaysholdwater合理;form- function is not a one-to-one relationship.
1) Declarative sentence-interrogative function
2) Interrogative sentence-statement or assertion function
3) Interrogative sentence-directive function
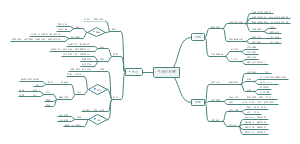
Austin's Speech Acts Theory
1)Declarations(宣告类)
2)Representatives(阐述类)
3)Expressives(表达类)
4)Directives(指令类)
5)Commissives(承诺类)
Speech Acts Theory
Three levels of Austin's Speech Acts
1)Locutionaryrlau'kju:fanaril言内speechacts
2)illocutionary speech acts:
3)Perlocutionary语效性speechacts:
Evaluation of Austin's SAT
1). Advantages: It makes clear what elements are involved in the production and interpretation of utterances.
2). Disadvantages: Implicit and explicit performatives are consequently not equivalent and it is also difficult to know exactly what the performative verb(or verbs) might be for some utterances.
Felicity conditions of SAT
子1.Generalconditions(基本条件)
2.Preparatoryconditions(准备条件
3.Contentconditions(内容条件)
4)Sincerityconditions(真诚条件
5)Essentialconditions(根本条件)
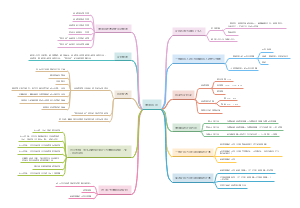
Indirect Speech Act Theory(ISAT)
Searle's classification of illocutionary acts:
1.Assertive(陈述类)speecmact Representatives
2.Directive(指令类) speech act
3.Commissive(承诺类) speech act
4.Expressive(表达类) speech act
5.Declarative(宣告类) speech act
Comments
1. By means of the performative hypothesis Austin had been able to demonstrate that people do not use language just to make statements about the world; they also use language to perform actions, which affect or change the world in some way.
2. The effect of Austin's insight revolutionized the way people look at lanquage and led directlv to the development of pragmatics as an area of linguistic investigation.
3. The performative remains significant, by excellence example of "how to do things with words