导图社区 词汇学
- 201
- 10
- 2
- 举报
词汇学
词汇学英专生。词汇学是语义学的一个分支学科。又称词汇语义学。在语文学时期,词汇学是语言学的组成部分,曾经与语音学、语法学并列;在现代语言学里,一般认为音系学、句法学、语义学是语言学的3个组成部分。
编辑于2023-03-22 20:38:46 湖南- 词汇
- 词汇学
- 英专生
- 英汉互译教程
英汉互译教程--翻译知识点,翻译是把一种语言文字的意义用另一种语言文字表达出来,以达到沟通思想情感,传播文化知识,促进社会文明,特别是推动译语文化兴旺昌盛的目的。
- 英语语言学
戴炜栋《新编英语语言学教程》,definition:Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of a general human language.语言学被定义为对语言进行的科学研究.
- 词汇学
词汇学英专生。词汇学是语义学的一个分支学科。又称词汇语义学。在语文学时期,词汇学是语言学的组成部分,曾经与语音学、语法学并列;在现代语言学里,一般认为音系学、句法学、语义学是语言学的3个组成部分。
词汇学
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- 英汉互译教程
英汉互译教程--翻译知识点,翻译是把一种语言文字的意义用另一种语言文字表达出来,以达到沟通思想情感,传播文化知识,促进社会文明,特别是推动译语文化兴旺昌盛的目的。
- 英语语言学
戴炜栋《新编英语语言学教程》,definition:Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of a general human language.语言学被定义为对语言进行的科学研究.
- 词汇学
词汇学英专生。词汇学是语义学的一个分支学科。又称词汇语义学。在语文学时期,词汇学是语言学的组成部分,曾经与语音学、语法学并列;在现代语言学里,一般认为音系学、句法学、语义学是语言学的3个组成部分。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
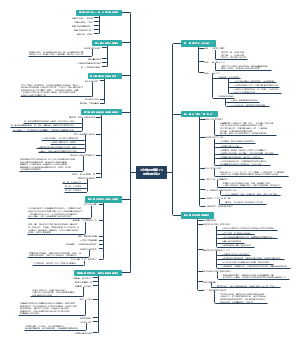
词汇学
第一章
word
定义:a word is a minimal free form of a language that has a given sound,meaning and syntactic function.
分类
使用频率
basic word stock基本词汇
5 basic features
all national character 全民性
stability 稳定性
productivity 能产性
polysemy 多义性
collocability 搭配能力强
non-basic vocabulary非基本词汇
terminology 专业术语
jargon 行话
slang 俚语(vivid,casual)
argot 隐语(黑话,罪犯的话语)
dialectal words 方言词
archaism 古语词
neologism 新词组
概念
content words实义词/notional words/lexical words(实词)
n.
v.
adj.
adv.
numerals
functional words功能词/empty words/form words/grammatical words(虚词)
preposition介词
conjunction连词
auxiliary助动词
artical冠词
起源
native words本土词
概念:并不是本土产生的,是5世纪由日耳曼部落如 the Angles,the Saxons,the Jutes 等等带到英国, 因此被称为 Angle-Saxon words
特征
neutral in style
frequent in use
borrowed words外来词
概念:从外语中借过来的词
类型
denizens 同化词:过去很早借用的单词,现在已经很好融入到英语中
aliens 非同化词:舶来词,保留了原有的发音和拼写
translation-loans 译借词:利用英语现有材料从其他语言翻译过来的单词和短语
semantic loans 语义借词:借用意义而非形式
结构
simple words简单词
compounds复合词
derived words派生词
vocabulary
与word的关系:All the words in a language make up what is generally known as its vocabulary.
含义
the total number of the words
all the words used in a particular historical period
Old English vocabulary 450-1150
特征
highly inflected language 高度屈折变化
small vocabulary(about 5万到6万个单词 )
小部分borrowings来自Latin和Scandinavian
Middle English vocabulary 1150-1500
Modern English vocabulary 1500-现在
特征
影响英语发展的最大事件可能是computer technology和Internet的建立
现代人更喜欢efficiency而不是formality
明显的变化
open compounds,abbreviations(缩略词),conversion,名词或代替从句的名词短语的使用增加
Lexicology(词汇学)
定义:语言学的一个分支,研究词汇的nature(本质),history,use,meaning以及the relationship between elements of words.
