导图社区 American Politics
- 38
- 1
- 0
- 举报
American Politics
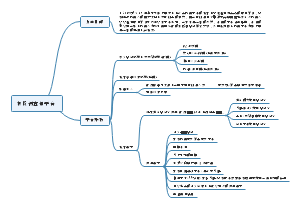
美国国内政治 US Domestic Politics,分享内容有: Two Ideologies Political Institutions Political Parties Domestic since 2016
编辑于2023-05-08 12:45:38 上海- 相似推荐
- 大纲
US Domestic Politics
Two Ideologies
Classical Liberalism (Conservative)
Origin
Rationality of Human Beings to create a better world
Renaissance, Reformation, British Glorious Revolution of 1688
Founding Fathers
John Locke, Two Teaties of Government
Adam Smith, Wealth of Nations
Definition
Commitment to individual
Society where individuals can satisfy personal interests
Core Values
Individualism
privacy and private property
Democracy
minimal gov't, check and balance
popular participation, political equality
Rationalism
capacity of human beings, limits
Freedom
free within law
free market
Rule of Law
law above politics, personal liberty
Influence
meta-ideology, shaping ideology, Constitution
reflects a rising industrial middle class
closely related to capitalism
Limits and side effects
social injustice, gap between rich and poor
financial crisis
Modern Liberalism
Origin
Great Depression 1929-1933
Founding Fathers
Franklin Roosevelt
Definition
Four Freedoms
of speech
of worship
from want
from fear
Active Liberalism, basic welfare
Core Values
Individualism
guarantee of minimum living standard
Democracy
anti-economic power, active gov't
Rationalism
capacity of gov't
Freedom
free market with proper intervention
Rule of Law
law above politics, personal liberty
Influence
shaping contemporary party system in US
DP and GoP
help recovery and becoming fairer
Limits and side effects
big gov't overload, stifle economic vitality
high tax, declining motivation
Political Institutions
Constitutional Basis
Separation of Powers, defend liberty, prevent tyranny
Independence and interdependence among branches
Comparison to Parliament
prevent over-strong executive
Congress
Structure
Bicameralism
fragmentation, two co-equal chambers
Senate
100, 2/state, 6years
House
438, depend of population, 2years
Congressional Committees
Legislation
Investigation
Spirit
Minority is subordinated to majority
Legal rights of Minority is protected
Functions
Legislation
Representation
link gov't and people
Scrutiny and oversight
constraint executive power
Recruitment and training
pool of talents
Legitimacy
Decline since 1970s
Growth of big gov't
redistribution of power to President
Disciplined Political Parties
vote by party
Organizational weakness
no effective leader
Executive/President
Structure
implementation of policies
President, highest executive leader
Functions
Ceremonial leadership
Policy-making leadership
initiate programs and push
Popular leadership
Bureaucratic leadership
ministers and secretaries
manage bureaucratic system
Crisis leadership
emergency power
Judiciary
Structure
decide legal disputes, interpret constitution
judges hold office for life
Supreme court, 9 persons
Limits
Supreme court judges appointed by president, confirmed by senate
affected by politics
after WWII
1954-1969
Warren court (liberal)
1969-1986
Burger court (conservative)
1986-2005
Rehnquist court (conservative)
Relationship between President and Congress
Strong President Weak Congress
control both chambers
Bush2001-2002, can do anything
Weak President Strong Congress
control no chamber
Clinton1994-1996, can do nothing
Balanced Model
control one chamber
Obama2010-2012
Trump Model
control both chamber but internally divided
GoP doesn't cooperate with Trump
Political Parties
Definition
a group of people to win gov't power
shared political preferences and ideological identity
social cleavages and democratization
Types
Function
Representative party
to secure votes in elections
reflect public opinion
Integrative party
mobilize, educate and inspire the masses
shape public opinion
Operation
Constitutional party
respect existing framework
Revoluntionary party
seize power, overthrow establishment
Ideology
Left-wing party
committment to change
Right-wing party
uphold exsiting social order
Functions
Representation
respond and articulate voters
Elite formation and recruitment
provide political leaders
Interest articulation and aggregation
Organization of gov't
give stability and coherence
Party Realignments in US
Definition
visible and continuous changes in domestic elecoral bases of both parties
1896
GOP (Northeast and West) dominated, DP (South)
polarized parties
1932
DP expand to NE and rise
Modern Liberalism becam dominant
1968-1980
Stagflation and Vietnam War
Gap enlarged
post cold war
DP: NE, West; GOP: Mid-West, South
equal strength
2016
Rustbelt turn to GOP
Interest Groups and elections
Definition
organized association
to influence gov't
narrow issue focus
Influence
PAC Political Action Committee
Hard Money
Soft Money
Revolving Door
retired member of Congress
Iron Triangle
Subgovernment
Deep State
Elections
SMP, Single-member plurality system
Domestic since 2016
Trump Revoltion
Populism/Anti-establishment
policies outside consensus of GOP
twitter governance
Nativism/Anti-globalism
trade protectionism, domestic reindustrialization
tariffs on EU
resistance to immigration
Racialism/White supremacy
middle/lower classes white people
GOP Christian conservative groups
radical organizations and conflicts
Dynamics
Hollow economy
social polarization between rich and poor
Cultural pluralism
impact dominance of WASP White Anglo-Saxon Protestant
Population Structure
fear of minorities and immigrants
Impacts
intensified social division in US
culture war
polarized politics
veto politics and retaliatory politics
split within DP and GOP
GOP into
mainstream
anti-establishment
DP into
radicals (Sanders)
moderates (Biden)
mid-right (Manchin)
Biden Centrism
Causes
rebuild middle class as DP's basis
reverse Trump
reunite DP
Efforts
Economy-first
Shelving culture war
Challenges
DP left and mid-right
GOP
overturn of Roe v. Wade
Foreign
主题
主题
主题