导图社区 Greek civilization
- 487
- 0
- 0
- 举报
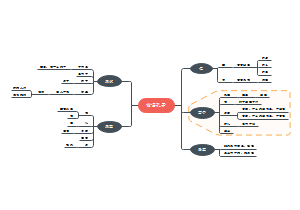
Greek civilization
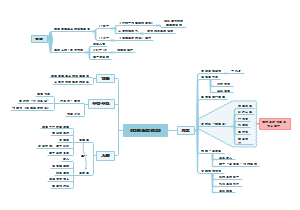
西方文明史课程学习成果,具体有: 1.The Bronze Age to The Dark Age 青铜时期到黑暗时期 3000-1200-800B.C.E 2.The Archaic age古风时期 700-500 B.C.E. 3. The Classical Age古典时期500-400 B.CE 4.The Hellenistic Age希腊化时期400-100 B.CE
编辑于2023-06-01 21:08:58 广东- 希腊
- 西方文明史
- Roman Civilization
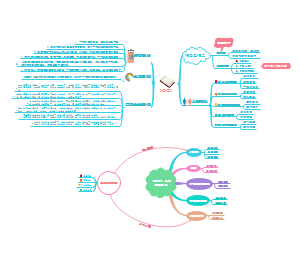
《西方文明史》古罗马文明部分英文思维导图,内容有The Regal Age王政时代1500-753-509 BC、The Republic Age 共和时代510-146-27 BC、The Empire Age 帝国时代27BC-395AD-476-1453。
- Greek civilization
西方文明史课程学习成果,具体有: 1.The Bronze Age to The Dark Age 青铜时期到黑暗时期 3000-1200-800B.C.E 2.The Archaic age古风时期 700-500 B.C.E. 3. The Classical Age古典时期500-400 B.CE 4.The Hellenistic Age希腊化时期400-100 B.CE
- Second Language Acquisition
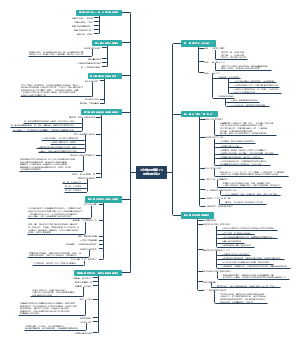
这是一篇关于Second Language Acquisition的思维导图,主要内容有Interaction, input,and outputa、Learning processes、Learner factors、Learner language。
Greek civilization
社区模板帮助中心,点此进入>>
- Roman Civilization
《西方文明史》古罗马文明部分英文思维导图,内容有The Regal Age王政时代1500-753-509 BC、The Republic Age 共和时代510-146-27 BC、The Empire Age 帝国时代27BC-395AD-476-1453。
- Greek civilization
西方文明史课程学习成果,具体有: 1.The Bronze Age to The Dark Age 青铜时期到黑暗时期 3000-1200-800B.C.E 2.The Archaic age古风时期 700-500 B.C.E. 3. The Classical Age古典时期500-400 B.CE 4.The Hellenistic Age希腊化时期400-100 B.CE
- Second Language Acquisition
这是一篇关于Second Language Acquisition的思维导图,主要内容有Interaction, input,and outputa、Learning processes、Learner factors、Learner language。
- 相似推荐
- 大纲
Greek civilization
1.The Bronze Age to The Dark Age 青铜时期到黑暗时期 3000-1200-800B.C.E
3 late Bronze Age cultures: the Cycladic, the Minoan, and the Mycenaean
lslands of Peace (vulnerable, open, no defense)
The Cyclades基克拉迪文明2500B.C.E
had influence on Crete
Minoan Crete米诺斯/克里特文明2000-1550B.C.E
Knossos, the legendary palace of Minos
Cretan Society and Religion
strongly stratified
Mainland of War (violent, strongly walled fortresses )
Mycenaean迈锡尼文明1600B.C.E
adopted artisanal and architectural techniques from Hittites
Freedom and equality
Women
The Dark Age黑暗时期/荷马时期 1200-800B.C.E
Mycenaean culture vulnerable: Self-destructed
Overpopulation, the fragility of the agrarian base, the risks of overspecialization in cash crops such as grain in Messenia and sheep raising in Crete, and rivalry among states
A New Material Culture
tribal groups merged with the indigenous populations
distinctive dialectic and cultural characteristics
first→poorer, more rural, and more simply organized→crudely imitating forms of Mycenaean production
later→differ from
The Evidence of Homer
two epic poems—the Iliad and the Odyssey
2.The Archaic age古风时期 700-500 B.C.E.
introduction
(1)Greeks of the Archaic Age set the agenda for the rest of Western history
(2)The first sign of radical change→a major increase in populationin the 8th century B.C.E
Revolutions
Political organization
Ethnos部族
mainland,Peloponnesus
governed by an elite, or oligarchy
root from the Dark Ages
Polis城邦
islands, Aegean
each town was independents, on an equal footing summon an assembly
innovation→democracy
Artistic traditions
Gods and Mortals
The gods belonged to all.
man strengths and virtues + weaknesses and vices神人同形共性
Doric temple 多利克式神庙
less centers of ritual than houses of gods
no group had the monopoly on the cult of the gods没有垄断祭礼的祭司阶层
Myth and Reason
The glue of the Greek world was the Common myths.
Myths explained and described the world both as it was and as it should be.
What is the place of humans in the cosmos?
Prometheus 普罗米修斯
Pandora潘多拉
Hercules大力神 赫拉克勒斯
Art and the Individual
Reflect the importance of the individual
Intellectual values
Technology of Writing
Phoenician writing system腓尼基文字
Phoenicia Alphabet腓尼基字母
希腊字母
拉丁字母和斯拉夫字母
not intended for central administrative record keeping→for private, personal use and was available to virtually anyone
arbitrary sounds
add vowels
Social structures
Democratic Athens
Social Tensions
3. The Classical Age古典时期500-400 B.CE
Alexander at Issus
The Empire of Alexander the Great
A new Achilles
Intend to conquer the whole world
Military genius, dedication to his troops, reckless disregard for his won safety, ability to move both men and supplies across vast distances at great speed
Defeated the Persian King Darius III at Issus and headed south toward the Mediterranean coast and Egypt. He turned again to the north and entered Mesopotamia and defeated Darius again.
Eastward to Indus River
Reorganized or founded cities, entrusting them to royal Macedonians
Alexander is remembered as a greater conqueror than ruler, but his plans for his reign, had he lived to complete them, might have won him equal fame.
No mortal had ever before accomplished such a feat conquest.
Merging local and Greek peoples and traditions
If there is one thing above all others a successful man should know it is when to stop.
He died at 32. The empire did not outlive the emperor.
Alexander vs Darius III (Persia)→Athens vs Sparta
Macedon
Macedonia under King Philip II moved into the resulting power vacuum.
4.The Hellenistic Age希腊化时期400-100 B.CE
Athenian culture in the Hellenic Age
The Examined Life
A Primary characteristic of Athenian culture was its critical and rational nature.
The Sophists
Socrates
Natural philosophy --- human world (individual's relationship with society)
Plato
Aristotle
Assembly, agora, courtroom, symposium
Understanding the Past
Herodotus
(Greco-)Persian Wars
Thucydides
Thucydides 's trap
Athenian Drama