所有words构成vocabulary,English Lexicology的研究实际上是对English vocabulary或English words的研究
研究词汇学的方法
Diachronic study(历时研究):语言学家可以在一段时间内研究the history and stages of language change,这就是historical lexicology(历史词汇学)
Synchronic study(共时研究):语言学家研究语言发展的 a certain age的语言使用,特征和变化,这就是descriptive lexicology(描述性词汇学)
第二章
英语属于Germanic语系
词汇的变化不是周期性,突然的,而且持续的,渐进的
外国语言对英语的影响
French words(Norman Conquest):politics,law,government
Italian words(European Renaissance):music,food,architecture
Indian words(British colonization):jungle,shampoo,curry
Asian languages(mainly in the 20th century):China’s words
英语得益于世界上所有语言和文化的贡献
共性
receptivity,adaptability,heterogeneity(接受性,适应性,异质性)
simplicity of inflection词形变化简单
古英语是synthetic language合成语言
现代英语是analytic language分析语言
relatively fixed word-order语序比较固定
新词的来源
rapid development of modern science and language
social,economic and political changes
the influence of other cultures and languages
词汇发展模式
creation:利用现有材料合成新词
semantic change(语义变化):旧的形式有了新的意义
borrowing:占所有新词的百分之二
第三章
Morpheme 语素
brief introduction
morphemes(语素) and syllables(音节) 是不对等的
the smallest meaningful grammatical unit 最小的意义单元, 语素是抽象的单位是真实的语言,表达意义的最小载体
a morpheme is realized by one or a string of morph(语素是由一个或一串形素构成的)
morph(形素) is a concrete part of a word that cannot be divided into smaller parts(形素在具体语境中使用)
a morpheme has variant forms,which is called allomorphs(语素变体)
classification
Free Morpheme(自由语素)can stand by themselves as individual words.可以单独作为词such as man,red,happy......
Bound Morpheme(粘着语素)不能单独作为词,such as -s and -es in English.
Derivational Morpheme(派生语素)是可以构成新词的语素 —creates new words
Inflectional Morpheme(屈折语素)表词与词之间的句法关系,作为语法标记 改变词的形式—merely change word form
屈折词缀
-s:lives(三单)
-’s:John′s(所有格)
-ing:working(正在进行,主动态)
-ed:worked(过去时,被动态)
-er:worker(表“...人”)
-est:poorest(最高级)
-s:books(复数)
-en:driven(完成体)
Lexical Morpheme(实义语素)又称content morpheme,用来派生新词
包括
content words 实词(一些自由语素)
名词
代词
数词
形容词
副词
动词
derivational morpheme 派生语素
Derivational Morpheme(派生语素)是可以构成新词的语素 —creates new words
grammatical Morpheme(语法语素) :起语法标记作用
包括
function words 虚词
冠词 a/an/the
介词
连词
感叹词 oh/hi
Inflectional morphemes 屈折语素
Inflectional Morpheme(屈折语素)表词与词之间的句法关系,作为语法标记 改变词的形式—merely change word form
屈折词缀
-s:lives(三单)
-’s:John′s(所有格)
-ing:working(正在进行,主动态)
-ed:worked(过去时,被动态)
-er:worker(表“...人”)
-est:poorest(最高级)
-s:books(复数)
-en:driven(完成体)
morphemization(语素化)
定义:用一个词或一个词的一部分创造一个语素的过程
新语素产生的方式
clipping 剪切
use an old form as a morpheme 旧形式作为语素
语素通常被标记为
root(词根):一个词的基本形式————去掉所有词缀
不是所有root都是free morpheme,例:prediction:pre(前缀)dic(root-bound morpheme)tion(后缀)
一些root
与运动,活动相关的词根
act表“行动”“活动”
activate、actuate开动,促使、enact制定法律、actualism现实主义
scribe,script表“写”“作品”
inscribe雕刻、manuscript手稿、transcribe抄写
tract表“拉”“拽”“牵引”
detract减损、extract提取、subtract减去,traction牵引
与过程,发展相关的词根
stem(词干):可以由一个词根语素构成,如iron;也可以由两个词根语素构成,如handcuff ————去掉所有屈折词缀
base(词基):可以添加任何类型的词缀————去掉任意一个词缀
affix(词缀)
定义:是附着在单词或单词元素上modify meaning and function。 几乎所有词缀都是bound morpheme(粘着语素),很少有词缀可以作为独立的词使用
分类
1、根据词缀功能
Inflectional affixes (屈折词缀)附在词尾表示grammatical relationships,thus known as Inflectional morphemes —所有的屈折词缀都是后缀,因为屈折词缀会改变词的形式
Derivational affixes (派生词缀) add to other morphemes to create new words
2、根据在构词中的分布
prefix(前缀)
suffix(后缀)
第四章
lexical prefix
prefixation is the formation of new words by adding prefixes to bases.
prefix don′t generally change the word-class of the base but only modify its meaning.
第六章
blending 合成词
定义:将两个单词的一部分或一个单词加上另一个单词的一部分组合成新词
例子
smog(smoke+fog)
sci-fi(science+fiction)
根据形态结果分类
头+尾
头+头
头+词(第一个词的第一部分+第二个的整体形式)
词+尾
词+头
conversion 转换
定义:将一个种类的词用作另一个种类的词
类型
转换成n.
v. to n.
he has a deep love for his country.
动词短语 to n.
hand out 分发 — hand-out 施舍物
adj. to n.
完全转化
常见形容词:a white
分词和其他词:bests
部分转化
the poor,the poorer,the poorest
转换成v.
tutor n.导师,v.辅导
转换为adj.
清辅音变为浊辅音
n. use /-s/ v. use /-z/
元音变化
n. bath v. bathe
重音变化
n. 'conduct v. con'duct
clipping 截短
定义:从原词中截取一部分,用剩下的词构成新词
原因:save time
bike,auto,taxi,gym,math
类型
back clipping 词尾截短(删掉单词末尾)
ad(advertisement),lib(liberation)
fore clipping 首部截短(删掉单词前面)
quake(earthquake),phone(telephone)
front and back clipping 首尾部截短(删掉单词开头与结尾)
flu(influenza),tec(detective)
middle clipping 中部截短(删掉中间的部分,不常见)
asst(assistant)
complex clipping/phrase clipping 短语截短(短语的缩短)
pop(popular music),op art(optical art)
特征
clipping may give rise to alterations in spelling and pronunciation.导致拼写和发音的改变
clipping may vary with social classes,groups or occupation,某些语句是它们各自群里特有的
通常用于不太正式的场合
acronymy and initialism 首字母缩略法
定义:将一个短语中各个单词的首字母组合在一起形成一个新词
It appears mainly in social and political organizations or phrases used as technical terms.
类型
根据发音
Initialism 首字母缩略词
定义:words formed by acronymy and pronounced as a sequence of letters. 是由首字母缩写组成的单词,发音为字母序列
类型
字母代表整个词
VOA—Voice of America
字母代表一个复合词的构成成分或词的一部分
TV—television
ID—identification card
Acronym 首字母拼音词
定义:a word formed from the initial letters but pronounced as a normal word. 由首字母组成但发音正常的单词
It remains a favourite with the military,but it also used by academics,bureaucrats,corporations,children,and all other classes of word coiners.
结构上
pure acronym 纯粹的首字母拼音词
hybrid acronym 混合的首字母拼音词
radar—radio detecting and ranging
syllabic acronym 首音节拼音词
Delmarva—Delaware,Maryland,and Virginia
Syllabic abbreviation(SA) is an abbreviation formed from initial syllables of several words 音节缩写是由几个单词的开头音节组成的缩写
interpol—International police
back-formation 逆生法
定义:去掉假定的词尾来创造单词的方法。 之所以这样叫是因为许多去掉的词尾不是后缀,而且单词不可分割的一部分
the opposite process of suffixation 后缀化的相反过程
babysit—babysitting
air condition—air conditioning
特征:从文体上,逆构法在很大程度上是非正式的
sound reduplication 语音重叠法
定义:the formation of compound words by repeating the same element with little or no change.
分类
imitate sounds(onomatopoetic words)拟声词
tick-tuck
suggest alternating movements 表示交替运动的词语
ping-pong
disparage by suggesting "instability,nonsense,insincerity,vacillation" 暗示“不稳定,胡说八道,不真诚,摇摆不定”来贬低的词语
hocus-pocus(骗术,花招)
intensify 加强语气的词
tip-top
Commonization of proper noun 专有名词普通化
专有名词
人名
地名
书名
商品名称(tradenames)
人名来源
科学家,发明家的名字
神话中的人物
历史人物
文学作品中的人物
第七章
word meaning
定义:reciprocal relation between name and meaning. 意义是名称与意思的联系
meaning and concept
meaning
定义:what the form stands for.
types of meaning
定义:word meaning is made up of various components which are interrelated and interdependent.These components are commonly described as types of meaning. 词义有各种相互联系与相互依存的不同成分组成,这些成分就是词义的种类.
types
grammatical meaning 语法意义 (语法意义是指语义中表示语法概念或关系的部分意义,例如词类,名词的单复数,动词的时态意义及它们的屈折形式)
lexical meaning 词汇意义 (词汇意义是词典中一个独立词的意义.在该词的所有形式中,其词汇意义相同)
conceptual meaning 概念意义 (概念意义是词典中所给的意义,是词义的核心)
associative meaning 联想意义 (联想意义是概念意义的补充意义,是次要意义)
connotative meaning 内涵意义(是由概念意义产生的言外之意或联想)
stylistic meaning 文体意义(文体色彩,以适应不同的文体风格)
formal,informal,literary文学的,archaic古语的,slang
affective meaning 情感意义(反映作者或说话人对所谈论的人或物,事态等表示的个人情感或态度,可通过感情词表达出来)
appreciative 赞赏性
pejorative/derogative 贬义性
collocative meaning 搭配意义(即与之一起使用的词语所赋予的那部分意义)
concept
定义:it is the general idea or meaning which is associated with a word or symbol in a person′s mind. 指词或符号在人脑中的大致印象或意义
两者的关系
closely connected but not identical. 紧密相连但不完全相同
相似点:they are both related directly to referents and are notions of the words . 都与指称物直接相关,都是单词的概念
不同点:belong to different categories. 属于不同的范畴
concept
which is beyond language,is the result of human recognition.
reflect the objective world in the human mind.
concept is universal to all men alike regardless of culture,race,language and so on.
a concept can have as many referring expressions as there are languages in the world.Even in the same language,the same concept can be expressed in different words.
meaning
belongs to language,so is restricted to language use.
reference and sense
reference 指称
定义:it is the relationship between language and the world. 指称是语言和客观外界世界之间的相互关系.
through reference,a speaker indicates which things in the world (including persons) are being talked about. 通过这种关系,说话人指称外界的事物或人
It is the relationship between words and the things,actions,events,and qualities they stand for.
sense 涵义
定义: the sense of an expression is its place in a system of semantic relationships with other expressions in the language. 词语的涵义是它在语义关系系统中同其它词语相对的位置.
两者的差异
reference denotes the relationship between words and the things,actions,events,and qualities they stand for.
sense denotes the relationships inside the language.
两者的联系
every word that has meaning has sense but not every word has reference. 每个词都有涵义,但不一定都有所指
componential analysis 成分分析
定义:a process of breaking down the sense of a word into its mininal components.(can be symbolized in terms of binarity/binary opposition对分法) 将单词的意义分解成为其最小成分的过程.
semantic features 语义特征
sense components 语义成分
成分分析是在语义对比(semantic contrast)的基础上进行的
词汇学
第一章
word
定义:a word is a minimal free form of a language that has a given sound,meaning and syntactic function.
分类
使用频率
basic word stock基本词汇
5 basic features
all national character 全民性
stability 稳定性
productivity 能产性
polysemy 多义性
collocability 搭配能力强
non-basic vocabulary非基本词汇
terminology 专业术语
jargon 行话
slang 俚语(vivid,casual)
argot 隐语(黑话,罪犯的话语)
dialectal words 方言词
archaism 古语词
neologism 新词组
概念
content words实义词/notional words/lexical words(实词)
n.
v.
adj.
adv.
numerals
functional words功能词/empty words/form words/grammatical words(虚词)
preposition介词
conjunction连词
auxiliary助动词
artical冠词
起源
native words本土词
概念:并不是本土产生的,是5世纪由日耳曼部落如 the Angles,the Saxons,the Jutes 等等带到英国, 因此被称为 Angle-Saxon words
特征
neutral in style
frequent in use
borrowed words外来词
概念:从外语中借过来的词
类型
denizens 同化词:过去很早借用的单词,现在已经很好融入到英语中
aliens 非同化词:舶来词,保留了原有的发音和拼写
translation-loans 译借词:利用英语现有材料从其他语言翻译过来的单词和短语
semantic loans 语义借词:借用意义而非形式
结构
simple words简单词
compounds复合词
derived words派生词
vocabulary
与word的关系:All the words in a language make up what is generally known as its vocabulary.
含义
the total number of the words
all the words used in a particular historical period
Old English vocabulary 450-1150
特征
highly inflected language 高度屈折变化
small vocabulary(about 5万到6万个单词 )
小部分borrowings来自Latin和Scandinavian
Middle English vocabulary 1150-1500
Modern English vocabulary 1500-现在
特征
影响英语发展的最大事件可能是computer technology和Internet的建立
现代人更喜欢efficiency而不是formality
明显的变化
open compounds,abbreviations(缩略词),conversion,名词或代替从句的名词短语的使用增加
Lexicology(词汇学)
定义:语言学的一个分支,研究词汇的nature(本质),history,use,meaning以及the relationship between elements of words.
所有words构成vocabulary,English Lexicology的研究实际上是对English vocabulary或English words的研究
研究词汇学的方法
Diachronic study(历时研究):语言学家可以在一段时间内研究the history and stages of language change,这就是historical lexicology(历史词汇学)
Synchronic study(共时研究):语言学家研究语言发展的 a certain age的语言使用,特征和变化,这就是descriptive lexicology(描述性词汇学)
第二章
英语属于Germanic语系
词汇的变化不是周期性,突然的,而且持续的,渐进的
外国语言对英语的影响
French words(Norman Conquest):politics,law,government
Italian words(European Renaissance):music,food,architecture
Indian words(British colonization):jungle,shampoo,curry
Asian languages(mainly in the 20th century):China’s words
英语得益于世界上所有语言和文化的贡献
共性
receptivity,adaptability,heterogeneity(接受性,适应性,异质性)
simplicity of inflection词形变化简单
古英语是synthetic language合成语言
现代英语是analytic language分析语言
relatively fixed word-order语序比较固定
新词的来源
rapid development of modern science and language
social,economic and political changes
the influence of other cultures and languages
词汇发展模式
creation:利用现有材料合成新词
semantic change(语义变化):旧的形式有了新的意义
borrowing:占所有新词的百分之二
第三章
Morpheme 语素
brief introduction
morphemes(语素) and syllables(音节) 是不对等的
the smallest meaningful grammatical unit 最小的意义单元, 语素是抽象的单位是真实的语言,表达意义的最小载体
a morpheme is realized by one or a string of morph(语素是由一个或一串形素构成的)
morph(形素) is a concrete part of a word that cannot be divided into smaller parts(形素在具体语境中使用)
a morpheme has variant forms,which is called allomorphs(语素变体)
classification
Free Morpheme(自由语素)can stand by themselves as individual words.可以单独作为词such as man,red,happy......
Bound Morpheme(粘着语素)不能单独作为词,such as -s and -es in English.
Derivational Morpheme(派生语素)是可以构成新词的语素 —creates new words
Inflectional Morpheme(屈折语素)表词与词之间的句法关系,作为语法标记 改变词的形式—merely change word form
屈折词缀
-s:lives(三单)
-’s:John′s(所有格)
-ing:working(正在进行,主动态)
-ed:worked(过去时,被动态)
-er:worker(表“...人”)
-est:poorest(最高级)
-s:books(复数)
-en:driven(完成体)
Lexical Morpheme(实义语素)又称content morpheme,用来派生新词
包括
content words 实词(一些自由语素)
名词
代词
数词
形容词
副词
动词
derivational morpheme 派生语素
Derivational Morpheme(派生语素)是可以构成新词的语素 —creates new words
grammatical Morpheme(语法语素) :起语法标记作用
包括
function words 虚词
冠词 a/an/the
介词
连词
感叹词 oh/hi
Inflectional morphemes 屈折语素
Inflectional Morpheme(屈折语素)表词与词之间的句法关系,作为语法标记 改变词的形式—merely change word form
屈折词缀
-s:lives(三单)
-’s:John′s(所有格)
-ing:working(正在进行,主动态)
-ed:worked(过去时,被动态)
-er:worker(表“...人”)
-est:poorest(最高级)
-s:books(复数)
-en:driven(完成体)
morphemization(语素化)
定义:用一个词或一个词的一部分创造一个语素的过程
新语素产生的方式
clipping 剪切
use an old form as a morpheme 旧形式作为语素
语素通常被标记为
root(词根):一个词的基本形式————去掉所有词缀
不是所有root都是free morpheme,例:prediction:pre(前缀)dic(root-bound morpheme)tion(后缀)
一些root
与运动,活动相关的词根
act表“行动”“活动”
activate、actuate开动,促使、enact制定法律、actualism现实主义
scribe,script表“写”“作品”
inscribe雕刻、manuscript手稿、transcribe抄写
tract表“拉”“拽”“牵引”
detract减损、extract提取、subtract减去,traction牵引
与过程,发展相关的词根
stem(词干):可以由一个词根语素构成,如iron;也可以由两个词根语素构成,如handcuff ————去掉所有屈折词缀
base(词基):可以添加任何类型的词缀————去掉任意一个词缀
affix(词缀)
定义:是附着在单词或单词元素上modify meaning and function。 几乎所有词缀都是bound morpheme(粘着语素),很少有词缀可以作为独立的词使用
分类
1、根据词缀功能
Inflectional affixes (屈折词缀)附在词尾表示grammatical relationships,thus known as Inflectional morphemes —所有的屈折词缀都是后缀,因为屈折词缀会改变词的形式
Derivational affixes (派生词缀) add to other morphemes to create new words
2、根据在构词中的分布
prefix(前缀)
suffix(后缀)
第四章
lexical prefix
prefixation is the formation of new words by adding prefixes to bases.
prefix don′t generally change the word-class of the base but only modify its meaning.
第六章
blending 合成词
定义:将两个单词的一部分或一个单词加上另一个单词的一部分组合成新词
例子
smog(smoke+fog)
sci-fi(science+fiction)
根据形态结果分类
头+尾
头+头
头+词(第一个词的第一部分+第二个的整体形式)
词+尾
词+头
conversion 转换
定义:将一个种类的词用作另一个种类的词
类型
转换成n.
v. to n.
he has a deep love for his country.
动词短语 to n.
hand out 分发 — hand-out 施舍物
adj. to n.
完全转化
常见形容词:a white
分词和其他词:bests
部分转化
the poor,the poorer,the poorest
转换成v.
tutor n.导师,v.辅导
转换为adj.
清辅音变为浊辅音
n. use /-s/ v. use /-z/
元音变化
n. bath v. bathe
重音变化
n. 'conduct v. con'duct
clipping 截短
定义:从原词中截取一部分,用剩下的词构成新词
原因:save time
bike,auto,taxi,gym,math
类型
back clipping 词尾截短(删掉单词末尾)
ad(advertisement),lib(liberation)
fore clipping 首部截短(删掉单词前面)
quake(earthquake),phone(telephone)
front and back clipping 首尾部截短(删掉单词开头与结尾)
flu(influenza),tec(detective)
middle clipping 中部截短(删掉中间的部分,不常见)
asst(assistant)
complex clipping/phrase clipping 短语截短(短语的缩短)
pop(popular music),op art(optical art)
特征
clipping may give rise to alterations in spelling and pronunciation.导致拼写和发音的改变
clipping may vary with social classes,groups or occupation,某些语句是它们各自群里特有的
通常用于不太正式的场合
acronymy and initialism 首字母缩略法
定义:将一个短语中各个单词的首字母组合在一起形成一个新词
It appears mainly in social and political organizations or phrases used as technical terms.
类型
根据发音
Initialism 首字母缩略词
定义:words formed by acronymy and pronounced as a sequence of letters. 是由首字母缩写组成的单词,发音为字母序列
类型
字母代表整个词
VOA—Voice of America
字母代表一个复合词的构成成分或词的一部分
TV—television
ID—identification card
Acronym 首字母拼音词
定义:a word formed from the initial letters but pronounced as a normal word. 由首字母组成但发音正常的单词
It remains a favourite with the military,but it also used by academics,bureaucrats,corporations,children,and all other classes of word coiners.
结构上
pure acronym 纯粹的首字母拼音词
hybrid acronym 混合的首字母拼音词
radar—radio detecting and ranging
syllabic acronym 首音节拼音词
Delmarva—Delaware,Maryland,and Virginia
Syllabic abbreviation(SA) is an abbreviation formed from initial syllables of several words 音节缩写是由几个单词的开头音节组成的缩写
interpol—International police
back-formation 逆生法
定义:去掉假定的词尾来创造单词的方法。 之所以这样叫是因为许多去掉的词尾不是后缀,而且单词不可分割的一部分
the opposite process of suffixation 后缀化的相反过程
babysit—babysitting
air condition—air conditioning
特征:从文体上,逆构法在很大程度上是非正式的
sound reduplication 语音重叠法
定义:the formation of compound words by repeating the same element with little or no change.
分类
imitate sounds(onomatopoetic words)拟声词
tick-tuck
suggest alternating movements 表示交替运动的词语
ping-pong
disparage by suggesting "instability,nonsense,insincerity,vacillation" 暗示“不稳定,胡说八道,不真诚,摇摆不定”来贬低的词语
hocus-pocus(骗术,花招)
intensify 加强语气的词
tip-top
Commonization of proper noun 专有名词普通化
专有名词
人名
地名
书名
商品名称(tradenames)
人名来源
科学家,发明家的名字
神话中的人物
历史人物
文学作品中的人物
第七章
word meaning
定义:reciprocal relation between name and meaning. 意义是名称与意思的联系
meaning and concept
meaning
定义:what the form stands for.
types of meaning
定义:word meaning is made up of various components which are interrelated and interdependent.These components are commonly described as types of meaning. 词义有各种相互联系与相互依存的不同成分组成,这些成分就是词义的种类.
types
grammatical meaning 语法意义 (语法意义是指语义中表示语法概念或关系的部分意义,例如词类,名词的单复数,动词的时态意义及它们的屈折形式)
lexical meaning 词汇意义 (词汇意义是词典中一个独立词的意义.在该词的所有形式中,其词汇意义相同)
conceptual meaning 概念意义 (概念意义是词典中所给的意义,是词义的核心)
associative meaning 联想意义 (联想意义是概念意义的补充意义,是次要意义)
connotative meaning 内涵意义(是由概念意义产生的言外之意或联想)
stylistic meaning 文体意义(文体色彩,以适应不同的文体风格)
formal,informal,literary文学的,archaic古语的,slang
affective meaning 情感意义(反映作者或说话人对所谈论的人或物,事态等表示的个人情感或态度,可通过感情词表达出来)
appreciative 赞赏性
pejorative/derogative 贬义性
collocative meaning 搭配意义(即与之一起使用的词语所赋予的那部分意义)
concept
定义:it is the general idea or meaning which is associated with a word or symbol in a person′s mind. 指词或符号在人脑中的大致印象或意义
两者的关系
closely connected but not identical. 紧密相连但不完全相同
相似点:they are both related directly to referents and are notions of the words . 都与指称物直接相关,都是单词的概念
不同点:belong to different categories. 属于不同的范畴
concept
which is beyond language,is the result of human recognition.
reflect the objective world in the human mind.
concept is universal to all men alike regardless of culture,race,language and so on.
a concept can have as many referring expressions as there are languages in the world.Even in the same language,the same concept can be expressed in different words.
meaning
belongs to language,so is restricted to language use.
reference and sense
reference 指称
定义:it is the relationship between language and the world. 指称是语言和客观外界世界之间的相互关系.
through reference,a speaker indicates which things in the world (including persons) are being talked about. 通过这种关系,说话人指称外界的事物或人
It is the relationship between words and the things,actions,events,and qualities they stand for.
sense 涵义
定义: the sense of an expression is its place in a system of semantic relationships with other expressions in the language. 词语的涵义是它在语义关系系统中同其它词语相对的位置.
两者的差异
reference denotes the relationship between words and the things,actions,events,and qualities they stand for.
sense denotes the relationships inside the language.
两者的联系
every word that has meaning has sense but not every word has reference. 每个词都有涵义,但不一定都有所指
componential analysis 成分分析
定义:a process of breaking down the sense of a word into its mininal components.(can be symbolized in terms of binarity/binary opposition对分法) 将单词的意义分解成为其最小成分的过程.
semantic features 语义特征
sense components 语义成分
成分分析是在语义对比(semantic contrast)的基础上进行的